Home Solar Inverter System
Home Solar Inverter System Related Searches
Home Solar System Inverter Home Solar Inverter Solar Home Inverter Solar Inverter System Solar Power Inverter System Inverter For Home Solar System Inverter Solar System Solar System Inverter For Home Solar Electric Inverter System Home Solar Power Inverter House Solar Inverter Solar Inverter Systems Household Solar Inverter Hybrid Solar Inverter System Solar House Inverter Hybrid Inverter Solar System Solar Hybrid Inverter System Domestic Solar Inverter Inverter Solar Systems Micro Inverter Solar System Home Depot Solar Inverter Home Solar Panel Inverter Solar And Inverter System Solar System Inverter Solar Inverter For Home Inverter For Home Solar Household Solar Power System Battery Inverter Solar System Solar Solar Inverter Solar System Hybrid InverterHome Solar Inverter System Supplier & Manufacturer from China
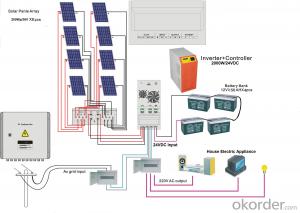
A Home Solar Inverter System is a crucial component in residential solar energy setups, converting the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used by household appliances and fed back into the power grid. This system typically includes an inverter, charge controller, batteries for energy storage, and sometimes a monitoring system to track energy production and consumption.The Home Solar Inverter System is widely used in various scenarios where there is a need for clean, renewable energy. It is particularly beneficial in off-grid locations where traditional electricity is not readily available, as well as in grid-tied systems where homeowners can reduce their electricity bills by generating their own power. Additionally, these systems can be used in combination with battery storage to provide backup power during outages, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity.
Okorder.com is a reputable wholesale supplier of Home Solar Inverter Systems, offering a vast inventory of high-quality products to meet the diverse needs of customers. With a commitment to providing reliable and efficient solutions, Okorder.com ensures that each Home Solar Inverter System is thoroughly tested and certified to perform optimally in various conditions, making it a trusted source for those looking to invest in sustainable energy solutions.
Hot Products