Section Steel Roll From China With High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 41000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Company Profile
CNBM International Corporation (CNBM International) is the most important trading platform of CNBM Group Corporation, a state-owned company under the direct supervision of State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council.
CNBM Group is integrated with four business segments: Manufacture, R&D,Sets of equipment and Logistics trading.Mill rolls are our main products.
CNBM International is highly recognized by its business partners and clients all over the world and has established good business relationship with the customers in over 120 countries and regions all over the world.
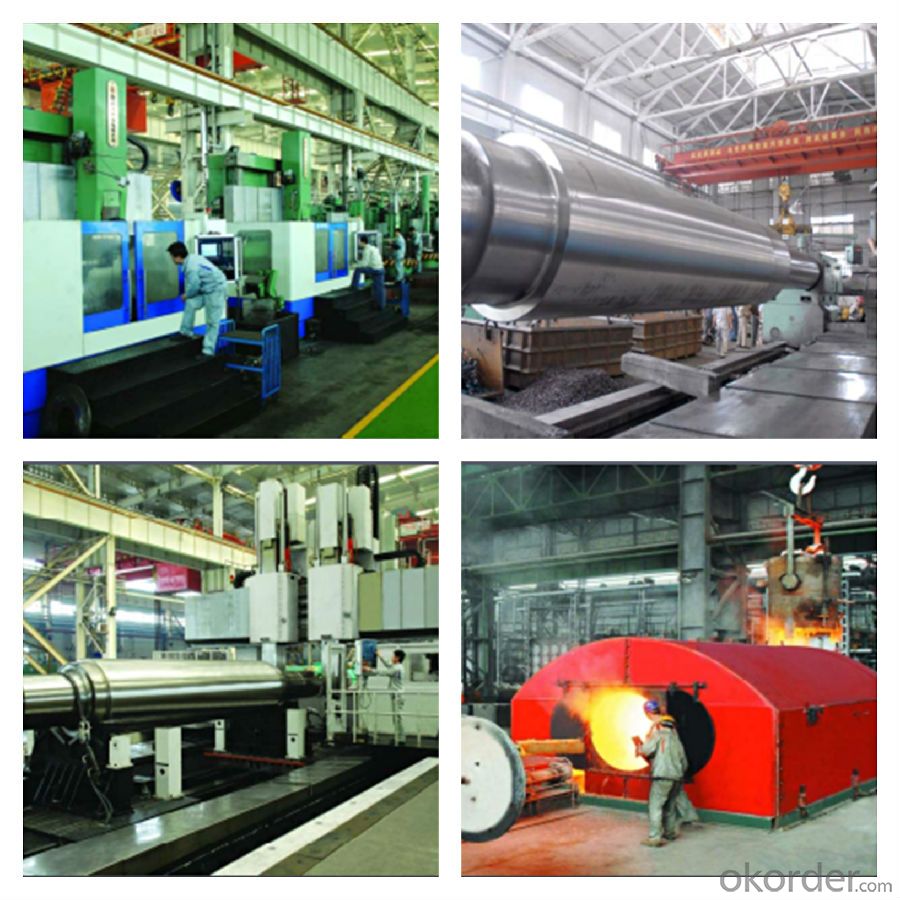
The product introduction of mill roll
Equipped with advanced technological facilities on melting, casting, forging, heat treating and mechanical machining, our factory has formed 9 professional complete roll manufacturing lines of cast steel, cast iron and forged steel rolls such as strip mill rolls, heavy section mill rolls, wire & bar rolls, special shaped rolls and small-sized cold rolls and specialized production lines of bloom and slab CCM, coke oven equipments and wind power products. Annual production capacity of mill rolls is 500,000 tons, metallurgical equipment is 80,000 tons.


Workshop
Workshop is the core of our company and undertakes all of scientific research work. The company specially produces and supplies all kinds of roll used for hot strip mill, cold strip mill, plate & heavy plate mill, large-sized section mill, universal mill etc.

Products & Specification
| Mill | Application | Material | Product Specification | ||
| Hot Strip Mill | Large-sized vertical roll | Special alloy cast roll, Adamite | All Sizes | ||
| Small-sized vertical roll | Adamite, HiCr iron | ||||
| Roughing work roll | Special alloy cast steel, Adamite, HiCr steel, Semi-HSS, HiCr iron | ||||
| Finish rolling | Early stand work roll | HiCr iron, HSS | |||
| Later stand work roll | ICDP, HSS | ||||
| Finishing back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | |||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | ||||
| Temper rolling | Work roll | HiCr iron | All Sizes | ||
| Alloy forged steel | |||||
| Back-up roll | ICDP | ||||
| Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000, W≤80t | ||||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000, W≤75t | ||||
| Mill | Application | Material | Product specification |
Cold strip mill & Single stand cold mill | Work roll | Alloy forged steel | All Sizes |
| Intermediate roll | Alloy forged steel | ||
| Temper roll | Alloy forged steel | ||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | |
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | ||
Largesized universal structural mill | Break-down roll | Special alloy cast steel, alloy nodular iron | All Sizes |
| Horizontal collar | High carbon adamite (duplex) | ||
| Vertical collar | High carbon adamite, HiCr iron | ||
| Edger roll Edger roll | High carbon adamite | ||
| Shaft | Alloy forged steel |
| Mill | Application | Marterial | Product Specification | |
| CSP | Vertical Roll | Adamite, Special alloy cast steel, HiCr iron | All Sizes | |
| Roughing work roll | Semi-HSS, HiCr Steel | |||
| Finish rolling | Early stand | HiCr iron, HSS | ||
| Later stand | ICDP, HSS | |||
| Roughing & Finishing back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
| Steckel Mill | Vertical roll | Adamite, Special alloy cast steel | All Sizes | |
| Roughing work roll | ICDP, HiCr iron | |||
| Finishing work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
| Plate & Heavy plate mill | Rough rolling | 2-hi work roll | Special alloy cast steel, Tool steel | All Sizes |
| 4-hi work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Finishing work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Single stand work roll | HiCr iron, ICDP | |||
| Back-up roll | Duplex cast steel | D≤¢2000,W≤80t | ||
| Alloy forged steel | D≤¢2000,W≤75t | |||
Quality Control
The company has the most advanced experimental and testing equipments in global mill roll industry, including direct-reading spectrometer, spectrum analyzer , X-ray fluorescence analyzer, scanning electronic microscope, energy disperse spectroscopy, X-ray diffractometer, image analyzer, high/low temperature metallographic microscope, X-ray stress meter, brittleness temperature tester, thermal analogue machine, dilatometer, macro and micro hardness tester, OMNISCAM-1X automatic flaw detection, USN60 ultrasonic flaw detector, magnetic powder and non-destructive flaw detection etc,. The advanced inspection equipments and experimental methods provide guarantee for quality control and experiment on material, usability test and performance.
The factories of CNBM invested 2.3 billion RMB for large-scale
CNBM international Corporation has completed equipment and technology upgrade transformation, which was concentrated on three projects, production line of centrifugal casting rolls for hot strip and plate mill, forged roll for cold/hot strip mill, national class technology center and roll material lab. Through upgrade transformation, the following targets have been achideved:
(1)It becomes the world's biggest specialized mill roll maker with the largest production scale, the most complete specifications of products and the most extensive coverage of various rolls used on rolling mill.
(2) The technology of equipments has reached international leading level.
(3) "Mechanization, automation, intellectualization, digitization" of equipments obviously improve the quality control ability.
(4) New types of research instruments improve the R&D capacity of products.
Customers Visit

FAQ
Q:Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A:CNBM is a large-scale central governmental industrial group with its own manufacturing sector, research and development sector, trading sector and logistics sector.
Q:I have some special requirement about specifications.
A:We have a well-rounded product range, which endows us with the capability of applying many special specifications. Please feel free to contact us with yours.
Q:Do you accept OEM service?
A:Yes, we do.
Q:What is your delivery time?
A:It depends on the size/complexity of your order and our own production schedule. Usually we provide a faster delivery than the industry's average.
Q:What is the payment term?
A:Our payment terms are negotiable.
Q:Can I have my own logo on the product?
A:Sure, we can apply your own logo on the products according to your requirement.
- Q: What are the safety precautions for operating metal casting machinery?
- The safety precautions for operating metal casting machinery include wearing appropriate personal protective equipment such as goggles, gloves, and fire-resistant clothing. It is important to ensure that the machinery is properly maintained and inspected regularly to prevent any potential hazards. Operators should receive adequate training on the equipment and its operational procedures. Additionally, it is crucial to follow established safety guidelines, such as using proper lifting techniques, securing workpieces, and avoiding loose clothing or jewelry that can get caught in the machinery. Finally, having fire extinguishers and emergency stop buttons readily accessible is essential in case of any accidents or emergencies.
- Q: How does metal casting machinery handle the data management and analysis of castings?
- Metal casting machinery does not handle the data management and analysis of castings directly. Instead, this responsibility falls on the manufacturing and quality control teams. They utilize various software and systems to collect and analyze data related to castings, such as design specifications, material properties, production parameters, and inspection results. This data is then used to ensure the quality and efficiency of the casting process, identify any issues or deviations, and make informed decisions for process improvement and optimization.
- Q: How long does it take to set up metal casting machinery?
- The time it takes to set up metal casting machinery can vary depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the machinery, the experience of the operators, and the specific requirements of the casting process. In general, setting up metal casting machinery can take anywhere from a few hours to several days. For smaller machines or simpler casting processes, the setup time can be relatively quick. This may involve tasks such as assembling the machinery, connecting power and water supplies, and calibrating any necessary settings. With proper planning and organization, this setup process can be completed within a few hours. However, for larger and more complex machinery, the setup time can be more extensive. These machines often require additional steps, such as aligning various components, installing specialized tools or molds, and conducting thorough testing and calibration. Furthermore, operators may need to undergo training or familiarization with the specific machinery and casting process, which can also add to the setup time. Additionally, the specific requirements of the casting process itself can influence the setup time. Different casting methods, such as sand casting, investment casting, or die casting, may involve different setup procedures and equipment. The complexity of the desired product, including its size, intricacy, and material requirements, may also impact the setup time. It is important to note that efficiency and experience play a significant role in the setup time. Experienced operators who are familiar with the machinery and the casting process can often complete the setup more swiftly. Adequate planning, organization, and preparation of materials and resources can also help streamline the setup process. Overall, while it is challenging to provide a specific timeframe for setting up metal casting machinery, it typically ranges from a few hours to several days, depending on various factors.
- Q: Can metal casting machinery be used for the production of defense components?
- Yes, metal casting machinery can be used for the production of defense components. Metal casting is a widely used manufacturing process in the defense industry for producing a wide range of components, including those used in weapons systems, vehicles, and aircraft. The versatility and flexibility of metal casting technology make it suitable for producing complex and intricate defense components with high precision and accuracy. Additionally, metal casting allows for the use of various materials, such as steel, aluminum, and titanium, which are commonly used in defense applications due to their strength and durability. Furthermore, metal casting machinery can be easily adapted to meet the specific requirements and specifications of defense components, ensuring that they meet the necessary standards for performance, reliability, and safety.
- Q: Can metal casting machinery produce complex shapes and intricate details?
- Yes, metal casting machinery is capable of producing complex shapes and intricate details. Metal casting processes such as investment casting, sand casting, and die casting allow for the creation of intricate designs and complex shapes with high accuracy and precision. These processes involve the use of molds or dies, which can be made from various materials including sand, plaster, or metal. The molds are designed to replicate the desired shape and details of the final product. With advancements in technology, computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems are often used to create highly intricate designs and patterns, which can then be translated into the molds or dies used in the casting process. Additionally, the use of advanced materials and alloys further enhances the capabilities of metal casting machinery to produce complex shapes and intricate details. Overall, metal casting machinery offers a versatile and efficient method for manufacturing components with complex geometries and fine details across various industries.
- Q: What are some factors that affect the cost of metal casting machinery?
- The cost of metal casting machinery can be affected by various factors. One crucial factor to consider is the size and capacity of the machinery. Larger machinery with higher capacity tends to be more expensive due to the need for additional materials and components to handle larger volumes of metal. Another factor that plays a role in determining the cost is the complexity and precision of the machinery. Machinery with advanced technology and intricate design features generally comes with a higher price tag. This is because the manufacturing process for such machinery may involve extra steps and require more sophisticated equipment. The quality and durability of the materials used in constructing the machinery also impact its cost. Machinery made from high-quality materials like stainless steel or high-grade alloys tends to be more expensive due to their increased strength, longevity, and resistance to wear and tear. Furthermore, the level of automation and technological advancements incorporated into the machinery can affect its cost. Machinery that utilizes advanced automation systems, computer numerical control (CNC) technology, or robotic systems will generally have a higher price due to the enhanced precision, efficiency, and productivity they offer. Lastly, market demand and competition within the industry can influence the cost of metal casting machinery. If there is high demand for a particular type of machinery, manufacturers may increase their prices. Conversely, intense competition among machinery suppliers may lead to lower prices as manufacturers try to attract customers. In conclusion, the cost of metal casting machinery is influenced by factors such as size and capacity, complexity and precision, quality of materials, level of automation, and market demand and competition. It is crucial for businesses to carefully evaluate their specific needs and consider these factors when purchasing metal casting machinery to ensure they receive the best value for their investment.
- Q: What are the different types of filters used with metal casting machinery?
- There are several types of filters commonly used with metal casting machinery, including ceramic filters, foam filters, and sand filters. Ceramic filters are made of ceramic material and are used to remove impurities and solid particles from molten metal. Foam filters, on the other hand, are made of porous foam material and are effective in capturing smaller impurities. Sand filters, as the name suggests, use layers of sand to filter out impurities and improve the quality of the cast metal. Each type of filter has its own advantages and is selected based on the specific requirements of the casting process.
- Q: How is the sand removed from the final product in metal casting machinery?
- In metal casting machinery, the sand is typically removed from the final product through a process called shakeout. Shakeout involves vibrating or shaking the castings to dislodge and remove the sand particles that are adhered to the surface. After the casting solidifies and cools down, it is typically placed on a vibrating conveyor or table. The vibrations cause the sand to become loose and separate from the casting. As the sand particles become dislodged, they fall through the gaps or openings in the conveyor or table, leaving the clean casting behind. In some cases, additional methods may be employed to further remove any remaining sand particles. These methods can include using compressed air or mechanical brushes to blow or brush away the sand from the casting's surface. Once the sand is removed, the casting may undergo further finishing processes such as grinding, polishing, or shot blasting to enhance its surface finish and remove any remaining traces of sand or other impurities. These processes ensure that the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards.
- Q: What are the cost considerations when using metal casting machinery?
- When using metal casting machinery, there are several cost considerations to take into account. Firstly, the initial investment in the machinery itself can be significant. Metal casting machinery can be quite expensive, depending on the size, type, and capabilities of the equipment. Therefore, it is essential to consider the budget and financial resources available before deciding on the specific machinery to purchase. In addition to the upfront cost, there are also ongoing expenses to consider. This includes the cost of raw materials, such as metal alloys, which can vary in price depending on the type and quality of the material being used. The cost of consumables, such as refractory materials and coatings, should also be taken into account. Operational costs are another important consideration. Metal casting machinery requires electricity to operate, so the energy consumption and associated utility costs must be factored in. Furthermore, regular maintenance and repair costs should be considered, as machinery may require routine servicing or occasional repairs to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Labor costs are an additional consideration. Skilled operators or technicians are often needed to operate the machinery efficiently and effectively. The wages and benefits of these personnel should be included in the overall cost analysis. Moreover, it is essential to consider the production output and efficiency of the metal casting machinery. Higher-quality machinery may be more efficient, resulting in increased production rates and reduced labor costs over time. However, it is important to balance the potential benefits of more advanced machinery with the associated costs. Lastly, it is crucial to assess the potential return on investment (ROI) when considering metal casting machinery. Factors such as increased production capacity, improved product quality, reduced scrap rates, and faster turnaround times should be considered when evaluating the financial impact of the machinery on the overall business operations. Overall, cost considerations when using metal casting machinery involve a comprehensive assessment of initial investment, ongoing expenses, operational costs, labor costs, production output, and potential ROI. Properly analyzing these factors will help determine the economic viability and long-term financial impact of utilizing metal casting machinery.
- Q: What are the steps involved in the operation of metal casting machinery?
- The operation of metal casting machinery involves several steps to ensure the accurate and efficient production of metal castings. These steps typically include: 1. Pattern creation: The first step is to create a pattern, which is a replica of the desired metal casting. The pattern is usually made from wood, plastic, or metal and is used to create the mold for the casting. 2. Mold preparation: Once the pattern is ready, it is used to create the mold. The mold is made by pressing or pouring a mixture of sand and bonding agents around the pattern. The mold is then allowed to harden and set. 3. Pattern removal: After the mold has hardened, the pattern is removed from the mold cavity. This can be done by either pulling the pattern out or by breaking the mold, depending on the type of pattern used. 4. Preheating the mold: Before pouring the molten metal into the mold, it is important to preheat the mold to prevent thermal shock. Preheating also helps to remove any moisture or volatile compounds from the mold. 5. Metal melting: The metal to be cast is melted in a furnace. The type of furnace used depends on the metal being cast and can range from electric induction furnaces to gas-fired furnaces. The metal is heated to its melting point to ensure it becomes molten and ready for pouring. 6. Metal pouring: Once the metal has melted, it is poured into the mold cavity. Care must be taken to ensure the metal is poured evenly and at the correct temperature to prevent defects or inconsistencies in the final casting. 7. Cooling and solidification: After the metal is poured, it begins to cool and solidify inside the mold cavity. The cooling time depends on the size and thickness of the casting, as well as the type of metal used. Cooling can be accelerated by using cooling fans or water-cooled molds. 8. Mold removal: Once the metal has completely solidified, the mold is removed. This can be done by shaking, vibrating, or breaking the mold, depending on its type. The mold is typically destroyed during this process, as it cannot be reused. 9. Finishing and cleaning: The final step involves removing any excess material, such as gates and risers, from the casting. The casting may also undergo additional processes, such as sandblasting, grinding, or machining, to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensions. Overall, the operation of metal casting machinery requires careful attention to detail and precision to ensure the production of high-quality metal castings.
Send your message to us
Section Steel Roll From China With High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 41000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches


































