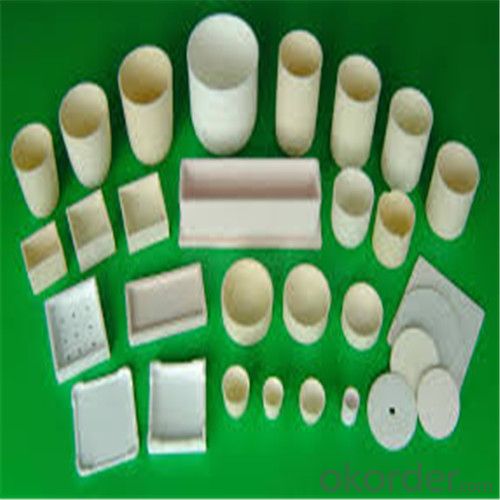
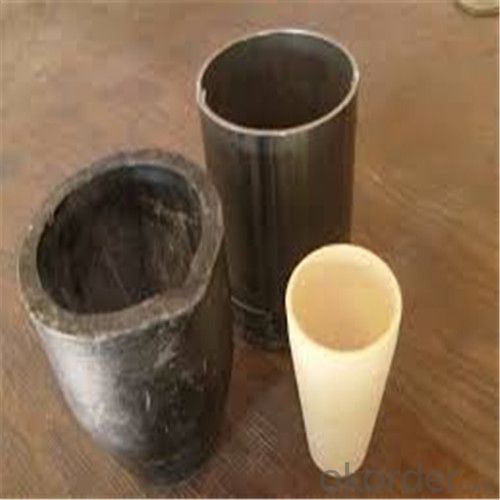
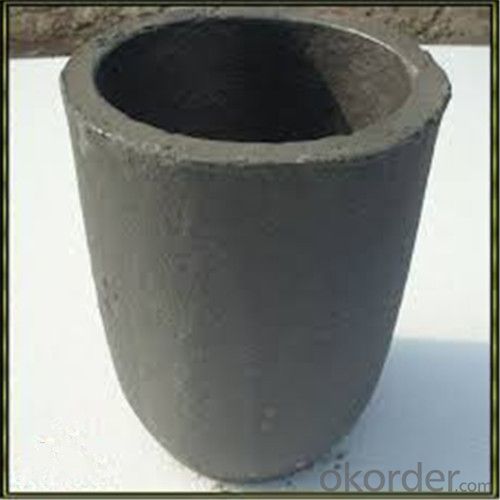
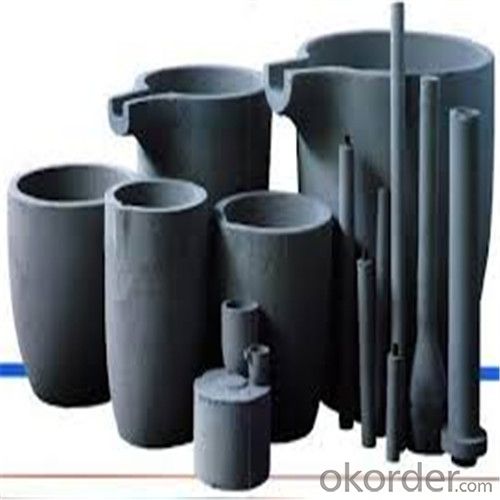
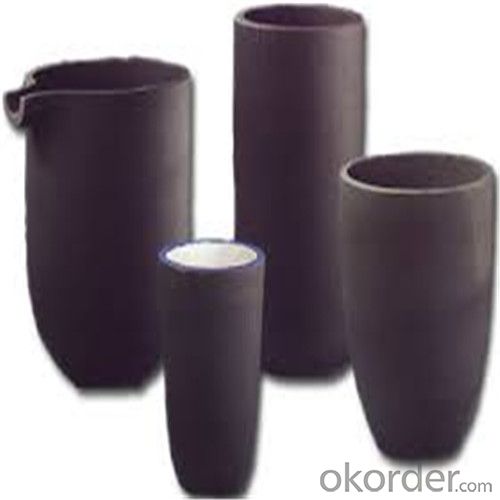
Graphite Vs Ceramic Crucible - SIC Graphite Crucibles for Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles For Gold, Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
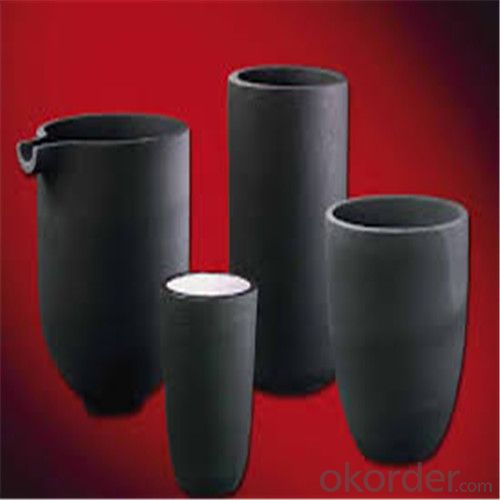

Physicochemical Properties of graphite crucible:
The crucible is an utensil or melting tank vessels that is made of refractory material (such as clay, graphite, quartz or difficult molten metal iron, etc.).
Graphite crucible, with is special advantages and Plasticity, is widely used in the smelting area, e.g. gold smelting, silver smelting, aluminum smelting, cooper smelting, etc.
high pure graphite | ||||
Item | Unit | baked twice | baked three time | baked four times |
impregnated once | impregnated twice | impregnated three times | ||
grain size | mm | ≤325μm | ≤325μm | ≤325μm |
Bulk density | g/cm3 | ≥1.68 | ≥1.78 | ≥1.85 |
Specific resistance | μΩ.m | ≤14 | ≤14 | ≤13 |
Bending strength | MPa | ≥25 | ≥40 | ≥45 |
Compressive strength | MPa | ≥50 | ≥60 | ≥65 |
Ash content | % | ≤0.15 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.05 |
Fine-grain Specialty Graphite FXG-1 | Fine-grain Specialty Graphite FXG-2 | ||||
Item | Unit | Guarantee value | Typical value | Guarantee value | Typical value |
Max grain size | mm | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
Bulk density | g/cm3 | ≥1.70 | 1.73 | ≥1.73 | 1.76 |
Specific resistance | μΩ.m | ≤8.5 | 7.5 | ≤8.0 | 7 |
Bending strength | MPa | ≥10.0 | 11 | ≥12.0 | 12.5 |
Compressive strength | MPa | ≥24.0 | 27 | ≥31.0 | 34 |
Thermal Condcutivity | W/(m.k) | ≥120 | 150 | ≥130 | 160 |
C.T.E.(100-600) °C | 10-6/°C | ≤2.5 | 2.2 | ≤2.5 | 2.1 |
Ash content | % | ≤0.3 | 0.09 | ≤0.3 | 0.09 |
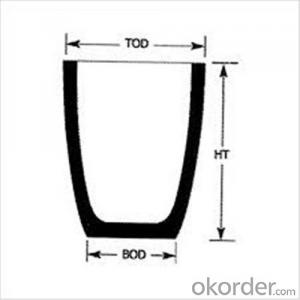
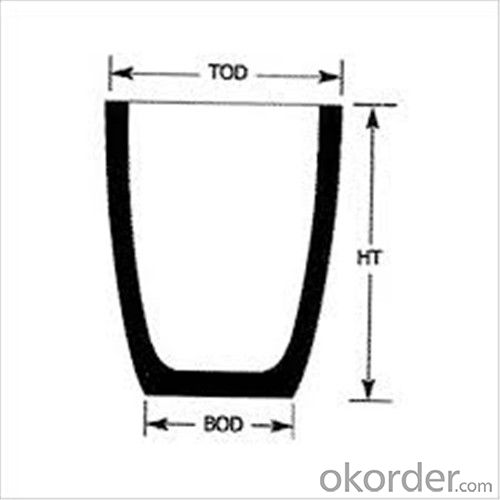
NO | Top diameter | Bottom diameter | Height | Tolerance | Capacity(Kg5%) |
2 | 90 | 50 | 55 | 2 | 0.3 |
3 | 105 | 80 | 93 | 2 | 0.5 |
4 | 102 | 80 | 100 | 2 | 0.6 |
5 | 112 | 82 | 130 | 2 | 0.8 |
6 | 120 | 82 | 141 | 2 | 0.9 |
8 | 138 | 90 | 153 | 2 | 1.2 |
12 | 148 | 100 | 181 | 2 | 1.8 |
16 | 156 | 110 | 190 | 2 | 2.3 |
20 | 180 | 120 | 230 | 2 | 3 |
25 | 186 | 128 | 248 | 2 | 3.7 |
- Q: Why does China choose quartz crucible directly in the aspect of Czochralski silicon?
- Because (1) the melting point of silicon is at 1450 degrees, the container for molten silica must be sufficiently high. (2) Czochralski silicon is the rearrangement of the atomic structure. High purity is essential and insoluble impurities. Quartz crucible material is SiO2, high temperature and stability, will not bring other impurities. That is, the O atoms of the quartz crucible also affect the quality of monocrystalline silicon. (3) when foreign countries engage in these scientific studies, China is still living long with the emperor, so these technologies were introduced into China in the last century of 50s, and the current development is still 50 years from home!
- Q: What graphite crucible is used to smelt aluminium by electromagnetic induction heating?
- Electromagnetic induction heating is the heating of graphite, and can soon rise to 1000 degrees, but aluminum is a magnetic material, will block the electromagnetic field, so this scheme is not feasible
- Q: How is graphite formed?
- 1 isostatic pressed graphite. That's what a lot of people call "three high" graphite, but not three highs or equal pressure.2, molded graphite </p3, extruded graphite, mostly electrode materials.According to the particle size of graphite, it can be divided into detail graphite (high purity graphite), medium graphite (general granularity about 0.8mm), and graphite electrode (2-4mm).
- Q: Are there different sizes available for graphite crucibles?
- Indeed, graphite crucibles are offered in various sizes to cater to diverse needs and applications. These crucibles come in a plethora of sizes, ranging from petite ones suitable for jewelry making or minor laboratory experiments to more substantial ones used for industrial purposes such as metal casting or melting. The necessary size of the crucible is contingent upon the quantity of material to be melted or processed, as well as the unique demands of the application at hand. Consequently, an array of sizes is made available to satisfy distinct requirements and guarantee the optimal and proficient utilization of graphite crucibles.
- Q: How do you use crucibles to process copper?
- How to play lining, you can check the relevant information on Baidu. The working principle of intermediate frequency furnace is induction heating, the inductor is energized, producing dense magnetic lines, cutting the metal in the crucible, generating an electric furnace, and the metal itself generates heat to melt the metal. The power frequency furnace can also pull copper wires.
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing contamination from graphite particles?
- There are several methods to prevent contamination from graphite particles. One approach is to use air filtration systems that effectively capture and remove graphite particles from the air. Another method is to implement proper ventilation systems that minimize the accumulation of graphite particles in the environment. Additionally, using specialized containment measures such as sealed containers or enclosures can prevent graphite particles from spreading and contaminating other surfaces. Regular cleaning and maintenance of equipment and work areas can also help to control graphite particle contamination.
- Q: What is the use of an iron crucible?
- The crucible crucible is used refractory materials (such as clay, graphite, kaolin, quartz or difficult to molten metal such as iron) made of the vessel or melting tank. A bowl shaped container with a ceramic bottom.
- Q: Are graphite crucibles suitable for use in a vacuum environment?
- Yes, graphite crucibles are suitable for use in a vacuum environment. Graphite has a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity, making it an ideal material for containing and heating materials in a vacuum. Additionally, graphite is chemically inert and has low outgassing properties, which ensures minimal contamination or reaction with the vacuum environment.
- Q: Which is a good quality graphite crucible?
- The silicon carbide crucible is a bowl shaped container with a ceramic bottom. When solids have to be heated by fire, the crucible must be used. Because it is more able to withstand high temperatures than glass. When used, the crucible does not usually fill the melt too much to prevent the heat from jumping out and allowing the air to pass in and out freely for possible oxidation.
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing graphite crucible breakage?
- There are several methods that can be employed to prevent graphite crucible breakage. 1. Proper handling and storage: One of the most effective ways to prevent graphite crucible breakage is by ensuring proper handling and storage. Crucibles should be handled with care, avoiding any rough or sudden movements that may cause impact or stress on the crucible. Additionally, crucibles should be stored in a safe and secure location, away from any potential hazards or sources of damage. 2. Controlled heating and cooling: Graphite crucibles are subjected to high temperatures during the melting process. To prevent breakage, it is important to follow proper heating and cooling procedures. Gradual heating and controlled cooling can help minimize thermal shock and stress on the crucible, reducing the risk of breakage. 3. Preheating: Preheating the graphite crucible before use can help prevent breakage. This process involves gradually heating the crucible to a specific temperature range prior to adding the molten material. Preheating helps to reduce the temperature differential between the crucible and the molten material, minimizing the risk of thermal shock and potential breakage. 4. Use of protective coatings: Applying a protective coating to the graphite crucible can provide an added layer of protection against breakage. Coatings such as boron nitride or alumina can help improve thermal shock resistance and reduce the likelihood of crucible failure. 5. Regular inspection and maintenance: Regularly inspecting the graphite crucible for any signs of damage or wear is crucial in preventing breakage. Any cracks, chips, or other defects should be addressed immediately to avoid further deterioration. Additionally, routine maintenance, such as cleaning and removing any build-up or impurities, can help prolong the life of the crucible and prevent breakage. By implementing these methods, individuals or industries can significantly reduce the risk of graphite crucible breakage, ensuring their longevity and performance in various high-temperature applications.
Send your message to us
Graphite Vs Ceramic Crucible - SIC Graphite Crucibles for Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass 2024
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords