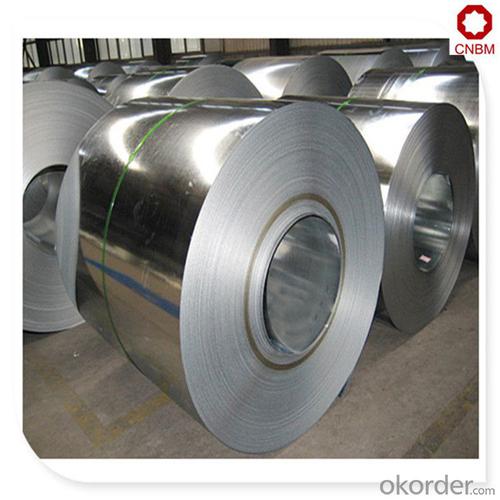
Standard steel coil sizes galvanized by hot dipped
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 34356 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications. Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
Standard and Grade :
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils | ||||
ASTM A653M-06a | EN10327:2004/ 10326:2004 | JISG 3302-2010 | AS-NZS 4534-2006 | |
Commercial quality | CS | DX51D+Z | SGCC | G1+Z |
Structure steel | SS GRADE 230 | S220GD+Z | SGC340 | G250+Z |
SS GRADE 255 | S250GD+Z | SGC400 | G330+Z | |
SS GRADE 275 | S280GD+Z | SGC440 | G350+Z | |
SS GRADE 340 | S320GD+Z | SGC490 | G450+Z | |
SS GRADE550 | S350GD+Z | SGC570 | G550+Z | |
S550GD+Z | G550+Z | |||
Technology test results:
Processability | Yield strength | Tensile strength | Elongation % | 180°cold-bending |
Common PV | - | 270-500 | - | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
Mechanical interlocking JY | - | 270-500 | - | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
Structure JG | >=240 | >=370 | >=18 | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
Deep drawn SC | - | 270-380 | >=30 | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |
EDDQ SC | - | 270-380 | >=30 | d=0,intact,no zinc removal |


FAQ
Q: How do you guarantee the quality of your product?
A: Every process will be checked by responsible QC which insures every product's quality.
Q: How much is your delivery time?
A: Normally within 30 days of receipt of LC original or prepayment, but mostly according to the specific requirements or the quantity
Q: I need sample, could you support?
A: We can supply you with the sample for free, but the delivery charges will be covered by our customers. For avoiding the misunderstanding, it is appreciated if you can provide the International Express Account for Freight Collect. Also you can have a visit to us, welcome to CNBM!
Certificate:
CNBM International is highly recognized by its business partners and clients all over the world and has obtained rapid development under the spirit of win-win. We will carry on the mutual beneficial, innovative and revolutionary trading structure as we did before, create value for our employees, share holders and clients and benefit the whole society in our future development

- Q: Can steel coils be coated with luminescent materials?
- Yes, steel coils can be coated with luminescent materials. This process involves applying a layer of luminescent material onto the surface of the steel coils, allowing them to emit light in the dark or under specific lighting conditions.
- Q: Are steel coils used in electrical equipment manufacturing?
- Yes, steel coils are commonly used in electrical equipment manufacturing. They are often used in the construction of transformers, motors, generators, and other electrical devices. The steel coils provide structural support, magnetic properties, and efficient conduction of electricity, making them an essential component in electrical equipment manufacturing.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the automotive stamping industry?
- Steel coils are used in the automotive stamping industry to provide a continuous supply of flat steel sheets that are then fed into stamping machines. These coils are unrolled, straightened, and then fed through the stamping presses to create various automotive parts, such as body panels, chassis components, and other structural parts. The use of steel coils ensures efficiency, precision, and a consistent quality in the production of automotive parts.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the manufacturing of food packaging?
- Steel coils are commonly used in the manufacturing of food packaging to create various types of containers such as cans and tins. These coils are formed into the desired shape and then coated with a food-grade lacquer to ensure the safety and preservation of the packaged food. The strength and durability of steel make it an ideal material for protecting and storing food products, allowing them to be transported and stored without compromising their quality.
- Q: What are the different types of steel coil grades?
- Various industries and applications utilize a range of steel coil grades. Some commonly employed types include: 1. Carbon Steel: This fundamental steel variant consists primarily of iron and carbon. Its widespread use in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries stems from its exceptional strength and durability. 2. Stainless Steel: This specific steel variant incorporates chromium, which imparts corrosion resistance, making it appropriate for applications requiring protection against oxidation and staining. Industries such as food processing, chemical, and medical frequently employ stainless steel. 3. High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel: HSLA steel comprises trace amounts of alloying elements like copper, phosphorus, niobium, and vanadium. This steel variant offers superior strength and improved mechanical properties when compared to carbon steel, rendering it suitable for structural applications. 4. Galvanized Steel: This type of steel undergoes a zinc coating process to safeguard against corrosion. Galvanized steel finds common use in outdoor applications like roofing, fencing, and automotive components. 5. Electrical Steel: Also known as silicon steel, electrical steel possesses high magnetic permeability, low electrical conductivity, and minimal core loss. It finds application in the production of transformers, motors, and other electrical equipment. 6. Tool Steel: Tool steel, a high-carbon steel variant, is specifically engineered for fabricating tools and dies. Its outstanding hardness, wear resistance, and toughness make it appropriate for cutting, forming, and shaping materials. These examples represent merely a fraction of the available steel coil grades. Each grade exhibits its own distinct properties and characteristics, rendering it suitable for specific applications within various industries.
- Q: How do steel coils contribute to energy savings in buildings?
- Steel coils contribute to energy savings in buildings through their use in HVAC systems. These coils are commonly used in air conditioning units and heat pumps, where they help transfer heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. By efficiently absorbing and dissipating heat, steel coils enable HVAC systems to regulate the temperature inside the building more effectively, reducing energy consumption and costs. Additionally, the durability and long lifespan of steel coils minimize the need for frequent replacements, further contributing to energy savings in the long term.
- Q: What are the different types of steel coil storage containers?
- There are several types of steel coil storage containers, including coil racks, coil cradles, coil saddles, and coil cars.
- Q: Cold rolled steel coil steel, what is the difference?
- Steel rolling process is different from the steel produced naturally different!
- Q: How are steel coils used in the production of consumer goods?
- Steel coils are used in the production of consumer goods as they are processed and shaped into various components, such as sheets, tubes, and wires. These components are then utilized in manufacturing a wide range of products, including automobiles, appliances, furniture, and construction materials. The high strength and durability of steel make it an ideal material for consumer goods, ensuring their longevity and performance.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the manufacturing of appliances?
- Steel coils are used in the manufacturing of appliances as a primary material for constructing the appliance's body or frame. The coils are shaped and molded to form the necessary components, providing strength, durability, and stability to the appliance.
Send your message to us
Standard steel coil sizes galvanized by hot dipped
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 34356 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords

























