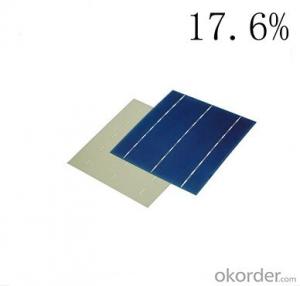
Alta Solar Cells
Alta Solar Cells Related Searches
Alta Devices Solar Cells High Temperature Solar Cells Better Solar Cells High Quality Solar Cells High Performance Solar Cells High Efficiency Solar Cells High Power Solar Cells Algae Solar Cells Hot Solar Cells High Output Solar Cells High Voltage Solar Cells Free Solar Cells High Wattage Solar Cells Chinese Solar Cells Bio Solar Cells Azur Solar Cells Photovoltaic Solar Cells Aerospace Solar Cells All About Solar Cells Large Solar Cells Nano Solar Cells Evergreen Solar Cells Home Depot Solar Cells Atj Solar Cells American Made Solar Cells Satellite Solar Cells Flex Solar Cells Highly Transparent Solar Cells Iii V Solar Cells Seattle Solar CellsAlta Solar Cells Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Alta Solar Cells, a leading provider of high-quality solar energy solutions, offers a diverse range of products including solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems. These products are designed to harness the power of the sun and convert it into usable electricity, making them an ideal choice for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Alta Solar Cells' products are engineered to deliver maximum efficiency and reliability, ensuring that users can benefit from a sustainable and cost-effective energy source.Alta Solar Cells' products are widely used in various scenarios, from powering homes and businesses to supporting large-scale solar farms. They are particularly beneficial in areas with abundant sunlight, where they can generate significant amounts of clean energy. By utilizing Alta Solar Cells' products, users can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, lower their energy bills, and contribute to a greener environment. The products are also easy to install and maintain, making them a practical choice for those looking to adopt solar energy.
Okorder.com is a reputable wholesale supplier of Alta Solar Cells' products, boasting a large inventory to cater to the growing demand for solar energy solutions. As a trusted distributor, Okorder.com ensures that customers have access to the latest and most efficient solar products at competitive prices. By partnering with Alta Solar Cells, Okorder.com is committed to providing customers with reliable and high-performing solar solutions that meet their energy needs and contribute to a sustainable future.
Hot Products