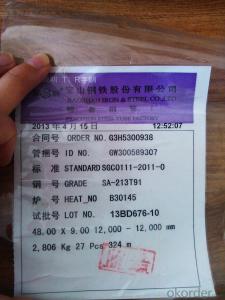
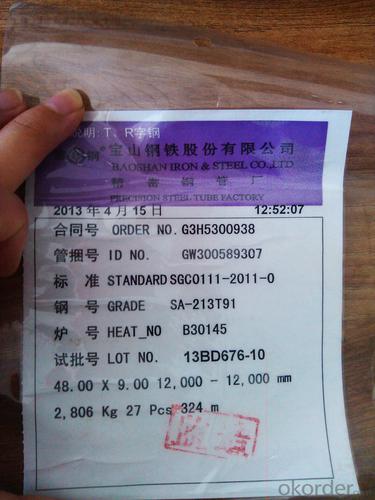
ASTM A213 T91 boiler tube 25
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Alloy pipe stock grade A335P11/P22/P12/P91/P92/P9/P5 A213 T11/T22/T12/T91/T91/T9/T5
T91 alloy pipe is America national tree like ridge and America combustion new martensitic heat-resistant steel engineering company metallurgical materials laboratory research work. It is to reduce the carbon content of 9Cr1MoV steel on the basis of the content of sulphur, phosphorus, strictly limit the vanadium, niobium, adding small amount of alloying elements.
The number of K90901 T91 alloy tube
T91 alloy tube
T91 alloy pipe specifications: 8-1240 x 1-200mm
Overview of T91 alloy tube:
T91 alloy tubes for ferrite and Olympic alloy steel seamless steel tube boiler, overheating and heat exchanger belongs to (ASTM A213 / A213M-07a)
Use:
For low and medium pressure boiler (work pressure is generally not more than 5.88Mpa, the operating temperature at 450 DEG C) of the heating surface tube; used for high pressure boiler (work pressure is generally above 9.8Mpa, operate at a temperature of 450 DEG to 650 DEG C between) the heating surface tubes, economizer, superheater, reheater, petrochemical industrial pipe.
Heat treatment of T91 alloy tube:
The final heat of T91 treatment for normalizing and high temperature tempering, normalizing temperature 1040 C, the holding time of not less than 10 min, the tempering temperature is 730 to 780 DEG C, the heat preservation time is not less than 1h, the final heat treatment on Microstructure of tempered martensite
- Q: What is the difference between carbon steel and stainless steel pipes?
- Carbon steel pipes are made primarily from carbon and iron and are known for their strength and durability. However, they are prone to corrosion over time. On the other hand, stainless steel pipes are made from a combination of iron, chromium, and nickel, which makes them highly resistant to corrosion. Stainless steel pipes are also known for their aesthetic appeal, as they have a sleek and shiny appearance. Overall, the main difference between carbon steel and stainless steel pipes lies in their corrosion resistance properties.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the construction of pipelines?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in the construction of pipelines due to their high durability, strength, and ability to withstand high pressure. These pipes are used to transport various fluids, such as oil, gas, and water, over long distances. They are welded together and laid underground or submerged to create a reliable and efficient transportation system for these resources.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the transportation industry?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in the transportation industry for various purposes such as the construction of pipelines, including oil and gas pipelines, water pipelines, and sewage pipelines. They are also used in the manufacturing of automotive parts, such as exhaust systems, and in the construction of infrastructure such as bridges and tunnels. Additionally, steel pipes are used in the transportation of goods through shipping containers and railway tracks.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the construction of dams?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in the construction of dams for various purposes. They are primarily used for the transportation of water within the dam structure, supplying water to turbines for hydroelectric power generation. Steel pipes are also used for drainage systems, allowing water to be discharged safely and efficiently. In addition, they are utilized for the construction of penstocks, which are large pipes that control the flow of water from the reservoir to the turbines. Overall, steel pipes play a crucial role in the infrastructure of dams, ensuring the efficient management and utilization of water resources.
- Q: Difference and application of seamless hot rolled pipe and cold drawn pipe in seamless steel tube
- purpose2.1 seamless tubes are widely used. General purpose seamless tubes are rolled from plain carbon structural steel, low-alloy structural steel or alloy structural steel, with the most output and are used primarily as pipes or structural parts for conveying fluids2.2, divided into three kinds according to the supply of different uses: the supply of a, according to the chemical composition and mechanical properties; the supply of B, according to the mechanical properties; the supply of C, according to the hydraulic pressure test. According to a, the B class steel supply, such as for under fluid pressure, but also to the pressure test.2.3. Seamless tubes for special purposes include seamless tubes for boilers, seamless tubes for geology, and seamless pipes for petroleum use
- Q: What is the load-bearing capacity of steel pipes?
- The load-bearing capacity of steel pipes depends on various factors such as the diameter, wall thickness, and grade of the steel used. Generally, steel pipes have high load-bearing capacity due to their inherent strength and durability. The load-bearing capacity can be determined through engineering calculations and testing methods. These calculations consider factors like the applied load, pipe dimensions, and the material properties of the steel. It is important to consult engineering standards and guidelines, as well as a structural engineer, to accurately determine the load-bearing capacity of specific steel pipes for a given application.
- Q: What is a flange and how is it used in steel pipes?
- A flange is a mechanical device that is used to connect two sections of steel pipes together. It consists of a flat or raised ring that is attached to the end of each pipe section. The flange provides a surface for the pipes to be bolted or welded together, creating a secure and leak-proof joint. It also allows for easy disassembly and reassembly of the pipes when necessary. Flanges are commonly used in various industries, such as oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing, where the connection between steel pipes needs to be strong and reliable.
- Q: Are steel pipes suitable for high-pressure applications?
- Yes, steel pipes are suitable for high-pressure applications. Steel pipes are known for their strength and durability, making them ideal for handling high-pressure applications. They can withstand the internal pressure exerted by fluids or gases under high pressure without deforming or bursting. The high tensile strength of steel allows it to resist the forces that occur in high-pressure environments, ensuring the safety and reliability of the piping system. Additionally, steel pipes can be manufactured with thicker walls to further enhance their ability to withstand high pressures. Steel pipes are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, power generation, and water distribution, where high-pressure applications are common.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in HVAC systems?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in HVAC systems for various purposes. They are used for transporting fluids such as water, steam, and refrigerant throughout the system. These pipes are durable and resistant to high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for the demanding conditions of HVAC applications. They are used for distributing and circulating the heated or cooled air, as well as for connecting different components of the system, including boilers, chillers, heat exchangers, and air handlers. Additionally, steel pipes are often used for ventilation and exhaust purposes in HVAC systems.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for agricultural irrigation?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for agricultural irrigation. They are a durable and long-lasting option that can withstand high pressures and extreme weather conditions. Steel pipes also provide excellent protection against corrosion and damage, making them suitable for various irrigation systems in agriculture.
Send your message to us
ASTM A213 T91 boiler tube 25
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords