Third Generation Solar Cells - Mono Solar Cell 125mm x 125mm x 0.5mm
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 40000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Details Of Mono Solar Cell 125mm
Specifications Of Mono Solar Cell 125mm
1.Mechanical data and design
Format | 125 mm × 125 mm ± 0.5 mm |
Thickness | 210 μm ± 40 μm |
Front(-) | 1.6 mm bus bars (silver),blue anti-reflection coating (silicon nitride) |
Back (+) | 2.5 mm wide soldering pads (silver) back surface field (aluminium) |
2.Temperature Coefficient of Cells
Voc. Temp . coef.%/K | -0.35%/K |
Isc . Temp . coef.%/K | +0.024%/K |
Pm. Temp. coef.%/K | -0.47%/K |
3.Electrical Characteristic
Efficiency(%) | Pmpp (W) | Umpp (V) | Impp (A) | Uoc (V) | Isc (A) | FF (%) |
18.35 | 2.841 | 0.532 | 5.342 | 0.631 | 5.67 | 79.41% |
18.20 | 2.817 | 0.53 | 5.319 | 0.631 | 5.64 | 79.16% |
18.05 | 2.794 | 0.527 | 5.301 | 0.63 | 5.63 | 78.77% |
17.90 | 2.771 | 0.527 | 5.259 | 0.629 | 5.62 | 78.39% |
17.75 | 2.748 | 0.526 | 5.224 | 0.629 | 5.61 | 77.88% |
17.60 | 2.725 | 0.524 | 5.201 | 0.629 | 5.59 | 77.50% |
17.45 | 2.702 | 0.52 | 5.196 | 0.629 | 5.586 | 76.90% |
17.30 | 2.678 | 0.516 | 5.183 | 0.626 | 5.577 | 76.71% |
17.15 | 2.655 | 0.513 | 5.175 | 0.623 | 5.565 | 76.58% |
17.00 | 2.632 | 0.51 | 5.161 | 0.622 | 5.559 | 76.12% |
16.75 | 2.593 | 0.508 | 5.103 | 0.615 | 5.477 | 76.98% |
16.50 | 2.555 | 0.506 | 5.047 | 0.608 | 5.396 | 77.88% |
4.Intensity Dependence
Advantage Of Mono Solar Cell 125mm
1: high quality cell, Level A cell (16.50%—18.35%)
2: Dimensione:125*125mm Diagonal:150mm / 165mm
Dimensione:156*156mm Diagonal:200mm
3: Qualified certification: TUV,CE certification.
4: Warranty: five years for whole unit
Usage/Application Of Mono Solar Cell 125mm
Packaging & Delivery Of Mono Solar Cell 125mm | |
Packaging Detai | Packaging Detail:Export Carton and Pallet or under customer request. |
Delivery Detail:10-20days | |


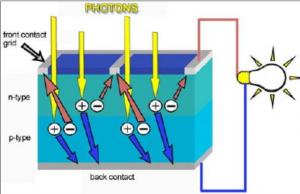
Converting the sun’s radiation directly into electricity is done by solar cells. These cells are made of semiconducting materials similar to those used in computer chips. When sunlight is absorbed by these materials, the solar energy knocks electrons loose from their atoms, allowing the electrons to flow through the material to produce electricity. This process of converting light (photons) to electricity (voltage) is called the photovoltaic effect.
When photons are absorbed by matter in the solar cell, their energy excites electrons higher energy states where the electrons can move more freely. The perhaps most well-known example of this is the photoelectric effect, where photons give electrons in a metal enough energy to escape the surface. In an ordinary material, if the electrons are not given enough energy to escape, they would soon relax back to their ground states. In a solar cell however, the way it is put together prevents this from happening. The electrons are instead forced to one side of the solar cell, where the build-up of negative charge makes a current flow through an external circuit. The current ends up at the other side (or terminal) of the solar cell, where the electrons once again enter the ground state, as they have lost energy in the external circuit.
Solar cells, which were originally developed for space applications in the 1950s, are used in consumer products (such as calculators or watches), mounted on roofs of houses or assembled into large power stations. Today, the majority of photovoltaic modules are used for grid-connected power generation, but a smaller market for off-grid power is growing for remote areas and developing countries.
Given the enormous potential of solar energy, photovoltaics may well become a major source of clean electricity in the future. However, for this to happen, the electricity generation costs for PV systems need to be reduced and the efficiency of converting sunlight into electricity needs to increase. To achieve this, the Commission supports photovoltaics development since many years by funding research projects and facilitating cooperation between stakeholders.
- Q: Can solar cells be used to power wireless communication networks?
- Yes, solar cells can be used to power wireless communication networks. Solar cells are capable of converting sunlight into electricity, which can be stored in batteries or directly used to power various devices, including wireless communication equipment. This renewable energy source offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution for powering wireless networks in remote or off-grid locations. Additionally, advancements in solar cell technology have made them more efficient and cost-effective, making them a viable option for powering these networks.
- Q: How many years should I spend in the solar cell industry to be a good solar cells sales person?
- I worked as the solar cell sales for a foreign company for 3 years, and I am already the best sales in my company.
- Q: Can solar cells be used to power irrigation systems?
- Yes, solar cells can be used to power irrigation systems. Solar panels can convert sunlight into electricity, which can then be used to power pumps, motors, and other components of an irrigation system. This renewable energy source can provide a sustainable and cost-effective solution for powering irrigation systems, especially in remote or off-grid locations.
- Q: What is the best way to deal with surplus solar cells abandoned after burning?
- Unfortunately abandoned solar cells are not easy to recycle. Only the aluminium frame can be reused, and the surplus is sometimes inseparable; because the solar cell contains silicon, tin, nickel, silver metal.
- Q: What is the role of solar cells in powering emergency response systems?
- Solar cells play a crucial role in powering emergency response systems by providing a reliable and sustainable source of energy. During emergencies, when the traditional power grid may be disrupted or unavailable, solar cells can generate electricity from sunlight, ensuring continuous operation of critical systems such as communication devices, lighting, and medical equipment. This renewable energy source helps emergency responders effectively carry out their duties, enabling them to provide aid, maintain connectivity, and save lives in challenging situations.
- Q: What's the benefit of using a solar cell?
- Because the sun energy is a kind of energy you can use forever, the solar cell is regarded as very energy-saving.
- Q: How do solar cells affect the local ecosystem?
- Solar cells have a minimal impact on the local ecosystem compared to traditional energy sources. They produce clean and renewable electricity, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and their associated pollution. While the manufacturing and disposal of solar cells may have some environmental impact, it is far outweighed by the benefits of using solar energy, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved air and water quality. Additionally, solar installations can provide habitat for certain wildlife species and contribute to the preservation of natural landscapes. Overall, solar cells have a positive effect on the local ecosystem by promoting sustainability and mitigating climate change.
- Q: Can solar cells be used in mining or extraction operations?
- Yes, solar cells can indeed be used in mining or extraction operations. They can be used to power various equipment and machinery required in these operations, such as lighting systems, communication devices, ventilation systems, and water pumps. By utilizing solar energy, mining and extraction operations can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and lower their environmental impact. Additionally, solar cells can be easily deployed in remote areas where traditional power sources may not be readily available.
- Q: How are solar cells installed?
- Solar cells are typically installed on rooftops or in open areas with maximum exposure to sunlight. The installation process involves mounting the solar panels onto a strong structure using racking systems, securing them in place. Electrical wiring is then connected between the panels, and an inverter is installed to convert the captured solar energy into usable electricity. Finally, the system is connected to the electrical grid or batteries, enabling the generated power to be used.
- Q: How do solar cells perform in regions with high levels of dust and sandstorms?
- Solar cells can be affected by high levels of dust and sandstorms in regions. The accumulation of dust particles on the surface of solar panels can reduce their efficiency by blocking sunlight and reducing the amount of energy they can generate. Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial in these areas to ensure optimal performance of solar cells and to prevent any long-term damage caused by the accumulation of dust and sand.
1. Manufacturer Overview
| Location | SanShui City, Guang Dong, China. |
| Year Established | 2009 |
| Annual Output Value | Above 10 billion RMB |
| Main Markets | Mid East;Western Europe;North America;Southeast Asia |
| Company Certifications | TUV ISO9001;SGS |
2. Manufacturer Certificates
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period |
3. Manufacturer Capability
| a) Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | Zhuhai, Foshan |
| Export Percentage | 0.4 |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | about 600 |
| Language Spoken: | English;Chinese; |
| b) Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | 66666.7m2 |
| No. of Production Lines | 12 |
| Contract Manufacturing | OEM Service Offered;Design Service Offered |
| Product Price Range | USD 0.3-0.45/Wp |
Send your message to us
Third Generation Solar Cells - Mono Solar Cell 125mm x 125mm x 0.5mm
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 40000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords