Supply Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet/Coil
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Hot-dip Zinc Coating Steel Building Roof Walls
1.Structure of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Description:
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications. Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
2.Main Features of the Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
• Excellent process capability
• Smooth and flat surface
• Workability, durability
• Excellent anticorrosive property
• High strength
• Good formability
• Good visual effect
3.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Images:


4.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Specification:
Standard: ASTM, JIS,EN
Grade: CS, DX51D+Z,SGCC, SS 230~550,S220GD+Z~S550GD+Z, SGC340~SGC570
Thickness: 0.1mm~5mm
Width: max 2000mm
Coil weight:3-12 MT
Coil ID:508/610mm
Surface structure: zero spangle, regular spangle or minimum spangle
Surface treatment: Chromate treatment, Oiled/dry, skinpassed/non-skinpassed
Packing: Standard seaworthy export package
Technology test results:
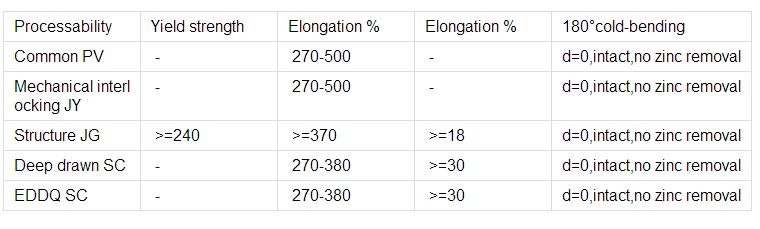
5.FAQ of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1.How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2.How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-30 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
- Q: How are steel coils processed for slitting or edge trimming?
- Steel coils are processed for slitting or edge trimming by feeding the coil into a slitting or trimming machine. The machine uses sharp rotating blades to cut the coil into smaller strips or remove the excess material from the edges. This process helps to create narrower coils or achieve precise edge dimensions for various applications.
- Q: I am using mild steel wire (very thin and bendable) for an art project, and would like to know if using a soldering torch is effective enough to get the job done. Or do I have to use a butane torch to heat the metal?BTW, is it better to use soft or hard solder?
- You can indeed by using the correct flux as normal soldering fluxes as used by plumbers will not work. I believe to solder steel it requires an acid flux which will corrode copper so when its done make sure its well cleaned afterwards and if possible apply a corrosion proofer afterwards ie paint or even petroleum jelly. I am curious as to why you would want to solder wire to a steel nail.
- Q: What are the challenges in coil slitting for thin gauge materials?
- Successfully operating coil slitting for thin gauge materials involves addressing a specific set of challenges. One major challenge is ensuring the proper handling and stability of the thin gauge material. The material's susceptibility to deformation, wrinkling, or tearing increases as it becomes thinner. To tackle this, careful attention must be given to the handling equipment and techniques used during the slitting process. This is necessary to maintain the appropriate tension and support throughout the operation. Another challenge is maintaining consistent and precise slitting widths. Thin gauge materials are often used in applications where accuracy is crucial, such as electronic components or automotive parts. Any variation in the slitting width can cause functional defects or assembly problems. Achieving precise slitting widths in thin gauge materials requires the use of high-quality slitting knives, well-maintained slitting machinery, and accurate tension control systems. In addition, thin gauge materials are more prone to surface defects, such as scratches or burrs, during the slitting process. These defects can impact the material's appearance, performance, or even its safety. To minimize the occurrence of surface defects, it is important to carefully select slitting knives and regularly maintain the slitting machinery. Furthermore, thin gauge materials often possess a higher yield strength, making them more resistant to deformation. This poses a challenge when it comes to achieving clean and straight edges during the slitting process. Special considerations must be taken to ensure that the slitting knives are sharp and properly aligned, allowing for clean cuts without introducing any edge defects. Lastly, thin gauge materials are generally more sensitive to external factors such as temperature, humidity, or static electricity. These factors can affect the material's dimensional stability, resulting in variations in slitting width or other quality issues. Therefore, it is crucial to establish appropriate environmental conditions and implement effective anti-static measures to minimize the impact of these factors. To summarize, the challenges associated with coil slitting for thin gauge materials revolve around handling and stability, maintaining precise slitting widths, minimizing surface defects, achieving clean and straight edges, and mitigating the influence of external factors. Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of suitable equipment, techniques, and operational controls to ensure high-quality slitting outcomes.
- Q: Building the bulwurk, general use on trawlers. What kind of steel is best suited.
- Best amusing on right here in a while ,simply heading to the harbour bar to look at the fleet are available ,Booboo edged for me ,preferred the Liverpool one ,probably subsequent time we ll inform Chrispen its just a pleasant raid ,however excellent ,the entire equal
- Q: Can steel coils be used in the production of consumer goods?
- Yes, steel coils can be used in the production of consumer goods. Steel coils are versatile and commonly used in various industries, including consumer goods manufacturing. They are often used as raw materials in the production of appliances, automotive parts, construction materials, furniture, and packaging. The durability and strength of steel coils make them suitable for these applications, ensuring the quality and longevity of the consumer goods produced.
- Q: Hi! does anyone know where can i find a building with a structure of steel frames, i need to do an analysis for school so i need joint details, girder details and such! PLEASE help me! thanks
- if u need to analyse a steel framed structure for joint details the best example would be of a mechanic workshop...the truss of such a workshop is always supported on a portal frame and in most of the case thats a steel structure...do keenly observe the joints at the footing plates that is connected to the girder section...nd also observe the joints in truss of such a frame....myslf m a civil engg. student.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the production of automotive body panels?
- Steel coils are used in the production of automotive body panels by being processed and shaped into the desired form through techniques like stamping, cutting, and bending. These coils provide the necessary strength and durability required for the structural integrity of the body panels, ensuring the safety and performance of the vehicle.
- Q: What are the common coil packaging methods?
- The common coil packaging methods include stretch wrapping, strapping, banding, and using coil covers.
- Q: Is there a difference between hot rolled and cold rolled steel coils?
- Yes, there is a significant difference between hot rolled and cold rolled steel coils. Hot rolled steel coils are produced at high temperatures and are typically used for applications that require malleability and ductility. On the other hand, cold rolled steel coils are produced at room temperature and undergo a process that results in a smoother, more precise finish. Cold rolled steel coils are often used in applications that require a higher degree of strength and surface quality.
- Q: I have taylormade burner steel irons and I was wondering what would the flex of steel be if you were to compare it to graphite shafts, like regular, stiff, super stiff, etc...THANKS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
- If i understand you correctly, i think you misunderstand shafts. Steel shafts vs. graphite shafts these days is more of a competition of weights, not flexibility. Both steel and Graphite have different flex profiles available from Ladies (L) to super stiff (X). Graphite may feel a little more whippy than steel because of the lighter weight. Shafts will vary by company as well. Stiff from True temper may not be as stiff as one from Aldila, or vice verse. You can also make a shaft play stiffer or more flexible by where you cut the length. This is called tipping. Take more from the bottom and it will be stiffer, more from the grip end and it will play more flexible.
Send your message to us
Supply Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet/Coil
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























