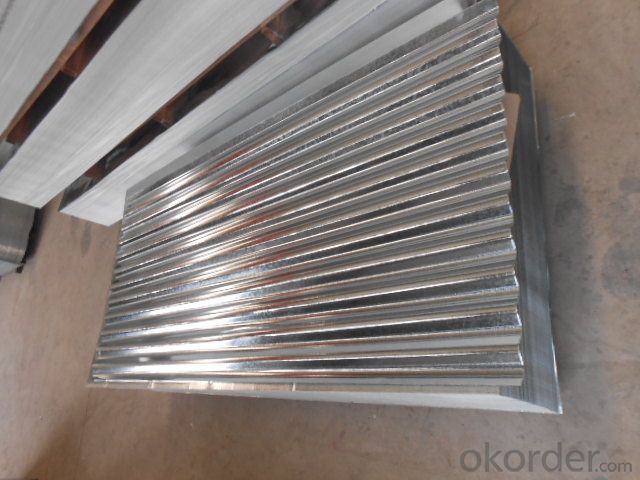
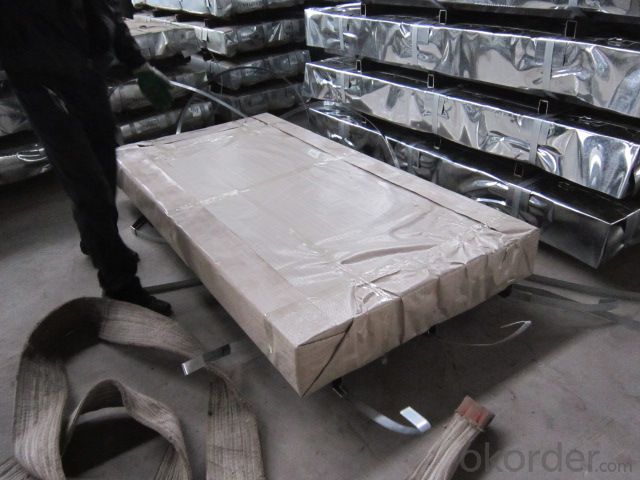
Corrugated Hot-Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheets
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 2500 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Corrugated Hot Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheets
Description:
The corrugated sheet is a high strength and durable steel, mostly used for a architectural decoration. We have scores of corrugated sheets production lines of different types, producing profiled sheets of all kinds of types and colors. Since it adopts high strength steel sheet and the dimension is designed reasonably, the corrugated sheets are widely used on roofs and walls of various buildings, which can be easily installed, be flexible and changeable, unrestricted by no factor of the buildings.
Corrugated steel sheet is the colored steel plate which has been wave formed with the cold rolling treatment, trough especial coated dispose, the color coated steel panel’s guaranty is 12-15 years.
Application:
It has been widely applied on civil construction like storerooms, special building roof and walls of wide-span steel structure building and so on.
With excellent cold bending molded manufacturablity, good decoration effect, strong anti-corrosion ability, are also pollution-free and easily recycled. Accordingly, they can be used as final products and basic plates of color coated steel coils and widely applied in construction, home appliances, decoration, ect.
Pressing steel panel with the clear line, and many colors for choice, suitable for any different building style materials, achieving satisfy effects;
Product Specification:
Thickness tolerance: (+/-0.01mm)
Zinc coating: 50-180g/m2
Standard:jis g 3302, sgch
Package: 2- 3 ton/pallet
Specs: 0.14-0.8mm x 900mm x 2000mm
Width:700-1250mm( 750mm,900mm,1215mm,1250mm,1000mm the most common)
Surface:regular/mini/zero spangle, chromated, skin pass, dry etc.
Package:Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is kraft paper,water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel ,sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock.
FAQ:
1.How many pieces for one package?
The pieces for one tone is decided by the thickness of the sheet, but we can make it according to your requirements in the reasonable range.
2. Do you have pallets for the package?
Yes, we must use pallets for the package in order to load.
3. Could you produce the sheets according to our design?
Yes, we can.
- Q: What are the different types of surface treatments available for steel sheets?
- There are several different types of surface treatments available for steel sheets, each serving a specific purpose and offering unique benefits. 1. Hot-dip galvanizing: This is a widely used method where steel sheets are dipped in a bath of molten zinc, creating a protective coating that prevents corrosion. Hot-dip galvanizing provides excellent corrosion resistance and durability. 2. Electro-galvanizing: In this process, a layer of zinc is electrochemically deposited onto the steel sheets, creating a thin, uniform coating. Electro-galvanizing provides good corrosion protection and is often used for decorative purposes. 3. Powder coating: This surface treatment involves applying a dry powder onto the steel sheets and then curing it using heat. Powder coating provides a durable and attractive finish, offering protection against corrosion, UV rays, and chemicals. 4. Paint coating: Steel sheets can be coated with various types of paints, including epoxy, polyurethane, and polyester. Paint coatings provide aesthetic appeal and offer protection against corrosion and weathering. 5. Phosphating: This treatment involves applying a phosphate coating to the steel sheets, which enhances their corrosion resistance and improves paint adhesion. Phosphating is often used as a pre-treatment before painting or powder coating. 6. Chromate conversion coating: Also known as chromating or passivation, this treatment involves applying a thin layer of chromate onto the steel sheets. Chromate conversion coatings enhance corrosion resistance and improve paint adhesion. 7. Anodizing: Although primarily used for aluminum, anodizing can also be applied to steel sheets. This process involves creating an oxide layer on the surface of the steel, which enhances corrosion resistance and provides a decorative finish. 8. Pickling: This treatment involves immersing the steel sheets in an acidic solution to remove scale, rust, and other impurities. Pickling leaves the steel sheets with a clean, smooth surface, ready for subsequent treatments or processes. Overall, the choice of surface treatment for steel sheets depends on the intended application, desired appearance, and level of corrosion resistance required.
- Q: What is the bending radius for steel sheets?
- The bending radius of steel sheets is influenced by several factors, including the sheet's thickness, the type of steel utilized, and the particular application at hand. Typically, a widely accepted guideline suggests employing a bending radius that is no less than twice the thickness of the steel sheet. Nevertheless, this figure can fluctuate depending on the specific demands and constraints of the undertaking. It is crucial to seek guidance from engineering and fabrication specialists experienced in handling steel sheets to ascertain the suitable bending radius for a specific application.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface cleaning for steel sheets?
- Surface cleaning of steel sheets offers various methods, each with its own advantages and applications. 1. Mechanical Cleaning: To physically eliminate dirt, rust, and other contaminants from steel sheet surfaces, one can utilize sandpaper, wire brushes, or abrasive blasting. This approach is ideal for heavy-duty cleaning and preparing surfaces for further treatment or coating. 2. Chemical Cleaning: By employing chemicals or detergents, one can dissolve or remove contaminants from the steel surface. This method is particularly effective in eliminating grease, oil, and other organic substances. It is crucial to select the appropriate chemical cleaner based on the type of contamination and the composition of the steel sheet, ensuring effective cleaning without surface damage. 3. Electrolytic Cleaning: This technique involves submerging the steel sheet in an electrolyte bath along with an electric current to dissolve and separate contaminants. Electrolytic cleaning is effective in removing stubborn rust, scale, and oxidation, while also providing a polished finish. 4. Power Washing: Also known as pressure washing, this method employs a high-pressure water stream to cleanse the steel surface. Power washing effectively removes loose debris, dirt, and mild contaminants. However, it may not be suitable for heavy-duty cleaning or the elimination of stubborn substances like rust. 5. Vapor Degreasing: Vapor degreasing utilizes solvent vapors to clean the steel surface. By exposing the steel sheet to these vapors, contaminants are dissolved and removed. This technique is particularly effective in eliminating oil, grease, and other organic substances. Vapor degreasing is a precise and controlled cleaning method commonly utilized in industrial applications. Before selecting a surface cleaning method, it is crucial to consider the type and severity of contamination, the desired level of cleaning, and the specific requirements of the steel sheets. Additionally, it is important to prioritize safety precautions and utilize appropriate protective equipment when performing any surface cleaning procedure.
- Q: Are steel sheets resistant to impact or damage?
- Steel sheets are known for their exceptional strength and durability, which makes them highly resistant to impact and damage. Due to their high tensile strength, steel sheets can withstand heavy loads and resist deformation or breakage when subjected to external forces. They are often used in applications where impact resistance is critical, such as in construction, automotive manufacturing, and industrial settings. Additionally, steel sheets can withstand extreme temperatures, corrosion, and environmental factors, which further contributes to their overall resistance to damage. However, it is important to note that the specific resistance to impact or damage may vary depending on the thickness, quality, and composition of the steel sheet.
- Q: Can the steel sheets be easily welded?
- Steel sheets can indeed be welded with ease. Joining steel sheets together is commonly achieved through the process of welding. This procedure entails melting the edges of the steel sheets, followed by allowing them to cool and solidify, resulting in a sturdy connection. It is worth mentioning, however, that the ease of welding may vary depending on factors such as the type and thickness of the steel sheets, as well as the expertise and experience of the welder. Furthermore, it is crucial to adhere to appropriate safety measures and welding techniques to guarantee a successful and secure welding procedure.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for solar panel frames?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for solar panel frames. Steel is a durable and strong material that can provide the necessary support for solar panels, ensuring their stability and longevity. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily fabricated and customized to meet specific design requirements, making them a popular choice for solar panel frames in various applications.
- Q: What is the average weight of a steel sheet per square foot?
- The average weight of a steel sheet per square foot can vary depending on the thickness and type of steel being used. However, a common range for the weight of a steel sheet per square foot is between 40 to 70 pounds. It is important to note that this is a general estimate and the actual weight may differ based on specific factors such as the alloy composition and manufacturing process.
- Q: What is the typical load-bearing capacity of a steel sheet?
- The typical load-bearing capacity of a steel sheet can vary depending on its thickness, size, and grade. However, on average, a steel sheet can typically bear loads ranging from 50,000 to 100,000 pounds per square inch (PSI).
- Q: Are steel sheets available in textured finishes?
- Yes, steel sheets are available in textured finishes. Textured finishes can be achieved through various processes such as embossing, etching, or brushing. These techniques create patterns or textures on the surface of the steel sheet, giving it a unique and visually appealing appearance. These textured finishes not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the steel sheet but also provide functional benefits like improved grip, reduced glare, or increased durability. Different types of textures can be applied to steel sheets to suit different applications and design preferences.
- Q: What is the weight of a typical steel sheet?
- The weight of a typical steel sheet can vary depending on its dimensions and thickness. However, on average, a standard steel sheet can weigh anywhere from 15 to 30 pounds per square foot.
Send your message to us
Corrugated Hot-Dipped Galvanized Steel Sheets
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 2500 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords