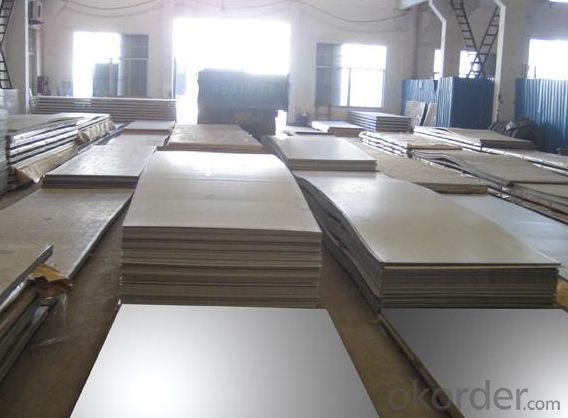
0.15-80mm Thickness SGS Certification and 300 Series
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like



- Q: How are stainless steel pipes made?
- The process of manufacturing stainless steel pipes, known as stainless steel pipe manufacturing, involves several steps to produce durable and corrosion-resistant pipes suitable for various applications. To begin, stainless steel, the raw material, is carefully selected based on its composition and desired properties such as strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. Stainless steel is primarily made up of iron, chromium, and other elements like nickel and molybdenum. Once obtained, the stainless steel is melted in an electric furnace at extremely high temperatures. The molten steel is then poured into molds to form solidified cylindrical bars called billets or ingots. The next step is to heat the billets or ingots in a furnace to make them more malleable. This process, called hot rolling, involves passing the heated billets through rollers to reduce their diameter and thickness. Continuous rolling refines the grain structure of the stainless steel and improves its mechanical properties. After hot rolling, the stainless steel is annealed by heating it to a specific temperature and gradually cooling it. Annealing relieves internal stresses and enhances the steel's ductility and toughness. The annealed stainless steel then undergoes cold rolling, where it is passed through rollers at room temperature. This further reduces the diameter and thickness of the stainless steel, resulting in a smoother surface finish and tighter tolerances. Once the desired dimensions are achieved, the stainless steel is either welded or manufactured into seamless pipes, depending on the type of pipe being produced. For welded stainless steel pipes, the cold-rolled stainless steel strip is formed into a cylindrical shape and then longitudinally welded using techniques like TIG or MIG welding. This welding process ensures the pipe's integrity and strength. On the other hand, seamless stainless steel pipes are made by piercing a solid cylindrical billet or ingot to create a hollow tube. This piercing process involves using a mandrel to create a cavity in the billet. The pierced billet is then elongated, rolled, and cut to the desired length and diameter. After the pipes are formed, they undergo various finishing processes such as heat treatment, pickling, passivation, and polishing. These processes enhance the pipes' corrosion resistance, remove surface impurities, and improve their aesthetic appearance. In conclusion, stainless steel pipes are manufactured through melting, hot rolling, annealing, cold rolling, welding or seamless pipe manufacturing, and various finishing processes. This meticulous production process ensures the production of high-quality stainless steel pipes that meet required specifications and standards.
- Q: What is the difference between 316 and 316H stainless steel pipes?
- The main difference between 316 and 316H stainless steel pipes lies in their carbon content. 316 stainless steel pipes have a maximum carbon content of 0.08%, which makes them suitable for applications where corrosion resistance is important, such as in marine environments. They are also known for their excellent welding and forming properties, making them a popular choice in various industries. On the other hand, 316H stainless steel pipes have a higher carbon content, typically around 0.04-0.10%. This increased carbon content provides improved high-temperature strength and creep resistance, making them suitable for applications where the pipes will be subjected to elevated temperatures, such as in high-pressure steam systems or in the petrochemical industry. In summary, while both 316 and 316H stainless steel pipes offer good corrosion resistance and overall performance, the 316H variant is specifically designed to withstand higher temperatures and offer better strength properties.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for geothermal applications?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are suitable for geothermal applications. Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand the high temperatures and pressures present in geothermal systems. Additionally, stainless steel pipes have excellent thermal conductivity, making them efficient for transferring heat in geothermal applications.
- Q: Stainless steel works. What saw can be sawed off?
- What is the best or bad, to the building materials market to find a store with a chainsaw to help cut or site also if things go to the talent market, a hydraulic, electric what, give him a little money he will help you cut out
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for natural gas?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for natural gas. Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and can withstand the high pressures and temperatures associated with natural gas transmission and distribution. Additionally, stainless steel pipes have excellent fire resistance properties, making them a safe choice for natural gas applications.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for wastewater treatment ponds?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are suitable for wastewater treatment ponds. Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, which is essential for withstanding the harsh and corrosive environment of wastewater treatment ponds. Additionally, stainless steel pipes are durable, have a long lifespan, and can handle high-pressure systems, making them a reliable choice for wastewater treatment applications.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for air pollution control systems?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for air pollution control systems. Stainless steel is a highly durable and corrosion-resistant material, making it suitable for handling harsh environments and corrosive gases that are commonly found in air pollution control systems. Stainless steel pipes also have the advantage of being able to withstand high temperatures, allowing them to be used in applications where thermal resistance is required. Additionally, stainless steel is known for its hygiene properties, making it an ideal choice for industries that require clean and sterile air handling. Overall, stainless steel pipes are a popular and reliable choice for air pollution control systems due to their strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to handle high temperatures.
- Q: How can the stainless steel tube eliminate stress?
- Or artificial stress, method: stresses both ends of the steel pipe fixed by the mold, through high-frequency shocks, so that the internal stress relief of the steel pipe
- Q: What is the difference between 440C and 440F stainless steel pipes?
- The 440 series encompasses two types of stainless steel, namely 440C and 440F. These variants differ slightly in their composition and properties. 440C stainless steel, a high-carbon martensitic type, boasts chromium content that bolsters its corrosion resistance and hardness. It is renowned for its exceptional wear resistance, commendable strength, and ability to maintain sharpness. Its elevated carbon content ensures excellent hardness, albeit at the expense of increased difficulty in machining when compared to stainless steels with lower carbon levels. Consequently, 440C finds common application in scenarios necessitating high strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance, such as cutting tools, bearings, and surgical instruments. Contrarily, 440F stainless steel represents a free-machining version of 440C. Like its counterpart, it is a high-carbon martensitic stainless steel; however, it incorporates sulfur to enhance its machinability. The sulfur acts as a lubricant during the machining process, facilitating easier and faster cutting. Nevertheless, the addition of sulfur marginally diminishes 440F's corrosion resistance and toughness in comparison to 440C. Consequently, 440F finds utility in applications demanding extensive machining, such as automotive components, fasteners, and valve parts. To sum up, the primary distinction between 440C and 440F stainless steel lies in their machinability and sulfur content. While 440C offers superior corrosion resistance and hardness, it may prove more challenging to machine. On the other hand, 440F is more manageable to machine but exhibits slightly reduced corrosion resistance and toughness. The selection between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application, with 440C being preferred when prioritizing corrosion resistance and wear resistance, and 440F being suitable for scenarios necessitating extensive machining.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for food storage facilities?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for food storage facilities. Stainless steel is a preferred material for food storage and processing due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and hygienic properties. It does not react with food or release any harmful substances, making it safe for storing various types of food products. Stainless steel pipes are also easy to clean and maintain, ensuring the highest levels of hygiene in food storage facilities. Additionally, stainless steel is resistant to high temperatures, making it suitable for both hot and cold food storage. Overall, stainless steel pipes are an excellent choice for food storage facilities due to their safety, durability, and hygienic properties.
Send your message to us
0.15-80mm Thickness SGS Certification and 300 Series
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords