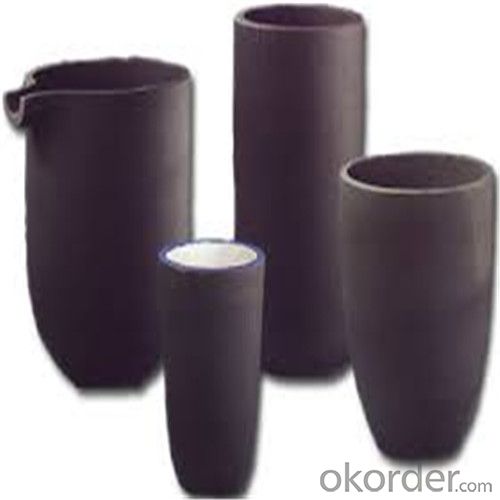
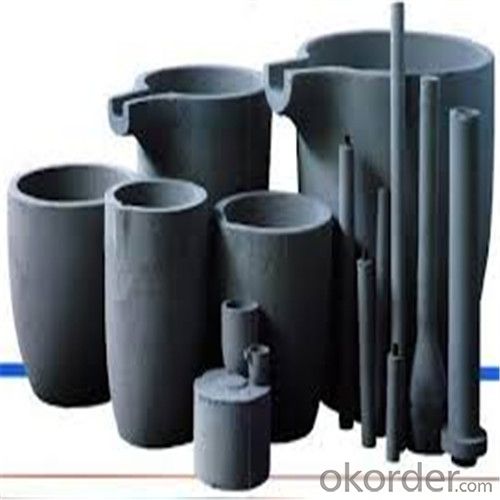
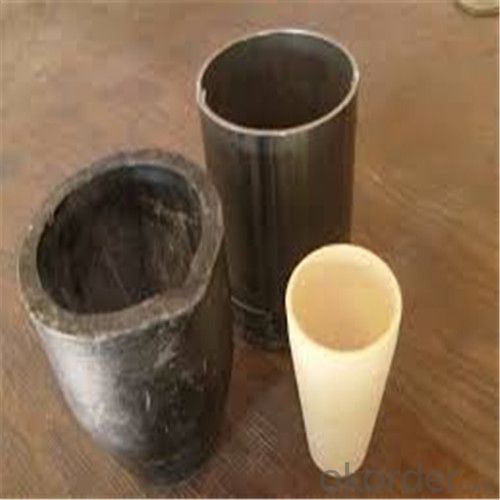
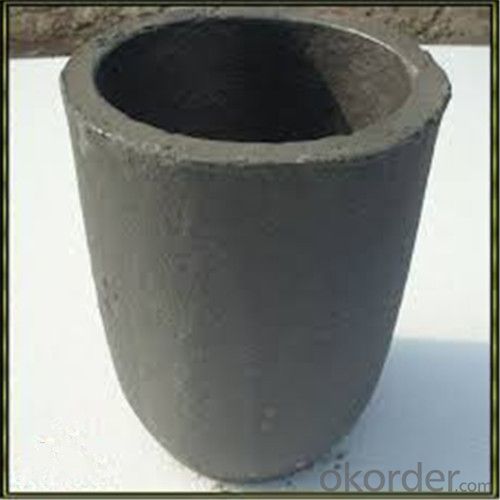
Large Graphite Crucible for Melting Aluminium, Copper, and Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
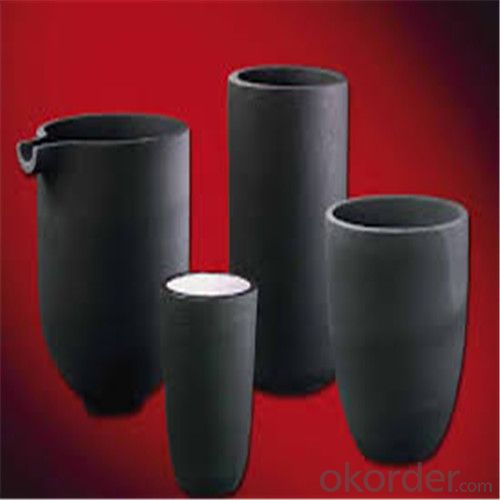
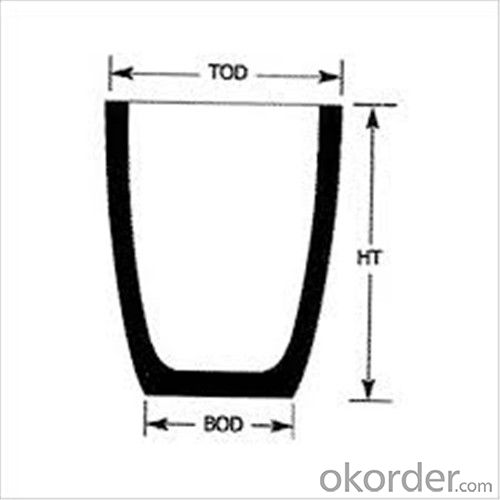

Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
- Q: How do you determine the appropriate crucible stirring mechanism for a specific application?
- To determine the appropriate crucible stirring mechanism for a specific application, several factors must be taken into account. Firstly, it is necessary to understand the requirements of the application, including the type of material to be stirred, the desired mixing intensity, and any specific parameters that must be maintained during the stirring process. Next, the available stirring mechanisms and their capabilities should be evaluated. There are different options, such as magnetic stirrers, mechanical stirrers, and gas bubbling stirrers. Each mechanism has its own advantages and limitations, so it is important to assess how well they align with the application requirements. Consideration should also be given to the properties of the material being stirred. Some materials may be sensitive to mechanical stress or temperature changes, making gentle magnetic stirring more suitable. Others may require more vigorous mixing, which can be achieved with mechanical or gas bubbling stirrers. In addition, the compatibility of the stirring mechanism with the crucible material should be assessed. Certain materials may react with specific stirring mechanisms, leading to contamination or degradation. It is important to ensure that the chosen stirring mechanism is compatible with the crucible material to avoid any adverse effects. Furthermore, the scalability and ease of use of the stirring mechanism should be considered. If the application requires large-scale production or frequent stirring, choosing a mechanism that is easily scalable and user-friendly can be beneficial. Finally, it is advisable to consult experts or conduct experiments to validate the suitability of the chosen stirring mechanism. This can involve performing small-scale trials or seeking advice from professionals familiar with the specific application or material being stirred. In conclusion, determining the appropriate crucible stirring mechanism requires careful consideration of the application requirements, material properties, compatibility, scalability, and expert advice.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for electrode production?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for electrode production. Graphite is an excellent material for making electrodes due to its high melting point, good electrical conductivity, and chemical stability. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in industries such as metallurgy, foundries, and electrical engineering for producing various types of electrodes. They can withstand high temperatures and provide a stable environment for electrode production. Additionally, graphite crucibles can be easily shaped or customized to meet specific electrode requirements, making them a preferred choice in many applications.
- Q: Does a graphite crucible require any special handling during transportation?
- Yes, a graphite crucible requires special handling during transportation. Graphite is a brittle material that can easily crack or break if subjected to excessive pressure or impact. To ensure the safe transportation of a graphite crucible, it should be packaged securely in a padded or cushioned container to protect it from any potential damage. Additionally, it is important to handle the crucible with care, avoiding any rough or sudden movements that could cause it to hit against other objects or surfaces. By taking these precautions, the risk of damage to the graphite crucible during transportation can be minimized.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for bronze casting?
- Certainly, bronze casting can utilize a graphite crucible. The utilization of graphite crucibles is widespread in metal casting procedures due to their remarkable thermal conductivity, high melting point, and resistance to thermal shock. In contrast to graphite, bronze, an amalgamation of copper and tin, generally possesses a lower melting point, making it a fitting material for casting within a graphite crucible. Moreover, graphite crucibles provide commendable chemical stability, a pivotal factor when operating with molten metals. Nevertheless, it is imperative to underscore the significance of adequately seasoning and preheating the crucible to avoid any potential reactions between the molten bronze and the graphite crucible.
- Q: What can replace a graphite crucible?
- Save and process.1. Graphite crucible is afraid of water, and must avoid moisture and water flushing.2. Note that the surface is raised instead of placing the crucible directly on the floor and placed on the tray.3. Not rolling horizontally on the floor, when pushing pads, requires something softer, such as cardboard or cloth, so as not to bruise, scrape, and stand on the floor at the bottom.4. You can't land or crash while handling. Please pay special attention to it.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for zinc melting?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for zinc melting. Graphite has a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity, making it suitable for containing and heating zinc to its melting point.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for both melting and casting?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for both melting and casting. Graphite is known for its excellent heat resistance and high melting point, which makes it an ideal material for containing molten metals during the melting process. Additionally, graphite crucibles have good thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer and uniform heating of the molten metal. Once the metal is melted, the graphite crucible can also be used for casting. The molten metal can be poured directly from the crucible into a mold, allowing for the creation of various shapes and forms. Graphite crucibles are typically durable and can withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles, making them suitable for both melting and casting processes. However, it is important to note that graphite crucibles may not be suitable for all types of metals. Some reactive or corrosive metals may react with graphite at high temperatures, leading to contamination of the molten metal. In such cases, alternative crucible materials like ceramic or refractory metals may be more appropriate.
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing graphite crucible leakage?
- There are several methods that can be employed to prevent graphite crucible leakage. One method is to ensure proper preparation and installation of the crucible. This includes thorough cleaning of the crucible surface and the mating surface of the crucible lid or cover. By removing any dirt or debris, a better seal can be achieved. Additionally, applying a thin layer of graphite lubricant or a high-temperature sealant to the mating surfaces can help create a tighter seal and prevent leakage. Another method is to use a gasket or an O-ring between the crucible and the lid. These gaskets are typically made of materials such as graphite, ceramic fiber, or metal and are designed to provide a reliable seal. The gasket is placed between the crucible and the lid, creating a barrier that prevents any molten metal or other substances from leaking out. Furthermore, proper tightening of the crucible lid or cover is crucial to prevent leakage. Over-tightening can cause damage to the crucible or the lid, leading to leaks. On the other hand, insufficient tightening can result in a loose seal, allowing for leakage. It is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations regarding torque specifications for the lid or cover to ensure a proper seal. Regular inspection and maintenance of the crucible are also important preventive measures. Any signs of cracks, chips, or deterioration should be addressed promptly. These issues can compromise the integrity of the crucible, leading to leakage. By replacing damaged crucibles or repairing them in a timely manner, the risk of leakage can be minimized. In addition to these methods, proper handling and usage of the crucible can also contribute to preventing leakage. Avoiding sudden temperature changes, thermal shocks, and excessive mechanical stresses can help prolong the lifespan of the crucible and maintain its integrity. It is important to follow the recommended operating procedures and guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure the crucible's longevity and prevent leakage. Overall, by employing these methods - proper preparation and installation, using gaskets or O-rings, tightening the lid correctly, regular inspection and maintenance, and proper handling - graphite crucible leakage can be effectively prevented, ensuring a safe and efficient operation.
- Q: What are the considerations for selecting a crucible stand for graphite crucibles?
- When choosing a crucible stand for graphite crucibles, it is important to take into account several key factors: 1. Material: The material of the stand must be able to withstand the high temperatures associated with graphite crucibles. Common options include stainless steel, cast iron, and ceramic. 2. Stability: The stand should be sturdy and stable to ensure the crucible remains steady during heating. This is especially crucial when working with high temperatures or conducting experiments involving stirring or transferring materials. 3. Size and shape: The stand should be designed to accommodate the specific size and shape of the graphite crucible being used. It should provide a secure fit to prevent any movement or potential accidents. 4. Heat resistance: The stand should possess excellent heat resistance properties to avoid deformation or damage when exposed to high temperatures. It should be able to withstand the thermal expansion and contraction that occurs during heating and cooling cycles. 5. Support: The stand should offer sufficient support for the crucible, ensuring it is held securely in place. It should be designed in a way that minimizes contact between the crucible and the stand, reducing the risk of contamination. 6. Accessibility: The stand should allow for easy access to the crucible for loading and unloading materials. It should have a design that enables easy handling and manipulation of the crucible, ensuring safety and efficiency during operations. 7. Compatibility: The stand should be compatible with the heating equipment being used. It should fit properly on the heating apparatus and be able to withstand the associated heat sources, such as Bunsen burners or electric furnaces. By considering these factors, one can choose an appropriate crucible stand that ensures the safe and effective use of graphite crucibles in various applications, including chemical analysis, metal casting, or laboratory experiments.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for metal powder sintering?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for metal powder sintering. Graphite is a commonly used material for crucibles due to its high melting point, chemical inertness, and thermal conductivity. Metal powder sintering involves heating the powder to a high temperature to bond the particles together, and graphite crucibles are able to withstand these high temperatures without reacting with the metal powders. Additionally, graphite crucibles have good thermal conductivity, which helps to evenly distribute heat and ensure uniform sintering of the metal powder. Therefore, graphite crucibles are a suitable choice for metal powder sintering processes.
Send your message to us
Large Graphite Crucible for Melting Aluminium, Copper, and Brass
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords