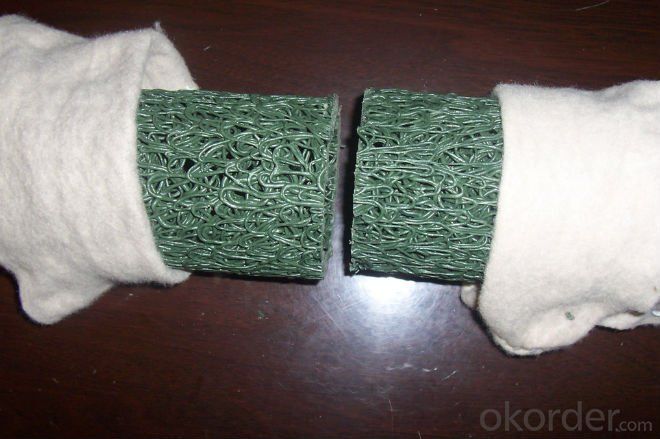
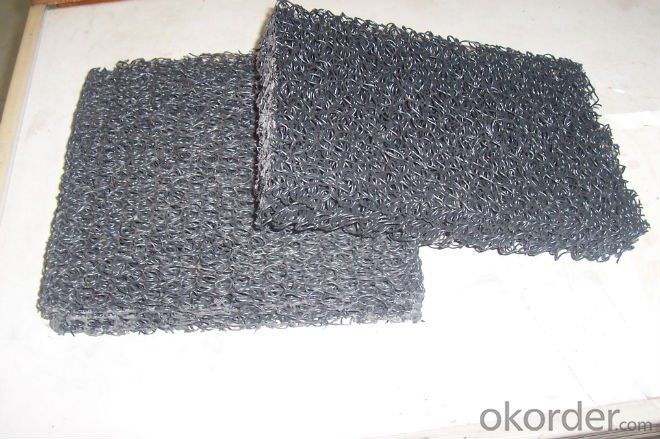
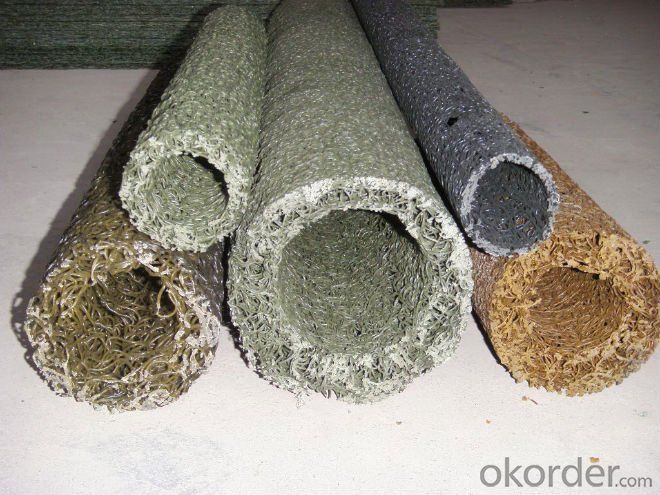
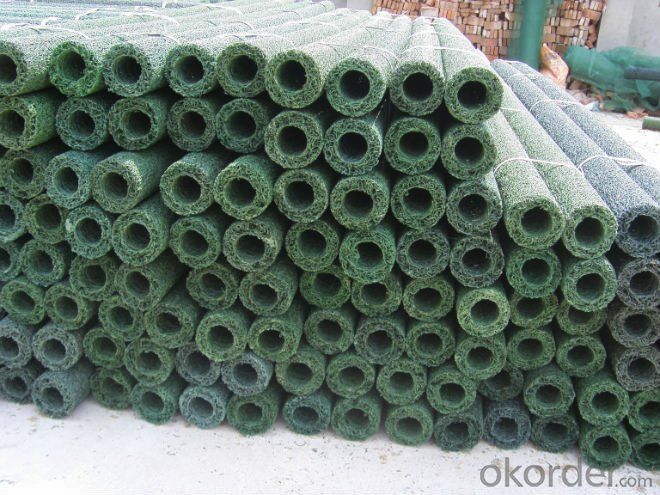
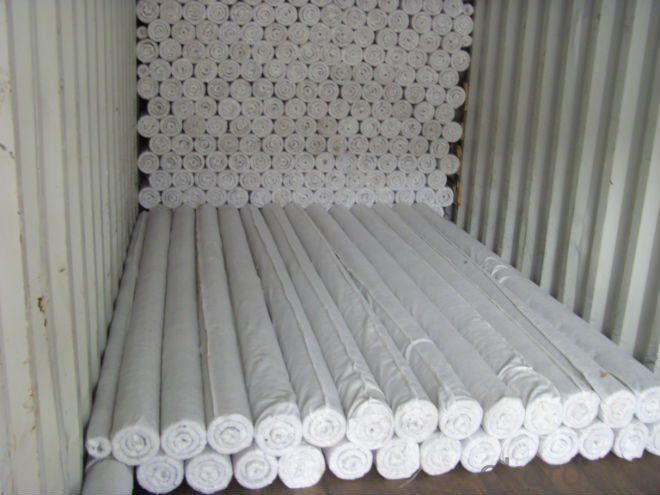
Plastic Blind Ditch used in Draiange
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m
- Supply Capability:
- 150000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Detail: | standard packing or according to client's request |
| Delivery Detail: | 15 days after receiving T/T |
Geocomposite drain pipe technical datas
Item | Square shape | Circular shape | |||||||||
Type | YA7030 | YA1235 | YA1550 | YB60 | YB80 | YB100 | YB150 | YB200 | YB250 | YB300 | |
Outer size(mm) | 70x30 | 120x35 | 120x50 | φ60 | φ80 | φ100 | φ150 | φ200 | φ250 | φ300 | |
Cannular size (mm)≥ | 40x10 | 40x10x2 | 40x20x2 | φ25 | φ45 | φ55 | φ80 | φ120 | φ170 | φ220 | |
Voidage (%)≥ | 70 | ||||||||||
Compress strength (kPa) | Flattening 5% | 70 | 60 | 50 | 85 | 80 | 70 | 50 | 40 | 35 | 30 |
Flattening 10% | 110 | 110 | 70 | 170 | 160 | 140 | 70 | 60 | 55 | 50 | |
Flattening 15% | 150 | 130 | 125 | 220 | 200 | 180 | 100 | 90 | 80 | 70 | |
Flattening 20% | 190 | 180 | 160 | 280 | 250 | 220 | 125 | 120 | 110 | 100 | |
plastic blind ditch
is made of plastic core and outer filtering cloth. In the state of hot melting, it is formed into three-D network structure. It has two shapes: rectangle and round. This kind of pipe has some advantages: good drainage, high pressure resistance, light weight, so it is very popular in some projects.Application:Highway and roadway subgrade,Retaining wall,Landfill,Roof garden,Building foundation,Underground irrigation.
- Q: What are the typical applications of geogrids in geotechnical engineering?
- Geogrids are commonly used in geotechnical engineering for various applications such as soil stabilization, reinforcement of retaining walls and slopes, erosion control, and pavement reinforcement. They provide mechanical support and increase the stability of soil structures, preventing soil movement and enhancing the overall performance of geotechnical projects.
- Q: What is the recommended geogrid roll width for specific applications?
- The recommended geogrid roll width for specific applications can vary depending on factors such as the type of soil, the slope angle, and the intended purpose of the geogrid. It is best to consult with a geotechnical engineer or a manufacturer's guidelines to determine the appropriate roll width for a specific application.
- Q: What are the design guidelines for geogrid-reinforced retaining walls?
- The design guidelines for geogrid-reinforced retaining walls include factors such as the type and strength of the geogrid, the wall height, soil properties, and the required level of stability. The guidelines typically emphasize the need for proper engineering analysis, considering factors such as internal and external stability, soil-geogrid interaction, and construction considerations. It is important to follow industry standards and consult with a qualified engineer to ensure a safe and effective design for geogrid-reinforced retaining walls.
- Q: What is the effect of creep rupture on geogrid performance?
- The effect of creep rupture on geogrid performance is detrimental as it leads to a significant decrease in the geogrid's strength and stability over time. Creep rupture refers to the gradual elongation or deformation of a material under constant load, which can eventually result in the geogrid failing and losing its ability to provide reinforcement or confinement. This can compromise the overall integrity and effectiveness of the geogrid in various civil engineering applications, such as soil stabilization, slope reinforcement, or retaining wall construction. Therefore, managing and minimizing creep rupture is crucial to maintaining the long-term performance and durability of geogrids.
- Q: Are geogrids suitable for use in soil reinforcement for bridge abutments?
- Yes, geogrids are suitable for use in soil reinforcement for bridge abutments. Geogrids provide strength and stability to the soil, reducing settlement and improving load-bearing capacity. They also help to prevent soil erosion and promote long-term stability of the bridge abutments.
- Q: How do geogrids help in reducing the risk of landslides?
- Geogrids help in reducing the risk of landslides by providing stability and reinforcement to the soil. They are typically made of high-strength polymers and are installed horizontally or vertically within the soil mass. By interlocking with the soil particles, geogrids improve the overall strength of the soil and enhance its resistance to shear forces. This reinforcement helps to prevent soil movement and sliding, thereby reducing the likelihood of landslides.
- Q: Can geogrids be used in soil reinforcement for load-bearing platforms?
- Yes, geogrids can be effectively used in soil reinforcement for load-bearing platforms. Geogrids are engineered materials that provide soil stabilization and improve the load-bearing capacity of soils. They are typically made of high-strength polymers and have a grid-like structure that interlocks with the soil particles, creating a stable foundation. Geogrids distribute the applied loads more evenly, reducing the potential for soil settlement and enhancing the overall stability of load-bearing platforms.
- Q: How do geogrids improve the performance of reinforced soil retaining walls?
- Geogrids improve the performance of reinforced soil retaining walls by providing additional tensile strength and stability to the structure. They enhance the soil's ability to resist lateral pressures and improve overall load distribution, which ultimately increases the wall's bearing capacity and structural integrity. Additionally, geogrids help prevent soil erosion and displacement, ensuring long-term stability and durability of the retaining wall system.
- Q: What are the design considerations for geogrid reinforcement?
- Some design considerations for geogrid reinforcement include the type and strength of the geogrid material, the required level of soil stabilization, the anticipated loads and stresses on the reinforced soil structure, and the desired lifespan of the structure. Other factors to consider include soil characteristics, installation and construction procedures, and environmental conditions. Additionally, the design should account for factors such as slope stability, drainage, and potential settlement.
- Q: Geogrid test items: what is the point of the joint point of penetration
- The conventional test items of geogrid are tensile strength, elongation, and welding point peeling force.
Send your message to us
Plastic Blind Ditch used in Draiange
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m
- Supply Capability:
- 150000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords