Aluminum CC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles for Cookware
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 3 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
1.Structure of CC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles Used for Cookware Description
CC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles Used for Cookwareare widly used in decoration field. For the painting, it depends on the using evironment. If you use in the open air, we recommend the PVDF coated aluminium coils. This kind of painting can last 15-20 years. If you use in the room, we recommend PE coated aluminium coils. The price is much more competitive.
Direct Continuous Aluminium Foil Stock in Coil is one semi-finished aluminium material. This strip can be rolled down to aluminium foil.The final thickess can be 5-20 microns. Aluminium foil is soft, ductile and with a silver-white luster which can be widely used in a large scare of fields.
2.Main Features ofCC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles Used for Cookware
a.Competitive price---We have our own mills and can produce mill finished aluminium coils, so we can control the production cost better.
b.Professional after-sale service---We have more than 15 years exportation experience and you need not worry about the exporation problems.
c.Fast delivery time---We can control the delivery time within 35 days.
3.CC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles Used for Cookware Images
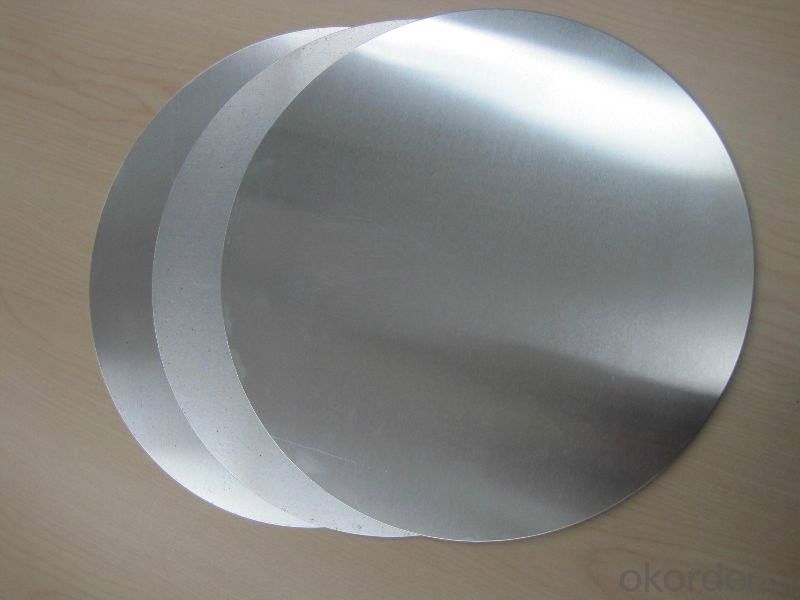



4.CC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles Used for Cookware Specification
Alloy | AA1050 |
Temper | H14, H16, H18, H22, H24, H26, H32, O/F |
Thickness | 0.5mm -- 4mm |
Diameter | 200mm -- 1200mm |
Standard | GB/T 3880-2006 |
5. FAQ of CC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles Used for Cookware
What is the quality standard?
---Usually our standard is GB3880-2006
What is the largest width?
---It is 2300mm
What is the MOQ?
---Usually we can accept 80 tons.
- Q: What measures should be taken to ensure safety when handling or using aluminum products?
- <p>When using aluminum products, safety precautions include handling with care to avoid sharp edges that may cause cuts. Ensure proper ventilation when working with aluminum powder or dust to prevent respiratory issues or fire hazards. Avoid using aluminum cookware for acidic or alkaline foods as it can react and leach aluminum into the food. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for use and cleaning, and wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves and masks when necessary.</p>
- Q: Explain the distinction between aluminum as a pure element and its alloys.
- <p>Aluminum is a lightweight, silvery-white metal found in the Earth's crust. It is a pure element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminum alloys, on the other hand, are mixtures of aluminum with other elements such as copper, magnesium, manganese, and silicon. These alloys are created to enhance certain properties like strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. While pure aluminum is soft and malleable, its alloys are stronger and more versatile, making them suitable for a wide range of applications from aerospace to construction.</p>
- Q: Explain the connection between aluminum and its interaction with electromagnetic radiation.
- <p>Aluminum has a unique relationship with electromagnetic radiation due to its reflective and conductive properties. It is a good reflector of visible light and infrared radiation, which is why it is used in applications such as mirrors and reflective coatings on windows to reduce heat transfer. Additionally, aluminum's high electrical conductivity makes it an excellent shield against electromagnetic radiation, as it can absorb and reflect a significant amount of electromagnetic waves. This property is utilized in various industries, including electronics and aerospace, to protect sensitive equipment from electromagnetic interference.</p>
- Q: This question asks about the health effects of consuming aluminum on human health.
- <p>Aluminum consumption can have various effects on human health, though the extent of its impact is still a subject of debate among researchers. High levels of aluminum intake have been associated with neurological disorders, particularly Alzheimer's disease, although a direct causal link has not been definitively established. Aluminum can also interfere with bone health, potentially leading to osteoporosis, and may affect the kidneys, causing dysfunction. It is important to note that the human body naturally excretes aluminum, so moderate exposure is generally not harmful. However, excessive intake, especially over a long period, could pose health risks.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to utilize recycled aluminum in the construction of buildings?
- <p>Yes, recycled aluminum can be used for building materials. It is commonly used in various construction applications due to its strength, durability, and lightweight properties. Recycled aluminum is not only environmentally friendly but also cost-effective compared to newly mined aluminum. It is used in the production of aluminum windows, doors, roofing materials, and structural components. Additionally, its recyclability reduces waste and conserves natural resources.</p>
- Q: Is it safe to use pure aluminum for baking or roasting food in a traditional oven or grill?
- <p>While pure aluminum is a common material in cookware, it's not recommended for direct use in baking or roasting food in a traditional oven or grill. Aluminum can react with acidic foods, potentially leaching aluminum into the food. Additionally, aluminum foil can burn and create a hazardous situation. For baking or roasting, it's safer to use materials specifically designed for these purposes, such as parchment paper, silicone baking mats, or oven-safe dishes.</p>
- Q: What are the potential health advantages of minimizing contact with aluminum?
- <p>Reducing exposure to aluminum may have health benefits, particularly in terms of neurological health. Aluminum has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's, although the evidence is not conclusive. Lowering exposure could potentially reduce the risk of cognitive decline. Additionally, aluminum may affect bone health and the immune system, so minimizing contact could support stronger bones and a more robust immune response. However, it's important to note that aluminum is naturally present in many foods and water sources, and moderate exposure is generally considered safe by health authorities.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to utilize aluminum as a material in battery construction?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be used in batteries. It is commonly used as a current collector in lithium-ion batteries due to its low density, high conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum's role is primarily structural, providing support and facilitating the flow of electricity. However, it is not used as an active material in the electrochemical reactions that generate power. Research is ongoing to explore the potential of aluminum as an anode material in next-generation batteries, aiming to improve energy density and reduce costs.</p>
- Q: Explain the economic and job market implications of using aluminum.
- <p>The use of aluminum has significant impacts on the economy and job market. It is a key material in various industries, including construction, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, which drives demand and economic growth. Aluminum production and processing create jobs directly in mining, refining, and manufacturing sectors, and indirectly in related services and supply chains. Additionally, its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make it valuable for energy-efficient transportation, contributing to environmental sustainability and opening new job opportunities in green technologies. However, it also presents challenges such as the need for energy-intensive production processes and the management of waste, which require innovative solutions and can lead to job creation in recycling and environmental management.</p>
- Q: This question asks for methods to prevent the corrosion of pure aluminum when exposed to environmental factors.
- <p>To prevent corrosion of pure aluminum in the environment, one can apply protective coatings such as paints or anodizing, which forms a dense oxide layer on the surface. Additionally, using aluminum alloys that contain elements like copper, magnesium, and silicon can enhance resistance to corrosion. Regular cleaning and maintenance to remove contaminants that may initiate corrosion are also important. In extreme environments, cathodic protection or the use of inhibitors can be employed to further protect aluminum from corrosion.</p>
Send your message to us
Aluminum CC Quality AA1050 Mill Finished Aluminum Circles for Cookware
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 3 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches