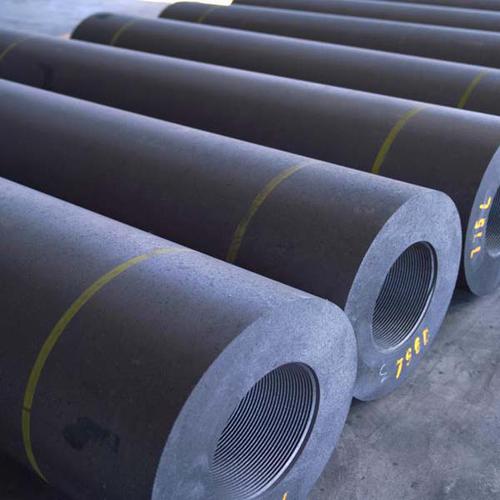
High-Performance Graphite Electrodes: RP, HP, UHP for Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking
- Loading Port:
- Dalian
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Welcome! As a professional intermediary, we bridge the gap between overseas buyers and China's splendid manufacturers. In collaboration with major Graphite Electrode manufacturers with 7 years of expertise in the industry, we specialize in supplying top-of-the-line graphite electrodes tailored to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our commitment to excellence and innovation ensures that our products deliver exceptional performance and reliability across various industrial applications. Explore our range of graphite electrodes and discover why businesses worldwide trust CNBM International Corporation for their electrode needs.
Product Display
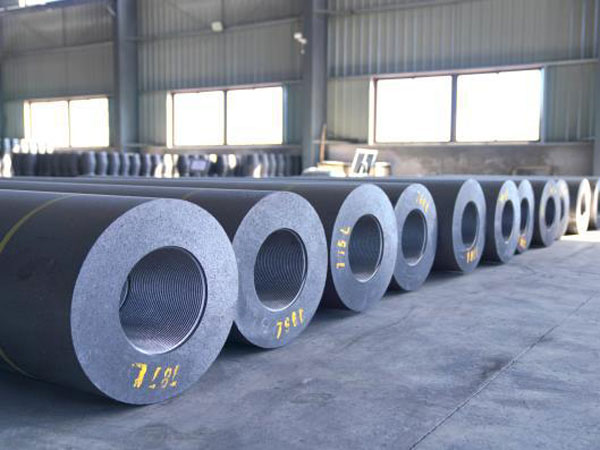
Discover our graphite electrode products through three captivating images. From electrodes to nipples and packed electrodes, each showcases our commitment to quality and precision engineering.

Graphite Electrodes

Electrode Nipples
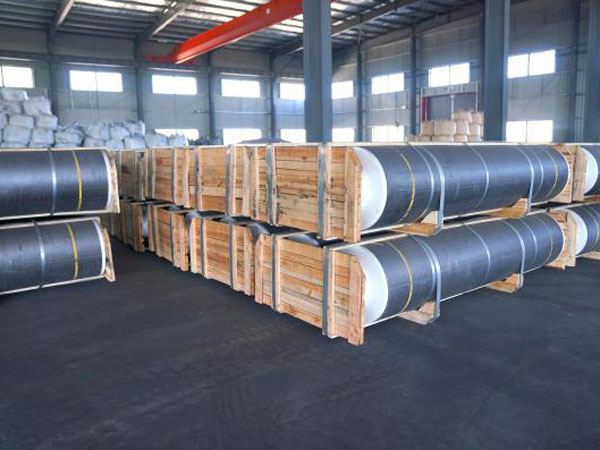

Packaged Electrodes
Designation of Graphite Electrode Sections
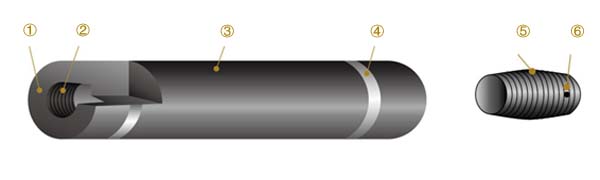
Electrode End Face
Electrode Threaded Fixing Hole
Electrode Body Trunk
Electrode Caution Cordon
Tapered Electrode Nipple
Connector Pin Hole
Technical Specification Charts of Graphite Electrodes
| Test Indicator | Test Object | Unit of Measure | Regular Power - RP | High Density - HD | High Power - HP | Ultra High Power - UHP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ø250-400 | Ø450-600 | Ø250-400 | Ø450-600 | Ø250-400 | Ø450-600 | Ø300-400 | Ø450-500 | Ø550-650 | Ø700-800 | |||
| Resistivity, max. | Electrode | μΩm | 9.0 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.2 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 5.8 |
| Nipple | μΩm | 8.0 | 8.0 | 6.3 | 6.3 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.2 | 4.0 | |
| Flexural Strength, min. | Electrode | MPa | 8.0 | 7.0 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 10.0 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 11.0 |
| Nipple | MPa | 15.0 | 15.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 19.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 22.0 | 23.0 | |
| Elastic Modulus, max. | Electrode | GPa | 9.3 | 9.3 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 |
| Nipple | GPa | 14.0 | 14.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 22.0 | 22.0 | |
| Bulk Density, min. | Electrode | g/cm3 | 1.54 | 1.54 | 1.64 | 1.64 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.67 | 1.66 | 1.66 | 1.68 |
| Nipple | g/cm3 | 1.72 | 1.72 | 1.74 | 1.74 | 1.74 | 1.74 | 1.75 | 1.76 | 1.78 | 1.78 | |
| CTE(100-600℃), max. | Electrode | 10-6/℃ | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Nipple | 10-6/℃ | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.3 | |
| Ash Content, max. | Electrode | % | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Nipple | % | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Nominal Diameter | Permissible Current Load (A) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Power - RP | High Density - HD | High Power - HP | Ultra High Power - UHP | |
| Ø250 | 7,000-10,000 | 8,000-12,000 | 8,000-13,000 | - |
| Ø300 | 10,000-13,000 | 11,000-16,000 | 13,000-17,400 | 15,000-22,000 |
| Ø350 | 13,500-18,000 | 15,000-22,000 | 17,400-24,000 | 20,000-30,000 |
| Ø400 | 18,000-23,500 | 20,000-28,000 | 21,000-31,000 | 25,000-40,000 |
| Ø450 | 22,000-27,000 | 24,000-34,000 | 25,000-40,000 | 32,000-45,000 |
| Ø500 | 25,000-32,000 | 28,000-42,000 | 30,000-48,000 | 38,000-55,000 |
| Ø550 | 28,000-34,000 | 31,000-48,000 | 34,000-53,000 | 45,000-65,000 |
| Ø600 | 30,000-36,000 | 34,000-54,000 | 38,000-58,000 | 50,000-75,000 |
| Ø650 | 32,000-39,000 | - | 41,000-65,000 | 60,000-85,000 |
| Ø700 | 34,000-42,000 | - | 45,000-72,000 | 70,000-120,000 |
| Nominal Diameter (mm) | Actual Diameter (mm) | Nominal Length (mm) | Actual Length (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max. | Min. | Min. (Rough Spot Removed) | Tolerance | Shorter Lengths | ||
| Ø250 | 256 | 252 | 248 | RP/HP 1600/1800/2000 | ±100 | -275 |
| Ø300 | 307 | 302 | 299 | RP/HP 1600/1800/2000/2200 UHP Ø300 1600/1800 UHP Ø350 1600/1800/2000 UHP Ø(400-450) 1600/1800/2000/2200 | ||
| Ø350 | 358 | 352 | 349 | |||
| Ø400 | 409 | 403 | 400 | |||
| Ø450 | 460 | 454 | 451 | |||
| Ø500 | 511 | 505 | 502 | 1800/2000/2200/2400 | ||
| Ø550 | 562 | 556 | 553 | 1800/2000/2200/2400/2700 | ||
| Ø600 | 613 | 607 | 604 | RP/HP 2000/2200/2400/2700 UHP 2200/2400/2700/3000 | ||
| Ø650 | 663 | 659 | 656 | ±100/±150 | ||
| Ø700 | 714 | 710 | 707 | |||
Note: A "rough spot" in the context of graphite electrodes refers to an irregular or uneven surface area on the electrode, which can negatively affect its performance during use, particularly in electric arc furnaces. These spots can lead to increased wear, inconsistent electrical conductivity, and may contribute to the formation of defects in the molten steel.
How to safely store graphite electrodes?
Do not stack electrodes and connectors directly on the ground. Instead, place them on wooden or metal racks to prevent damage or contamination from soil. Do not discard the packaging of unused electrodes temporarily, as the packaging effectively prevents dust and debris from settling on the electrode surface or threads.
Graphite electrodes should be stored neatly in the warehouse, with both sides of the electrode stacks leveled to prevent sliding. The stacking height of the electrodes should generally not exceed 2 meters and preferably not exceed 4 layers.
Graphite electrodes should be protected from rainwater and moisture. If the electrodes become damp, they should be dried before use to prevent cracking, spalling, and increased oxidation consumption during the steelmaking process.
Do not store electrode nipple joints in high-temperature environments to prevent the melting of joint bolts due to excessively high temperatures.
Last Updated: 2024-09-25
- Q: What are the factors affecting the service life of graphite electrode in ultra high power arc furnace?
- China's graphite electrode quality standard (YB/T4090-2000) to evaluate the quality of the ultra high power graphite electrode is defined 6 physicochemical indexes, including resistivity, flexural strength, elastic modulus, bulk density and linear expansion coefficient as the quality evaluation index, ash as a reference index.
- Q: How to improve the efficiency of graphite electrode milling, please tell me
- When the tool is broken, it will not only stop the continuous processing of the steel, but also affect the quality of the product, which will lead to the scrap of the parts and the waste of the material. Considering the foreseeable future, the graphite electrode will occupy a high position, usually used equipment for processing graphite electrode the highest efficiency mold manufacturers will unremittingly, expand and between those determined to use the hard steel processing manufacturer competition gap. The foundation of micro cutting tools, in terms of graphite electrodes, is one of its most magical words: "high speed."". The spindle speed of the high speed machining center is up to 30000~60000r/min, and the feed speed can be increased to shorten the processing period and improve the quality of the surface and edge. The motor needed to drive this type of spindle is relatively small and light, which helps to reduce cutting power and reduce tool breakage. This is critical because many of the electrodes are complex, and their production involves small, easily broken micro tools (see Figure 1).
- Q: What are the skills of hardfacing process for wear-resistant alloy powder blocks?
- Because the carbon containing ash, a graphite resistor 2-3 times, so the use of graphite electrode is better.
- Q: Why graphite can be used as conductive material?
- Graphite used in the electrical industry requires a high degree of particle size and grade. Such as alkaline batteries and some special electric carbon products, requiring graphite particle size control within the scope of the project, grade above, harmful impurities are required in the following. The graphite used in a picture tube for television is required below. As a wear-resistant and lubricating material, graphite is often used as a lubricant in the mechanical industry.
- Q: Is graphite flammable?Why do I bake pencil cores with a fever that doesn't burn?
- In anaerobic conditions, the ignition temperature is at least above 3000 degrees. There are many types of graphite, different types of ignition points, and the burning point of pyrolytic graphite...
- Q: Graphite can be used in acid towers in chemical plants because of graphite
- Ultra high power graphite electrode. A graphite electrode that allows current densities greater than 25A/ cm 2 is allowed. Mainly used in ultra high power steelmaking arc furnace
- Q: MITSUBISHI machine graphite electrode processing, how does not accumulate carbon?
- The three is difficult cold start, is sparking difficult, not easy car, and finally the combustion chamber carbon Yan will cause a heavy cylinder knock, low speed and acceleration noise, causing damage to the piston and crankshaft, causing the engine temperature which can seriously affect the automobile safety. Emission standards exceeded, not only through the annual inspection, but also directly aggravate the pollution of the environment
- Q: How should carbon deposits be treated?
- At certain temperature, can make alloy and carbon can react in the engine surface coated with a layer of graphene film, graphene nano particles can fill the pores, wear scratches, on the friction surface repair function.
- Q: What about graphite electrodes for steel mills?
- For steel and iron alloys, graphite electrodes are used, when powerful currents pass through electrodes into the melting zone of the electric furnace to produce an arcThe electric energy is converted into heat energy, and the temperature is increased to about 2000 degrees, so as to achieve the purpose of smelting or reaction. In addition, the electrolytic goldWhen the magnesium, aluminium and sodium are used, the anode of the electrolytic cell is also made of graphite electrode. The resistance furnace for carborundum is also made of graphite electrode as the burnerConductive material.
- Q: How do graphitized electrodes differentiate between high power and low power?
- In electrolysis industry, using graphite anode plate as the anode has a history of more than 100 years, the metal anode is in recent decades, the research and application of metal anode in China late last century, only in 70s the technology related to the research and experiment of metal anode, anode on electrolysis industry, mainly through the silver (2%) (0.5%): low silver lead silver alloy, lead and silver tin antimony alloy, lead calcium alloy and lead silver alloy adding nucleating agents and several stages.
Send your message to us
High-Performance Graphite Electrodes: RP, HP, UHP for Electric Arc Furnace Steelmaking
- Loading Port:
- Dalian
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches





























