Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG750MX
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Structure of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG750MX Description
A solar inverter, or PV inverter, or Solar converter, converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a photovoltaic (PV) solar panel into
autility frequency alternating current (AC) that can be fed into a commercial electrical grid or used by a local, off-grid electrical network.
It is acritical BOS–component in a photovoltaic system, allowing the use of ordinary AC-powered equipment. Solar inverters have
special functions adapted for use with photovoltaic arrays, including maximum power point tracking and anti-islanding protection.
Suitable for 50Hz/60Hz grid, could be used in Asia, North America and Europe.
2. Main Features of the Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG750MX
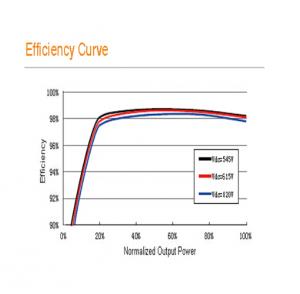
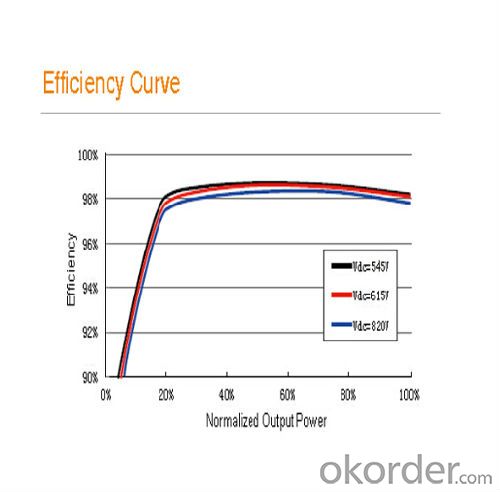
• Transformerless inverter, max. efficiency of 98.7%, CEC efficiency of 98.5% for SG800MX,max. efficiency of 98.6%, CEC efficiency of 98.0% for SG750MX
• Employing a patented thermal management system, the inverter is able to operate from -13˚F to 140˚F (-25˚C to 60˚C), and up to 19,600’ (6,000 m).
• High power density, small equipment footprint
• DC disconnect, AC circuit breaker, separate DC & AC cabinets
• Max. DC input voltage is 1000V, can be mounted on a skid or an e-house, giving maximum design flexibility and lowering installation costs
• Continuous active power control
• Advanced grid support functionality, meet grid requirements around the world
• Full remote and local power curtailment, PF, HVRT, LVRT, FRT controls via ModBus & Ethernet
• Designed for 20+ years of operating life
• NEMA4X electronics cabinet
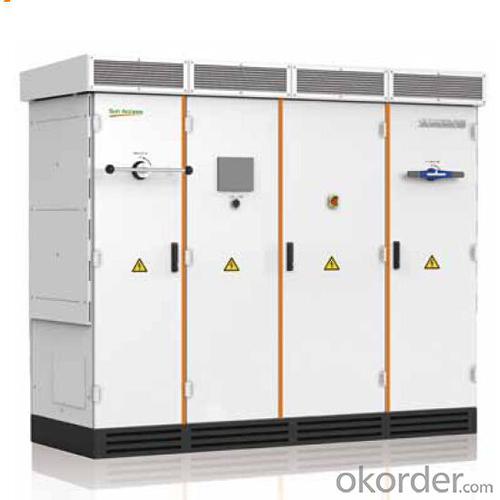
3. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG750MX Images
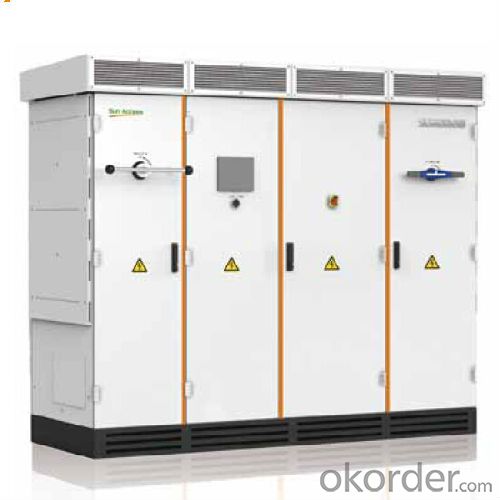

4. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG750MX Specification
Input Side Data |
|
Max. PV input power | 850kW |
Max. PV input voltage | 1000V |
Start voltage | 520V |
Min. operation voltage | 500V |
Max. PV input current | 1600A |
MPP voltage range | 500~820V |
No. of DC inputs | 1, 6-12 |
PV array configuration | Negative ground (standard), Floating or Positive Ground (optional) |
Output Side Data |
|
Nominal AC output power | 750kW |
Max. AC output apparent power | 825kVA |
Max. AC output current | 1512A |
THD | <3% (nominal power) |
Nominal AC voltage | 315V |
AC voltage range | 277~347Vac |
Nominal grid frequency | 50/60Hz |
Grid frequency range | 47~52Hz/57~63Hz |
Power factor | >0.99@default value at nominal power, adj. 0.8 overexcited~0.8 underexcited |
Isolated transformer | No |
DC current injection | <0.5 % In |
Efficiency |
|
Max. efficiency | 98.60% |
European efficiency | 98.30% |
CEC efficiency | 98.00% |
Protection |
|
Input side disconnection device | DC load switch |
Output side disconnection device | Breaker |
DC overvoltage protection | Yes |
AC overvoltage protection | Yes |
Grid monitoring | Yes |
Ground fault monitoring | Optional |
Over temperature protection | Yes |
Insulation monitoring | Optional |
General Data |
|
Dimensions(W×H×D) | 2598x2164x1000mm |
Weight | 2340kg |
Operating ambient temperature range | -25~+60℃(>55℃ derating) |
Noise emission | <70dB |
Night power consumption | <100W |
External auxiliary supply voltage | 480/600V(3/N/PE) |
Cooling method | Temperature controlled air-cooling |
Ingress protection rating | NEMA 3R(IP54) |
Allowable relative humidity range | 0~95% no condensing |
Max. operating altitude | 6000m (>3000m derating) |
Fresh air consumption | 4425 m³/h |
Display | LCD |
Communication | RS485/Modbus, Ethernet(Opt.) |
5. FAQ of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG750MX
Q1. What is the difference between inverter and solar inverter?
A1. Inverter only has AC inpput, but solar inverter both connect to AC input and solar panel, it saves more power.
Q2. What is the difference between MPPT&PWM?
A2. MPPT has higher efficiency, it can track the max power point and won't waste energy.
- Q: Are there any safety concerns with solar inverters?
- Yes, there are some safety concerns with solar inverters. These concerns mainly revolve around electrical safety and fire hazards. Solar inverters handle high voltage DC electricity and convert it into AC electricity, which can pose a risk of electric shock if not installed or maintained properly. Additionally, faulty or poorly designed inverters may overheat or catch fire, potentially endangering the surrounding area. It is crucial to ensure that solar inverters meet the necessary safety standards and are installed by qualified professionals to mitigate these risks.
- Q: How do you calculate the maximum power point current for a solar inverter?
- The maximum power point current for a solar inverter can be calculated by using the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm. This algorithm constantly adjusts the operating conditions of the inverter to maximize the power output from the solar panels. It does this by varying the input voltage and current to find the point at which the power output is at its highest. This maximum power point current can be determined using mathematical calculations and algorithms employed by the solar inverter.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be easily integrated into an existing electrical system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be easily integrated into an existing electrical system. It is designed to convert the direct current (DC) power generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) power that can be used by the electrical system. The inverter can typically be connected to the existing electrical system through a simple installation process, allowing the solar energy to be seamlessly integrated and utilized alongside the conventional power supply.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a three-phase power system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a three-phase power system. In fact, many commercial and industrial solar installations utilize three-phase power systems to effectively distribute and manage the generated solar energy. A three-phase solar inverter is designed to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that is compatible with the three-phase power grid. This allows for efficient power transmission and utilization of solar energy in three-phase systems.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle islanding detection and prevention?
- A solar inverter handles islanding detection and prevention by constantly monitoring the grid and its own power output. If it detects a loss of grid connectivity, it initiates a process called anti-islanding, where it stops supplying power to the grid to prevent the formation of an island. The inverter accomplishes this by monitoring the frequency and voltage levels of the grid, and if it detects a deviation beyond a certain threshold, it disconnects from the grid within a specific timeframe. This ensures that the inverter does not continue to supply power to an isolated grid, which could pose safety risks to utility workers and damage electrical equipment.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle voltage fluctuations in the grid?
- A solar inverter handles voltage fluctuations in the grid by continuously monitoring the grid voltage. When the voltage exceeds or drops below the acceptable range, the inverter adjusts the power output of the solar panels accordingly. It stabilizes the voltage by regulating the flow of electricity from the solar panels, ensuring a consistent and safe supply of power to the grid.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different AC voltages?
- No, a solar inverter cannot be used with different AC voltages. It is designed to convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into a specific AC voltage, typically matching the grid voltage in the area. Using a solar inverter with a different AC voltage can result in damage to the inverter and potential safety hazards.
- Q: How do you size a solar inverter for a solar power system?
- To size a solar inverter for a solar power system, you need to consider the maximum power output of your solar panels. Calculate the total wattage of your solar panels and choose an inverter with a capacity slightly larger than that. It is important to ensure that the inverter's capacity can handle the maximum power output of your solar panels to avoid any performance issues or damage to the system.
- Q: How does MPPT improve the efficiency of a solar inverter?
- MPPT, or Maximum Power Point Tracking, improves the efficiency of a solar inverter by constantly adjusting the operating voltage and current to maximize the power output of the solar panels. This optimization ensures that the inverter extracts the maximum available power from the solar panels, thereby increasing overall system efficiency and maximizing the energy harvest from the solar installation.
- Q: What are the common issues and troubleshooting steps for a solar inverter?
- Solar inverters can encounter various problems, such as failure to turn on, lack of power output, insufficient power output, intermittent power output, or error messages displayed on the inverter. Below are some steps you can take to troubleshoot these issues: 1. Verify the power supply: Ensure that the inverter is properly connected to the power source and that there are no electrical supply problems. Check the circuit breaker or fuse box to ensure it has not been tripped. 2. Inspect the wiring: Examine the wiring connections to ensure they are secure and undamaged. Loose or disconnected wires can cause power issues. If any damage is found, consider seeking the assistance of a professional electrician for repair or replacement. 3. Clean the solar panels: Dust, debris, or shading on the solar panels can reduce power output. Use a soft cloth or hose to clean the panels. If nearby trees or structures cast shade on the panels, consider trimming or removing them if feasible. 4. Check for error messages: If the inverter displays an error message, consult the user manual or manufacturer's website for the error code's meaning and recommended troubleshooting steps. If necessary, contact the manufacturer's customer support for further guidance. 5. Monitor weather conditions: Solar inverters may generate less power during cloudy or overcast days. However, if power output consistently remains low even in ideal weather conditions, there may be an issue with the inverter itself. 6. Reset the inverter: Some inverters offer a reset button or option. Attempt to reset the inverter to its factory settings, but bear in mind that this may erase any customized settings or configurations. 7. Update the firmware: Check if there are any firmware updates available for your specific inverter model. Updating the firmware can sometimes resolve issues and enhance performance. 8. Seek professional consultation: If the above troubleshooting steps do not resolve the issue, it is advisable to contact a professional solar installer or electrician. They possess the expertise and equipment required to diagnose and address more complex problems with solar inverters. Always prioritize safety when troubleshooting electrical equipment. If you are uncertain or uncomfortable with any troubleshooting steps, it is best to seek professional assistance to prevent potential hazards.
Send your message to us
Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter SG750MX
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords