Seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High-Temperature
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Abstract
This specification covers seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe for high-temperature service. The pipe shall be suitable for bending, flanging (vanstoning), and similar forming operations, and for fusion welding. Grade P2 and P12 steel pipes shall be made by coarse-grain melting practice. The steel material shall conform to chemical composition, tensile property, and hardness requirements. Each length of pipe shall be subjected to the hydrostatic test. Also, each pipe shall be examined by a non-destructive examination method in accordance to the required practices. The range of pipe sizes that may be examined by each method shall be subjected to the limitations in the scope of the respective practices. The different mechanical test requirements for pipes, namely, transverse or longitudinal tension test, flattening test, and hardness or bend test are presented.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers nominal wall and minimum wall seamless ferritic alloy-steel pipe intended for high-temperature service. Pipe ordered to this specification shall be suitable for bending, flanging (vanstoning), and similar forming operations, and for fusion welding. Selection will depend upon design, service conditions, mechanical properties, and high-temperature characteristics.
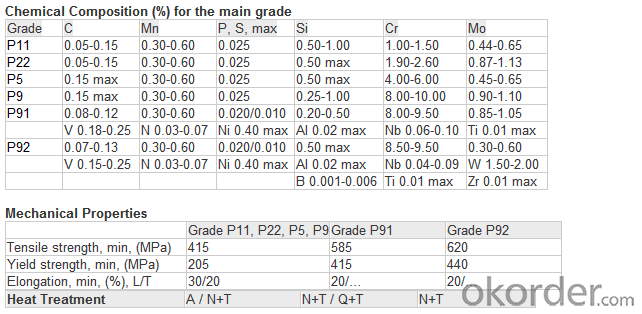
1.2 Several grades of ferritic steels (see Note 1) are covered. Their compositions are given in Table 1.
Note 1—Ferritic steels in this specification are defined as low- and intermediate-alloy steels containing up to and including 10 % chromium.
1.3 Supplementary requirements (S1 to S7) of an optional nature are provided. These supplementary requirements call for additional tests to be made, and when desired, shall be so stated in the order together with the number of such tests required.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation of this specification is specified in the order.
Note 2—The dimensionless designator NPS (nominal pipe size) has been substituted in this standard for such traditional terms as “nominal diameter,” “size,” and “nominal size.”
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
A New designation established in accordance with Practice E527 and SAE J1086, Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS).
B Grade P 5c shall have a titanium content of not less than 4 times the carbon content and not more than 0.70 %; or a columbium content of 8 to 10 times the carbon content.
C Alternatively, in lieu of this ratio minimum, the material shall have a minimum hardness of 275 HV in the hardened condition, defined as after austenitizing and cooling to room temperature but prior to tempering. Hardness testing shall be performed at mid-thickness of the product. Hardness test frequency shall be two samples of product per heat treatment lot and the hardness testing results shall be reported on the material test report.
2. Referenced Documents (purchase separately)
ASTM Standards
A999/A999M Specification for General Requirements for Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe
E92 Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials
E213 Practice for Ultrasonic Testing of Metal Pipe and Tubing
E309 Practice for Eddy-Current Examination of Steel Tubular Products Using Magnetic Saturation
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, Blooms, and Forgings
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
E570 Practice for Flux Leakage Examination of Ferromagnetic Steel Tubular Products
ASME Standard
B36.10M Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe
ASTM A335 Seamless Alloy-Steel Pipe
Standard: BS 1139, BS 3059-2, JIS G3454-2007
Grade: 10#-45#, 15NiCuMoNb5, 10Cr9Mo1VNb
Detailed introduction to ASTM A335 seamless alloy steel pipe:
ASTM A335 seamless alloy steel pipe

FAQ:
1) why you chose us ?
Professional Manufacturer and supplier of Steel pipe
More than 14 years’ professional producing experience
We can get the lowest ex-factory prices. The price are quite reasonable and it is lower than our commercial peers. also, we can guarantee the qualities of our products.
BV, ISO certificates and SGS test can be provided to assure the quality of our products.
2) Our minimum order quantity:
10 Metric Tons or one 20ft or 40ft Container.
3) How about the Delivery Time?
The steel pipe will be produced since we getting your deposit by T/T or Your original L/C. For normal size, some stocks in our factory now, we can supply once you need.
4)What kind of payment does your company support?
T/T, 100% L/C at sight, Cash, Western Union are all accepted.
5) Do you charge for the samples?
According to our company principle, we just charge for samples, you pay for the freight /courier charge.
6) Main market:
Mid East, South America, Africa, Southeast Asia, India etc
- Q: How are steel pipes protected against electrolytic corrosion?
- Steel pipes are protected against electrolytic corrosion through a variety of methods. One common method is the application of protective coatings on the surface of the pipes. These coatings act as a barrier, preventing direct contact between the steel and the surrounding environment, which includes moisture and other corrosive substances. Coatings such as epoxy, polyethylene, and zinc are commonly used for this purpose. Another method of protection is the use of sacrificial anodes. Sacrificial anodes are made from a metal that is more reactive than steel, such as zinc or aluminum. These anodes are attached to the steel pipes and, as they corrode over time, they sacrifice themselves to protect the steel. This process is known as cathodic protection and is highly effective in preventing electrolytic corrosion. In addition to coatings and sacrificial anodes, proper insulation and electrical isolation are crucial in protecting steel pipes from electrolytic corrosion. Insulating materials, such as rubber or plastic sleeves, are used to prevent direct contact between the pipes and other metals or electrolytes. Electrical isolation can be achieved through the use of dielectric unions or insulating flanges, which prevent the flow of electric current between different sections of the pipeline. Regular maintenance and inspection also play a key role in protecting steel pipes against electrolytic corrosion. Periodic checks for coating integrity, anode condition, and potential electrical leakage are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of the corrosion protection system. Overall, a combination of protective coatings, sacrificial anodes, insulation, electrical isolation, and regular maintenance is necessary to protect steel pipes against electrolytic corrosion. By implementing these measures, the lifespan of steel pipes can be significantly extended, ensuring the safety and reliability of various applications such as water distribution, oil and gas transportation, and structural support in buildings and infrastructure.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the manufacturing industry?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in the manufacturing industry for various purposes such as transporting fluids and gases, providing structural support, and facilitating the flow of materials in industrial processes. They are essential for conveying liquids and gases over long distances or within manufacturing plants, ensuring efficient and reliable transportation. Additionally, steel pipes are utilized in the construction of infrastructure, machinery, and equipment, serving as a robust and durable component. Overall, steel pipes play a crucial role in the manufacturing industry due to their versatility, strength, and ability to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions.
- Q: What are the different types of steel pipe connections?
- There are several types of steel pipe connections, including threaded connections, welded connections, flanged connections, grooved connections, and compression connections.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for drinking water supply?
- Drinking water supply can indeed utilize steel pipes. For water distribution systems, steel pipes are widely employed owing to their robustness, longevity, and capacity to endure high pressures. Nevertheless, it is crucial to highlight that the steel employed in these pipes must be purposefully engineered and endorsed for potable water applications. This ensures the water remains uncontaminated by any detrimental substances. Furthermore, regular inspections and appropriate upkeep are imperative to avert the development of rust or corrosion, which may impact water quality.
- Q: Are steel pipes suitable for underground gas lines?
- Yes, steel pipes are suitable for underground gas lines. Steel pipes are known for their strength and durability, making them a reliable choice for underground gas distribution. They have high resistance to external factors such as corrosion and impact, which is important for maintaining the integrity of the gas system. Additionally, steel pipes can withstand high pressure and temperature variations, ensuring the safe and efficient transportation of gas underground. However, it is important to note that proper installation techniques, such as corrosion protection measures, should be followed to ensure the longevity of the steel pipes and prevent any potential leaks or accidents.
- Q: Are steel pipes suitable for solar power plants?
- Yes, steel pipes are suitable for solar power plants. Steel pipes are often used in the construction of solar power plants due to their durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. They can be used for various purposes in a solar power plant, including the transportation of fluids such as water or heat transfer fluids, as well as providing structural support for solar panels and other equipment. Steel pipes are capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressure, making them ideal for the efficient operation of solar power plants. Additionally, steel pipes are readily available and cost-effective, making them a popular choice in the construction of solar power plants.
- Q: How do steel pipes resist corrosion?
- Steel pipes resist corrosion through a process called passivation, where a protective layer of chromium oxide forms on the surface of the steel, preventing direct contact with corrosive elements and slowing down the oxidation process. Additionally, steel pipes can be coated with protective layers such as zinc or epoxy to provide an extra barrier against corrosion.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in heating systems?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in heating systems to transport hot water or steam from the boiler to the radiators or heating units. The durability and strength of steel make it an ideal choice for withstanding high temperatures and pressure. These pipes are typically installed underground or within the walls and floors of buildings to distribute heat efficiently throughout the space.
- Q: What are the different types of steel pipe unions?
- Various industries and applications commonly utilize several types of steel pipe unions. Some of the most frequently used types are as follows: 1. Threaded Union: This union features female threads on both ends, facilitating easy attachment to two male threaded pipes. It ensures a reliable connection that is resistant to leaks. 2. Socket Weld Union: On one end, this union has a socket, while the other end is equipped with a female threaded connection. It is specifically designed for socket welding, where the pipe is inserted into the socket and then welded around the joint, resulting in a robust and long-lasting connection. 3. Butt Weld Union: This specific union is employed for joining two pipes with butt weld ends. It necessitates beveling the pipes and subsequently welding them together, creating a sturdy and permanent connection. 4. Compression Union: Typically used for connecting pipes made of softer materials like copper or plastic, compression unions consist of a compression nut and a compression ring. These components are tightened onto the pipe, ensuring a tight and secure seal. 5. Flanged Union: This union is equipped with flanges on both ends, allowing it to be bolted onto two flanged pipes. Flanged unions are commonly utilized in applications where easy disassembly and reassembly are necessary. 6. Grooved Union: Grooved unions possess grooves on their ends, which are utilized for connecting pipes by inserting them into the grooves and securing them with a coupling. They are often utilized in fire protection systems and other applications where quick installation and easy maintenance are of utmost importance. These examples represent only a fraction of the numerous types of steel pipe unions available. The selection of a union depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the pipe material, size, and operating conditions. Seeking advice from a professional or consulting industry standards can aid in determining the most suitable union for a particular project.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the construction of biomass power plants?
- Steel pipes are used in biomass power plants for various applications such as transporting biomass fuel, carrying water for steam generation, and distributing hot water or steam throughout the plant. They provide a sturdy and reliable infrastructure for the efficient functioning of the plant, ensuring the safe and effective operation of the biomass power generation process.
Send your message to us
Seamless Ferritic Alloy-Steel Pipe for High-Temperature
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























