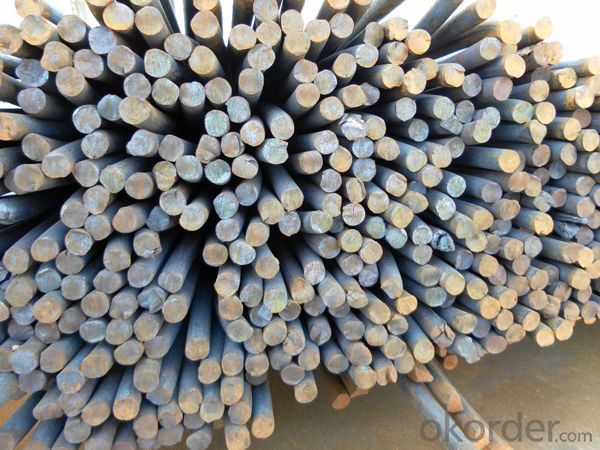
SAE1018 Steel Wire Carbon Rod 5.5mm Construction
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
SAE1018 Steel Wire Carbon Rod 5.5mm Construction
Product Information:
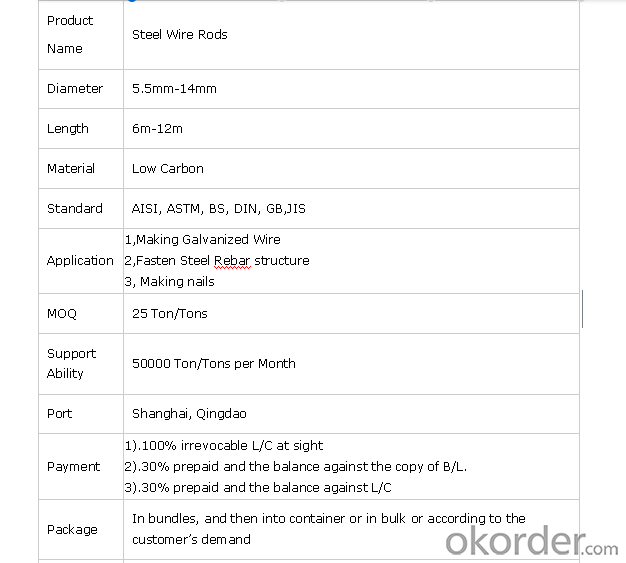
Product Overviews:
| Product Name | Typical Grades | Diameter(mm) | Standard adopted |
| Carbon Steel | 20 (1020/S20C/C22) | Ø16-Ø300 | GB/SAE/JIS/DIN |
| 40 (1040/S40C/C40) | |||
| 45 (1045/S45C/C45) | |||
| Bearing Steel | GCr9 (51100/SUJ1) | Ø12-Ø250 | |
| GCr15 (52100/SUJ2/100Gr6) | |||
| GCr9SiMn (A485-Gr.1/SUJ3) | |||
| Cr-Mo Steel | 20Cr (5120/SCr420H/20Cr4) | Ø12-Ø250 | |
| 40Cr (5140/SCr440/41Cr4) | |||
| 42CrMo(4140/SCM440/42CrMo4) | |||
| Gear Steel | 20CrNiMo | Ø16-Ø600 | |
| 20CrMn(5115/SMnC420/20MnCr5) | |||
| 20CrNiMo(8620/SNCM220/20CrMiMo2) |
Product Show:

Our Advantages:
· Industry experience over 20 years.
· Shipment of goods -More than 70 countries worldwide.
· The most convenient transport and prompt delivery.
· Competitive price with best service.
· High technical production line with top quality products.
· High reputation based on best quality products.
With our experienced, enthusiastic and dynamic staffs, we assure to bring you the products with best quality, reasonable prices and good after-sales services under the motto: Friends First, Business After.
Communication, Experience, Expertise and Best efforts are our Promises to you.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the aerospace aftermarket industry?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the aerospace aftermarket industry by providing critical components that are essential for the safe and efficient operation of aircraft. The high strength, durability, and temperature resistance of special steel make it an ideal material for various aerospace applications. One of the primary ways special steel contributes to the aerospace aftermarket industry is through the production of engine components. Special steel alloys, such as nickel-based superalloys, are used to manufacture turbine blades, compressor discs, and shafts, which are vital elements of jet engines. These components must withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and mechanical stresses, and special steel alloys offer the necessary properties to ensure reliable and long-lasting performance. Moreover, special steel is also used in the manufacturing of structural components in aircraft. Steel alloys with high strength-to-weight ratios, such as titanium alloys, are employed for the construction of critical parts like landing gear, wing spars, and fuselage frames. These components need to be both lightweight and strong to withstand the forces and stresses experienced during flight. Special steel alloys provide the required mechanical properties to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the aircraft. In addition to engine and structural components, special steel also contributes to the aerospace aftermarket industry through the production of fasteners, bearings, and other small yet vital parts. These components are responsible for holding various parts together and ensuring proper functioning of systems. Special steel alloys with excellent corrosion resistance, fatigue strength, and wear resistance are utilized to ensure the reliability and longevity of these critical components. Furthermore, special steel plays a crucial role in the maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) activities of the aerospace aftermarket industry. With the rigorous demands placed on aircraft components, regular inspections, repairs, and replacements are necessary to ensure their continued airworthiness. Special steel materials are often used for MRO purposes due to their compatibility with existing aircraft systems and their ability to meet the stringent requirements of aerospace regulations. Overall, special steel is an indispensable material in the aerospace aftermarket industry. Its unique properties and characteristics enable the production of high-performance engine components, lightweight structural parts, and reliable small components. The use of special steel ensures the safety, efficiency, and longevity of aircraft, contributing to the overall success and growth of the aerospace aftermarket industry.
- Q: What are the different applications of tool special steel?
- Tool special steel has various applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing. It is commonly used for making cutting tools, dies, molds, and components that require high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Additionally, tool special steel finds use in power transmission systems, machine parts, and even surgical instruments. Its versatility and ability to withstand extreme conditions make it a crucial material in many applications where precision and reliability are paramount.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the electronics manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the electronics manufacturing industry. Special steels, such as stainless steel and high-performance alloys, offer excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and good heat resistance. These properties make them suitable for various applications in electronics manufacturing, including the production of circuit boards, connectors, and other electronic components.
- Q: How does special steel perform in surface hardening applications?
- Special steel is known for its excellent performance in surface hardening applications. Surface hardening is a process used to increase the hardness and wear resistance of the outer layer of a metal component, while maintaining a tough and ductile core. Special steel, also known as alloy steel, is specifically designed to possess certain desirable properties, such as high strength, toughness, and resistance to corrosion and heat. When it comes to surface hardening, special steel exhibits superior characteristics compared to regular steel. Its alloying elements, such as chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium, enhance its hardenability, allowing for effective heat treatment processes like carburizing, nitriding, or induction hardening. These processes modify the surface microstructure of the steel, resulting in increased hardness and wear resistance. Special steel's ability to be hardened to a greater depth than regular steel makes it ideal for surface hardening applications. The hardened layer formed on the surface provides protection against abrasion, erosion, and fatigue, thus significantly extending the lifespan of the component. Additionally, the improved wear resistance and hardness of special steel make it suitable for applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where components are subjected to extreme conditions and high levels of stress. Furthermore, special steel's exceptional mechanical properties make it highly durable even after surface hardening. It retains its toughness and strength, ensuring that the component can withstand heavy loads and impacts without failure. This combination of hardness and toughness is crucial for applications where both wear resistance and structural integrity are essential. In conclusion, special steel is highly effective in surface hardening applications due to its superior hardenability, wear resistance, and mechanical properties. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions and maintain its durability makes it a preferred choice for industries that require components with enhanced surface hardness and longevity.
- Q: What are the main advantages of using special steel in the mining industry?
- The main advantages of using special steel in the mining industry are its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. This allows for the construction of heavy-duty equipment and machinery that can withstand the harsh and demanding conditions of mining operations. Special steel also has the ability to retain its properties at high temperatures, making it suitable for applications such as drilling and cutting through tough materials. Additionally, it offers increased safety by minimizing the risk of equipment failure, ensuring a more efficient and productive mining process.
- Q: What are the environmental benefits of using special steel?
- Special steel, also known as stainless steel, offers numerous environmental benefits. Firstly, it is highly durable and long-lasting, resulting in reduced waste and resource consumption over time. Additionally, stainless steel is 100% recyclable, allowing it to be repurposed indefinitely without any loss in quality. This recycling process requires significantly less energy compared to the production of new steel, leading to a considerable reduction in carbon emissions and environmental impact. Moreover, special steel is corrosion-resistant, eliminating the need for frequent replacements and reducing the use of resources and energy associated with maintenance. Overall, the environmental benefits of using special steel include decreased waste generation, lower energy consumption, reduced carbon emissions, and increased resource efficiency.
- Q: What are the different mechanical defects in special steel?
- Some of the different mechanical defects in special steel include cracks, voids, inclusions, segregation, and deformation.
- Q: Can special steel be used in construction?
- Yes, special steel can definitely be used in construction. Special steel refers to steel alloys that have been specifically designed and manufactured to possess certain properties and characteristics that make them suitable for various applications, including construction. One of the most common types of special steel used in construction is known as structural steel. This type of steel is specifically designed to have higher strength, durability, and flexibility compared to regular carbon steel. Structural steel is often used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects due to its ability to withstand heavy loads and resist external forces such as wind, earthquakes, and impact. Special steel also offers other advantages in construction. For example, stainless steel is commonly used in the construction of architectural features and building facades due to its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Additionally, weathering steel, which forms a protective rust-like coating when exposed to the elements, is often used in outdoor structures and bridges to eliminate the need for regular painting and maintenance. Furthermore, special steel can be tailored to meet specific requirements in construction projects. For instance, high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel is used in the construction of tall buildings and structures to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity. This allows for more efficient use of materials and cost savings. In summary, special steel is widely used in construction due to its superior strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and other desirable properties. Its versatility allows for the optimization of construction projects, ensuring safety, longevity, and cost-effectiveness.
- Q: How is special steel used in the construction industry?
- Special steel is used in the construction industry for various purposes such as reinforcing concrete and providing structural support in high-rise buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects. It is also used for manufacturing construction equipment, tools, and machinery due to its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
- Q: What is the significance of alloying elements in special steel?
- Alloying elements in special steel play a crucial role in enhancing its properties and performance. These elements, such as chromium, nickel, manganese, and molybdenum, are added to improve characteristics like strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. The combination and proportion of alloying elements determine the specific properties of the steel, making it suitable for various applications, such as manufacturing aircraft parts, automotive components, or tools. Overall, alloying elements greatly contribute to the versatility and functionality of special steel.
Send your message to us
SAE1018 Steel Wire Carbon Rod 5.5mm Construction
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























