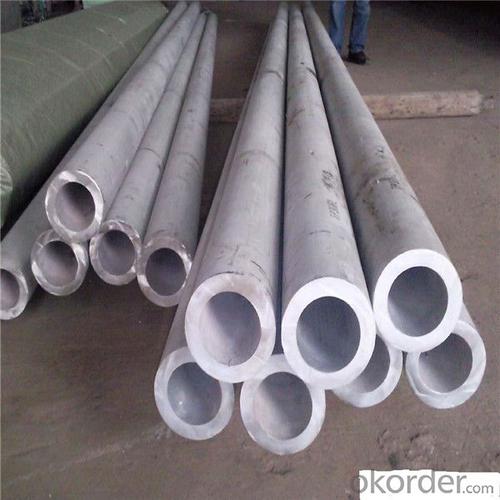
304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipe in Wuxi ,China
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 6 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 25000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
316 stainless steel pipe
Product Description
Name | Stainless Steel Seamless & Welded Tube &Pipe | |||||
Items | Square tubes, round tubes, oval pipes, special shaped pipes, empaistic pipes, fittings | |||||
Standard | ASTM A554, A249, A269 and A270 | |||||
Material Grade | 201: Ni 0.8%~1% | |||||
202: Ni 3.5%~4.5% | ||||||
304: Ni 8%, Cr 18% | ||||||
316: Ni 10%, Cr 18% | ||||||
316L: Ni10%~14% | ||||||
430: Cr16%~18% | ||||||
Outer Diameter | 9.53mm--159mm | |||||
Thickness | 0.3mm - 3.0mm | |||||
Length | 6m or as customers' request | |||||
Tolerance | a) Outer Diameter: +/- 0.2mm | |||||
b) Thickness: +/- 0.02mm | ||||||
c) Length: +/- 5mm | ||||||
Surface | 180G, 240G, 320G Satin / Hairline 400G, 600G Mirror finish | |||||
Application | handrail,railing, staircase, weldmesh screen,door,window, balcony,fence,bench,furniture,etc | |||||
Test | Squash test, extended test, water pressure test, crystal rot test, heat treatment, NDT | |||||
Chemical Composition of Material | Material
Composition | 201 | 202 | 304 | 316L | 430 |
C | ≤0.15 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.12 | |
Si | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | |
Mn | 5.5-7.5 | 7.5-10 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤1.00 | |
P | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.040 | |
S | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | |
Cr | 13-15 | 14-17 | 18-20 | 16-18 | 16-18 | |
Ni | 0.7-1.1 | 3.5-4.5 | 8-10.5 | 10-14 | ||
Mo | 2.0-3.0 | |||||
Mechanical Property | Material Item | 201 | 202 | 304 | 316 | |
Tensile Strength | ≥535 | ≥520 | ≥520 | ≥520 | ||
Yield Strength | ≥245 | ≥205 | ≥205 | ≥205 | ||
Extension | ≥30% | ≥30% | ≥35% | ≥35% | ||
Hardness (HV) | <105< span=""> | <100< span=""> | <90< span=""> | <90< span=""> | ||
Mechanical Properties: MaterialY.S(N/MM2)T.S(N/MM2)ElongationHRB304>205>520>40<95304L>175>480>40<90316>205>520>40<90316L>175>480>40<90430>205>450>22<89
Applications: SurfaceApplication2BMedical equipment, Food industry, Construction material, Kitchen utensils.BAKitchen utensils, Electric equipment, Building construction.No.1Chemical tank, pipe.No.4Kitchen utensils, Building construction,Medical equipment.HLBuilding Construction.
|
| ---Packing & Transport--- Packing
Transport
|


- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for food storage tanks?
- Stainless steel pipes are an excellent choice for food storage tanks due to their high suitability. They possess remarkable corrosion resistance, making them ideal for the storage of food and beverages. Unlike other materials, stainless steel pipes guarantee the safety and quality of the stored food as they do not release any harmful substances. Moreover, their easy maintenance and cleaning contribute to maintaining proper hygiene in food storage tanks. Additionally, stainless steel pipes are durable and capable of withstanding high temperatures, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the tanks. In conclusion, stainless steel pipes are the preferred option for food storage tanks due to their sanitary properties, corrosion resistance, and durability.
- Q: What are the different types of stainless steel pipe tees?
- Different applications and requirements call for various kinds of stainless steel pipe tees. 1. An equal tee is designed with three outlets of the same size, forming a 90-degree angle. It is commonly utilized to branch off or combine flow in a pipeline with equal diameters. 2. A reducing tee, as the name implies, has one outlet smaller than the other two. Its purpose is to connect pipes of different sizes, facilitating a seamless transition in fluid or gas flow. 3. In high-pressure or high-temperature applications, a barred tee provides additional support and reinforcement with a welded bar across the branch opening. This prevents stress concentration and potential failure. 4. For pipeline diversion or angled connections, a lateral tee with one outlet at a 45-degree angle is often employed. 5. A cross tee, featuring four outlets forming a cross-shaped configuration, is used when flow needs to be split or combined in multiple directions, primarily in complex piping systems. 6. Unions and socket weld tees have sockets or unions at the branch connection, allowing for easy disassembly and maintenance. They are commonly used when regular inspection, cleaning, or replacement is required. 7. Threaded tees have threaded branch connections that can be screwed onto the pipe without welding. They are frequently used in low-pressure applications or situations where frequent disassembly is necessary. Each type of stainless steel pipe tee offers specific advantages and is chosen based on the requirements of the particular piping system, including flow rates, pressure, temperature, and compatibility with the transported fluids or gases.
- Q: What is the difference between 904L and 2205 stainless steel pipes?
- 904L and 2205 stainless steel pipes differ in various aspects. Firstly, their composition varies significantly. 904L stainless steel is a high alloy austenitic stainless steel with elevated levels of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. It also has a low carbon content, granting it remarkable resistance to corrosion and pitting. Conversely, 2205 stainless steel is a duplex stainless steel that combines austenite and ferrite phases. It contains lower amounts of chromium and nickel compared to 904L, but boasts higher levels of molybdenum and nitrogen. Secondly, the mechanical properties of these steels differ. 904L stainless steel exhibits exceptional toughness and high strength, making it suitable for applications in aggressive environments such as chemical processing plants and offshore oil and gas platforms. Conversely, 2205 stainless steel possesses good overall mechanical properties, including high tensile and yield strength. It is commonly utilized in industries like marine, paper, and pulp, wherein resistance to stress corrosion cracking is crucial. Additionally, their resistance to corrosion separates them further. Although both steels are corrosion-resistant, 904L stainless steel showcases remarkable resistance to a wide range of corrosive environments, including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and saltwater. This makes it an ideal choice for industries that demand extreme corrosion resistance. On the other hand, 2205 stainless steel, while not as corrosion-resistant as 904L, still offers good resistance to many corrosive substances, rendering it suitable for various applications. Cost constitutes another distinguishing factor between these steels. Due to its high alloy content and superior properties, 904L stainless steel generally carries a higher price tag than 2205 stainless steel. Therefore, the selection between the two will depend on the specific requirements of the application and the allocated budget. In conclusion, the main disparities between 904L and 2205 stainless steel pipes emerge in their composition, mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and cost. Comprehending these distinctions aids in selecting the appropriate stainless steel pipe for a given application.
- Q: How do you prevent rusting in stainless steel pipes?
- There are several measures that can be taken to prevent rusting in stainless steel pipes: 1. Keeping the pipes clean regularly is important. Use mild soap or detergent and warm water to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can cause corrosion. 2. Avoid using abrasive cleaners, steel wool, or harsh chemicals as they can scratch the surface of the stainless steel and compromise its protective layer. 3. Protect the pipes from exposure to chlorides, such as those found in saltwater or certain cleaning agents. If the pipes are installed in areas with these substances, apply protective coatings or use specialized stainless steel grades that are resistant to chloride-induced corrosion. 4. Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent moisture buildup, which can accelerate the rusting process. Ensure that the stainless steel pipes have adequate airflow to keep them dry and reduce the risk of corrosion. 5. Regularly inspect the pipes for signs of rust or corrosion. If any damage or rust spots are detected, address them promptly to prevent further deterioration. 6. Consider passivation, a chemical treatment process that enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. This involves removing contaminants from the surface and promoting the formation of a protective oxide layer. It is recommended to have professionals with experience in handling stainless steel perform the passivation process. 7. In certain cases, cathodic protection can be used. This involves using sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems to create an electrochemical reaction that protects the stainless steel from corrosion. By following these preventive measures, the risk of rusting in stainless steel pipes can be significantly reduced, ensuring their longevity and durability.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be wrapped with fiberglass insulation?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be wrapped with fiberglass insulation.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be insulated with polyurethane?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be insulated with polyurethane. Polyurethane insulation is commonly used for both thermal and acoustic insulation in various industries, including plumbing and HVAC systems. It offers excellent thermal conductivity properties and low moisture absorption, making it an ideal choice for insulating stainless steel pipes. Polyurethane insulation can be applied as a foam or in the form of pre-insulated pipe sections. It provides effective insulation by reducing heat loss or gain, preventing condensation, and improving energy efficiency. Additionally, polyurethane insulation is durable, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion, making it a suitable choice for insulating stainless steel pipes in various applications.
- Q: How do you prevent discoloration in stainless steel pipes?
- To prevent discoloration in stainless steel pipes, there are several measures that can be taken: 1. Proper cleaning: Regularly clean the stainless steel pipes using mild soap or detergent and warm water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that can damage the surface and cause discoloration. 2. Rinse thoroughly: After cleaning, make sure to rinse the pipes thoroughly with clean water to remove any residue or cleaning agents that may cause discoloration. 3. Avoid contact with corrosive substances: Keep stainless steel pipes away from direct contact with corrosive substances such as strong acids, alkaline solutions, or chlorides. These substances can lead to chemical reactions and cause discoloration. 4. Use protective coatings: Applying a protective coating, such as a clear lacquer or a special stainless steel protective spray, can help prevent discoloration by creating a barrier between the metal surface and the environment. 5. Control temperature: Excessive heat can cause discoloration in stainless steel pipes. It is important to control the temperature of the surrounding environment or the fluid passing through the pipes to prevent overheating. 6. Regular maintenance: Perform routine inspections and maintenance to identify any signs of discoloration or damage and address them promptly. This includes checking for leaks, corrosion, or any other factors that may contribute to discoloration. By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of discoloration in stainless steel pipes and maintain their aesthetic appeal and functionality for a longer period.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for high-temperature applications?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are suitable for high-temperature applications. Stainless steel has excellent heat resistance properties and can withstand extreme temperatures without losing its structural integrity. It is commonly used in industries such as power generation, oil and gas, chemical processing, and aerospace, where high-temperature environments are prevalent.
- Q: How do you choose the right stainless steel grade for a specific application?
- When choosing the right stainless steel grade for a specific application, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, it is important to understand the environment in which the stainless steel will be used. Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances. Different stainless steel grades have varying levels of resistance to corrosion, so selecting a grade that is suitable for the specific environment is crucial. Secondly, the required mechanical properties of the stainless steel should be evaluated. This includes the desired strength, ductility, and toughness. Different stainless steel grades have varying mechanical properties, so it is important to choose a grade that meets the specific requirements of the application. Additionally, the fabrication process should be taken into account. Some stainless steel grades are easier to weld, machine, or form than others. Therefore, it is important to select a grade that is compatible with the intended fabrication techniques. Furthermore, cost considerations should be taken into consideration. Different stainless steel grades have varying price points, so it is important to choose a grade that fits within the budget of the specific application. Lastly, consulting with a materials engineer or a stainless steel supplier can provide valuable expertise and guidance in choosing the right grade. These professionals can help evaluate the specific requirements of the application and recommend the most suitable stainless steel grade. In conclusion, choosing the right stainless steel grade for a specific application requires considering factors such as the environment, mechanical properties, fabrication process, cost, and seeking expert advice. By taking these factors into account, one can make an informed decision and select the most appropriate stainless steel grade for their specific application.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for solar energy systems?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for solar energy systems. Stainless steel is a durable and corrosion-resistant material, making it suitable for transporting heat transfer fluids in solar water heating and solar thermal systems. It can withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in solar energy applications, ensuring reliable performance and longevity.
Send your message to us
304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipe in Wuxi ,China
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 6 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 25000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords