Quick Details
Standard: ASTM
Grade: SHS
Type: Steel Coil
Surface Treatment: Galvanized
Application: Solution hardened steel
Width: 600-1534mm
Length: Coil
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Standard: ASTM
Grade: SHS
Type: Steel Coil
Surface Treatment: Galvanized
Application: Solution hardened steel
Width: 600-1534mm
Length: Coil
| Packaging Details: | Oscillated wound: one coil per bundle, inner is the protecting humidity-proof wax paper. Medium is plastic film. Outer is sackcloth or compound paper packing. Coil to be laid on single type pallet (one pile per pallet) |
|---|---|
| Delivery Detail: | Depends on specification and order quanity. |
Feature:
(1) Type of zinc coating finish: regular spangle, minimized spangle and skin-pass.
(2) Types of surface qualities: as coated surface, improved surface and best quality surface.
(3) Surface treatment: chemically passivated, chromate-free passivation, phosphate, anti-finger print, phosphateand, self lubricating film, and untreated.
(4) Type of oiling: oiled and unoiled.
(5) Coil ID: 508/610mm.
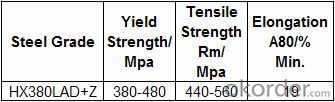
(6) Grade: HX380LAD+Z; Application: high strength steel for cold forming.
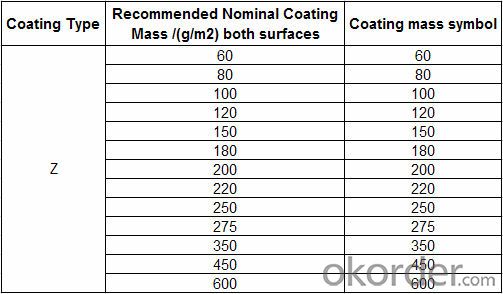
Zinc Coating
Tensile Test Characteristics
What is the application of Steel Coil?
There are two sides,one is out side: Workshop, agricultural warehouse, residential precast unit, corrugated roof, roller shutter door, rainwater drainage pipe, retailer booth;the other is inside: Door, doorcase, light steel roof structure, folding screen, elevator, stairway, vent gutter.

Send your message to us
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords