Solartec 3000 on grid inverter with WIFI
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Solartec 1500,2000,2500,3000,3600,4000,4600,5000
1MPPT, single phase
IP 65
New mold with Pure thick aluminum crust.
Efficient
■ Efficiency of up to 97.6 %
■ TransformerlessSafe
■ Integrated DC switch
■ Comprehensive protection functionsFlexible
■ LCD backlight
■ For indoor and outdoor installationSimple
■ ‘Plug and play’connection for easy installation
■ Friendly interface, easy to install and maintain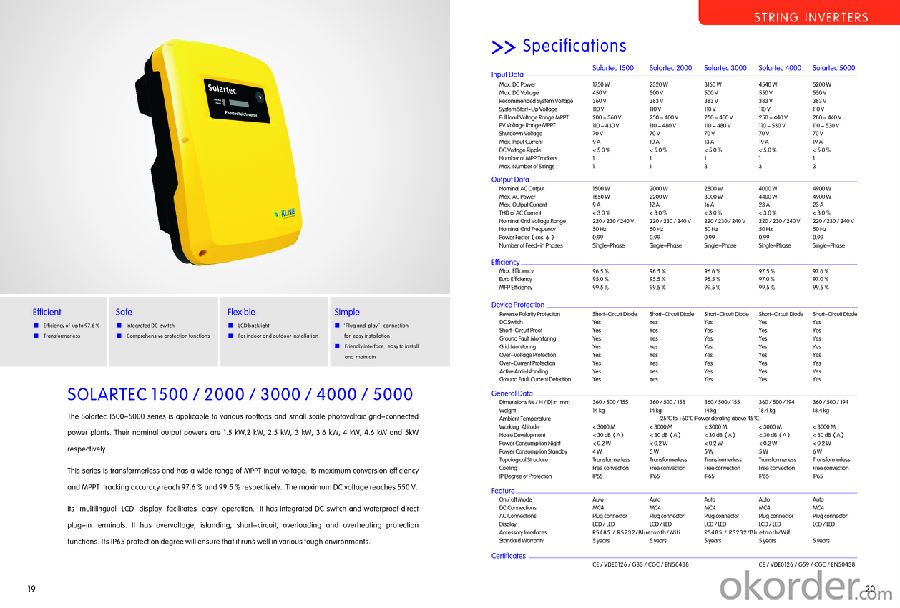

- Q: What are the common maintenance requirements for a solar inverter?
- The common maintenance requirements for a solar inverter include regular inspections to ensure proper functioning, cleaning of the unit and its components to remove dust and debris, checking and tightening of electrical connections, monitoring for any signs of damage or wear, and updating firmware or software as needed. Additionally, keeping the inverter's surrounding area clean and free from obstructions is also important for optimal performance.
- Q: What are the different types of solar inverters?
- There are three main types of solar inverters: string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. String inverters are the most common and cost-effective option, where multiple solar panels are connected in a series and the inverter converts the DC power from the panels into AC power for use in the home. Microinverters are installed on each individual solar panel, converting DC power to AC power directly at the panel level. Power optimizers are installed with string inverters and optimize the output of each solar panel individually, ensuring maximum energy production.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in areas with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI)?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in areas with high levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) as long as the inverter is designed and tested to withstand such conditions. Inverters with robust shielding and advanced filtering mechanisms can effectively mitigate the effects of EMI, ensuring stable and reliable operation even in challenging electromagnetic environments.
- Q: What is the maximum power rating of a solar inverter?
- The maximum power rating of a solar inverter typically depends on its size and capacity, but it can range from a few hundred watts to several megawatts.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle grid voltage variations?
- A solar inverter handles grid voltage variations by continuously monitoring the voltage levels of the grid. When the grid voltage increases or decreases beyond a certain range, the inverter adjusts its output voltage accordingly to maintain a stable and consistent supply of electricity. This ensures that the solar power system remains synchronized with the grid and prevents any damage to the inverter or the connected equipment.
- Q: Can a solar inverter work without sunlight?
- No, a solar inverter cannot work without sunlight as it relies on solar energy to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in regions with high altitude conditions?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in regions with high altitude conditions. However, it is important to consider certain factors such as temperature, air density, and potential voltage fluctuations that can affect the performance of the solar inverter at high altitudes. Specialized inverters or adjustments may be required to ensure optimal functioning in such conditions.
- Q: What is the standby power consumption of a solar inverter?
- The standby power consumption of a solar inverter refers to the amount of power that the inverter consumes when it is in standby mode or not actively converting solar energy into usable electricity. This power consumption is generally very low, typically ranging from 1 to 5 watts, as the inverter only needs to maintain its internal circuitry and monitor the solar energy availability.
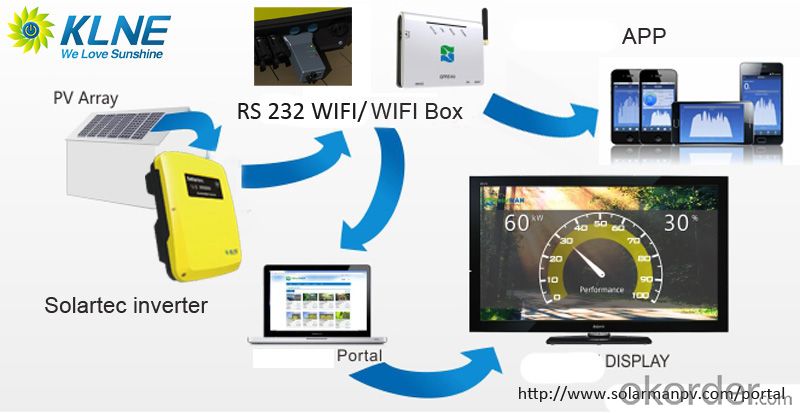
- Q: Can a solar inverter be connected to a home automation system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be connected to a home automation system. By integrating the solar inverter with the home automation system, homeowners can monitor and control their solar power production, track energy usage, and automate various energy-saving functions such as adjusting thermostat settings, turning off appliances, or scheduling energy-intensive tasks during peak solar production hours. This integration enhances the overall efficiency and convenience of managing solar energy within a smart home environment.
- Q: How is a solar inverter different from a regular inverter?
- A solar inverter is specifically designed to convert the DC (direct current) electricity generated by solar panels into AC (alternating current) electricity that can be used to power household appliances and be fed back into the grid. On the other hand, a regular inverter is generally used to convert DC power from batteries or other sources into AC power. Therefore, the main difference lies in their purpose and the source of the DC electricity they handle.
Send your message to us
Solartec 3000 on grid inverter with WIFI
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords