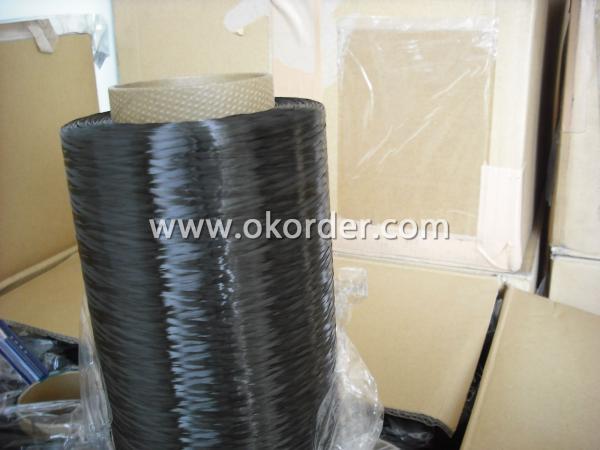
Carbon Fiber 3K
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 Ton m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000Ton m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Carbon Fiber 3K
1. Material: carbonized polyacrylonitrile fiber
2. Filament number:3k
3. Fiber type: T300
4. Tensile strength: 360kgf/mm2
General Data of Carbon Fiber 3K
Weaving Style: Unidirectional, Plain, Twill
Input Available: 3k, 6k, 12k Carbon fiber
Weight: 15 0 ~ 600g / m2
Roll length: To be specified
Storage of Carbon Fiber 3K
It is recommended that the carbon fiber fabric are stored in a cool and dry environment. Recommended temperature range of storage is between 10 ~ 30 degree and relative humidity between 50 ~ 75%.The carbon fiber fabric should remain in the packaging until just prior to use.
Packaging & Delivery of Carbon Fiber 3K
Product is manufactured in form of a roll wound on a paper tube and then packed in a plastic film and placed within a cardboard carton. Rolls can be loaded into a container directly or on pallets.
Packaging Detail: carton
Delivery Detail: within 20 days


- Q: Want advanced reinforcement, but I do not know where the high furnace rock carbon, looking for someone to guide...
- Mall. In fact, BUG can be card out! Inside the palace there is that BUG, but I personally think that no use, I used to strengthen the use of advanced carbon weapons on 12, even 3 did not become a storm, this is only the way to make money TX it
- Q: Why is the solubility of carbon in austenite larger than that in ferrite?
- Its properties are similar to that of pure iron, and its plasticity and toughness are good, and its strength and hardness are low. It is usually massive or flaky in steel.The austenite structure is a face centered cubic lattice with a gap radius (0.414~0.225). Because of the larger size of the lattice gap, the solubility of carbon in gamma -Fe is relatively large. It has good plasticity.
- Q: How does carbon affect the formation of permafrost thawing?
- Carbon can have a significant impact on the formation of permafrost thawing. Permafrost is a layer of frozen soil, rock, and organic matter that remains at or below freezing for at least two consecutive years. It acts as a natural carbon sink, storing large amounts of organic carbon from dead plants and animals that have accumulated over thousands of years. When permafrost thaws, this stored carbon starts to decompose, releasing greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. The carbon released from permafrost thawing contributes to the overall increase in greenhouse gas concentrations, exacerbating climate change. Additionally, as permafrost thaws, it becomes more vulnerable to erosion and subsidence, leading to changes in the landscape and the release of even more carbon. This process can create a positive feedback loop, where the released carbon further accelerates permafrost thawing, resulting in more carbon emissions. Furthermore, permafrost thawing can also impact the stability of infrastructure built on frozen ground, such as roads, buildings, and pipelines, leading to significant economic and environmental consequences. In summary, carbon plays a crucial role in the formation and thawing of permafrost. The release of carbon from thawing permafrost contributes to climate change, accelerates the thawing process, and has various environmental and economic impacts. Addressing carbon emissions and finding ways to mitigate permafrost thawing is essential to combatting climate change and preserving the stability of these frozen ecosystems.
- Q: What is carbon offsetting in the food industry?
- Carbon offsetting in the food industry refers to the practice of neutralizing or compensating for the greenhouse gas emissions associated with food production and distribution processes. It is a way for food companies to take responsibility for their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts in mitigating climate change. Food production and distribution contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, mainly through activities such as deforestation, land use changes, energy consumption, and transportation. Carbon offsetting allows companies in the food industry to invest in projects or initiatives that reduce or remove an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, effectively balancing out their emissions. There are various methods of carbon offsetting in the food industry. One common approach is investing in renewable energy projects, such as wind farms or solar power installations, to offset the emissions produced from energy consumption in food processing facilities or transportation. Another method is supporting projects that promote sustainable agriculture practices, such as reforestation or afforestation efforts, which can sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Carbon offsetting in the food industry also extends to supply chain management. Companies can work with their suppliers to implement more sustainable farming practices, reduce waste, and optimize transportation routes to minimize emissions. By collaborating with farmers, producers, and distributors, food companies can collectively work towards reducing their overall carbon footprint and achieving carbon neutrality. It is important to note that carbon offsetting should not be seen as a substitute for reducing emissions at the source. Instead, it should be viewed as a complementary measure to support the transition towards more sustainable and low-carbon practices in the food industry. By offsetting their emissions, food companies can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and contribute to the global fight against climate change.
- Q: What is carbon sequestration?
- Carbon sequestration is the process by which carbon dioxide (CO2) is captured from the atmosphere and stored for an extended period of time, preventing it from being released and contributing to climate change. This technique aims to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere, as this greenhouse gas is a major driver of global warming. Carbon sequestration can occur naturally through biological processes, such as photosynthesis in plants and algae, or it can be achieved through various artificial methods. Natural carbon sequestration occurs when plants, trees, and other vegetation absorb CO2 during photosynthesis and store it in their tissues. This process, known as terrestrial sequestration, plays a crucial role in reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. Additionally, oceans also act as a significant sink for CO2, absorbing and storing vast amounts of it. This is referred to as oceanic sequestration. Artificial carbon sequestration techniques involve capturing CO2 emissions from industrial processes, power plants, and other sources before they are released into the atmosphere. There are several methods for carbon capture, including pre-combustion capture, post-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion. Once the CO2 is captured, it can be transported and stored underground in geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas fields or saline aquifers. This process is commonly known as carbon capture and storage (CCS) or carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS). Carbon sequestration has gained significant attention due to its potential to mitigate climate change. By reducing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, it helps to slow down the pace of global warming and reduce the impacts of climate change. It is considered to be a crucial part of the broader strategy to achieve net-zero emissions, as it not only reduces future emissions but also removes CO2 that has already been emitted. However, carbon sequestration is not a silver bullet solution to climate change. It should be seen as a complementary approach to other mitigation efforts, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency. Additionally, the long-term storage of CO2 requires careful monitoring and management to ensure its effectiveness and prevent any leakage or environmental risks. Overall, carbon sequestration is a vital tool in the fight against climate change, offering the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Q: How does carbon affect the water cycle?
- The water cycle is affected by carbon in various ways. To begin with, carbon plays a vital role in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide (CO2). Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes have caused an increase in the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere. This rise in carbon dioxide levels leads to global warming and climate change, which then impacts the water cycle. One significant consequence of increased carbon dioxide is the alteration of precipitation patterns. Carbon emissions cause warmer temperatures, resulting in more evaporation from bodies of water. This leads to an increase in water vapor in the atmosphere. The additional moisture can lead to intensified rainfall in certain areas, causing floods. On the other hand, some regions may experience droughts as evaporation rates surpass precipitation rates. These changes disrupt the balance of the water cycle and affect the availability of water resources for both humans and natural systems. Moreover, carbon dioxide dissolved in water forms carbonic acid, which lowers the pH level of oceans and bodies of water. This process, known as ocean acidification, has a negative impact on marine life, including shellfish, corals, and other organisms that rely on calcium carbonate to build their shells or skeletons. Consequently, the disruption of these species can have a domino effect through the food chain, ultimately affecting the entire ecosystem. Additionally, carbon influences the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. Increased carbon emissions have caused a rise in global temperatures, which accelerates the melting process. As the ice melts, it releases freshwater into the oceans, leading to a rise in sea levels. This can have devastating consequences for coastal communities, increasing the risks of flooding and erosion. In conclusion, carbon emissions, mainly in the form of carbon dioxide, have a significant impact on the water cycle. They disrupt precipitation patterns, contribute to ocean acidification, and accelerate ice melting. All of these effects disturb the delicate balance of the water cycle and have far-reaching consequences for ecosystems and communities worldwide.
- Q: Carbon fiber refractory?
- 3, pre oxidized carbon fiber cloth, can withstand 200--300 degrees of high temperature
- Q: Carbon Finance: Carbon Finance
- The "Framework Convention" is the world's first comprehensive control of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions, the International Convention for the human economic and social adverse effects in response to global warming, a basic framework is also the international society for international cooperation in tackling global climate change on the issue. According to statistics, 191 countries have ratified the Convention at present. These countries are called parties to the convention. The parties to the Convention have made many pledges aimed at addressing climate change. Each party must submit periodic reports, which contain the greenhouse gas emission information of the contracting parties and indicate plans and specific measures for the implementation of the convention. The Convention came into force in March 1994 and laid the legal foundation for international cooperation in dealing with climate change. It was an authoritative, universal and comprehensive international framework. The Convention consists of a preamble and 26 main texts. The Convention is legally binding to control emissions of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and stabilize the concentration of greenhouse gases from the destruction of the climate system. The Convention differs from the developed countries and developing countries in terms of their obligations and procedures for fulfilling their obligations.
- Q: There are several allotropes of carbon
- Allotrope of carbon: diamond, graphite, carbon 60 (fullerene), amorphous carbon (charcoal, coke, activated carbon, etc.)
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | Jiangsu,China |
| Year Established | 2002 |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | Europe, America, Africa, Oceania and Japan, Korea, southeast Asia |
| Company Certifications | ISO9000 |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Carbon Fiber 3K
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 Ton m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000Ton m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords