Geogrids Nptel Permeable Hard Geotube Drain Pipe for Drainage Ditch
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m
- Supply Capability:
- 150000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications
1. Water Drainage Ditch
2.Material:Polyethylene
3.Application:anti-aging,anti-corrosion,environmental protection
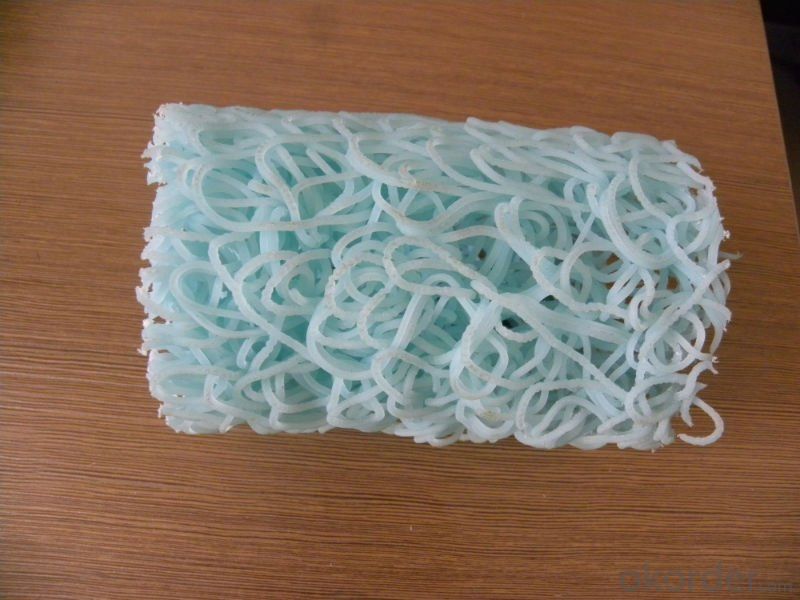
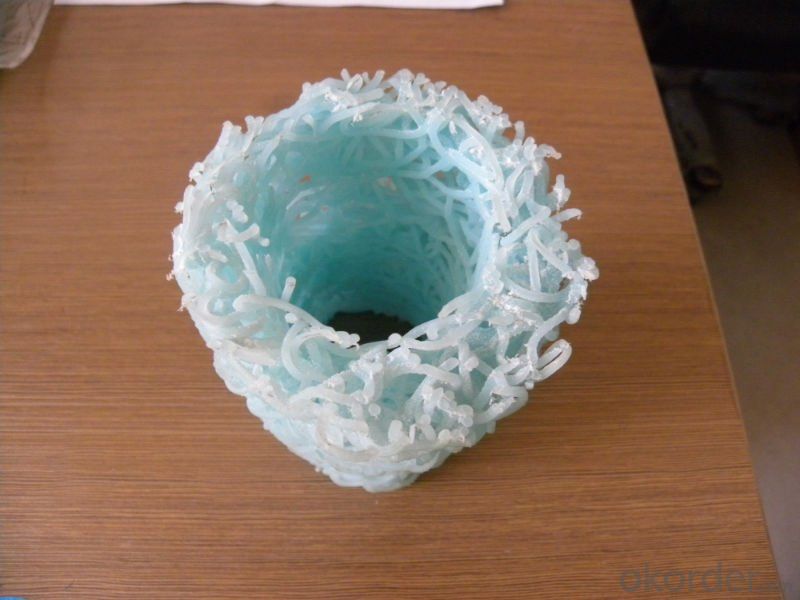
The introduction and application of plastic ditch drainage:
1.Plastic blind drain is also named blind ditch or under drain. It is three-dimensional
multi-hole material by melting joint of fiber extruded from melted thermoplastic
composite resin. There are a variety of products of round or square sections. We can manufacture products with different characteristics of high temperature resistance, anti-flaming, high PH resistance, high elasticity, and high hardness
made of different formula tailored for customers.
2.Engineering application of plastic blind drain:
1) Drainage of road and railway ground and shoulder.
2) Drainage of back of retaining wall (vertical and horizontal drainage).
3) Drainage of tunnel and underground channel.
4) Drainage of slopes such as hillside and bank slope.
5) Horizontal drainage of weak ground treatment.
6) Drainage in sports ground, golf course, airport, park and other greening places.
7) Drainage in coal depot, landfill waste site and fertilizer depot.
8) Drainage bedding of decompression.
9) Drainage system of underground irrigation of agriculture and gardening.
10) Drainage of roof garden.
11) Filtering material of sewage treatment.
The spec and property indexes of plastic ditch drainage:
Items | Square | Round | ||||||||
Type | YA7030 | YA1435 | YA1550 | YA1235 | YB60 | YB80 | YB100 | YB150 | YB200 | |
Exterior feet (mm≥) | 70*30 | 140*35 | 150*50 | 120*35 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 150 | 200 | |
Hollow feet (mm≥) | 40*10 | 40*10*2 | 40*10*2 | 40*10*2 | 25 | 45 | 55 | 80 | 120 | |
Weight (g/m≥) | 350 | 650 | 750 | 600 | 400 | 750 | 1000 | 1800 | 2900 | |
Voidage (%≥) | 82 | 82 | 85 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 84 | 85 | 85 | |
Compressive strength | Flattening 5% | 60 | 80 | 50 | 70 | 80 | 85 | 80 | 40 | 50 |
Flattening10% | 110 | 120 | 70 | 110 | 160 | 170 | 140 | 70 | 70 | |
Flattening15% | 150 | 160 | 125 | 130 | 200 | 220 | 180 | 100 | 90 | |
Flattening20% | 190 | 190 | 160 | 180 | 250 | 280 | 220 | 125 | 120 | |


- Q: What are the differences between geogrids and geocells in terms of installation?
- Geogrids and geocells differ in terms of installation primarily in the way they are placed and secured. Geogrids are generally unrolled and laid on the soil surface, then anchored with stakes or other means to prevent movement. On the other hand, geocells are typically assembled on-site, forming a three-dimensional honeycomb structure that is filled with soil or aggregate material. This assembly process requires connecting the individual cells together and often involves the use of clips or connectors. Overall, geocells require more labor and time for installation compared to geogrids.
- Q: Can geogrids be used in temporary construction access mats?
- Yes, geogrids can be used in temporary construction access mats. Geogrids are commonly used to improve the stability and load-bearing capacity of access mats, making them suitable for temporary construction sites. They help distribute the weight of heavy equipment and vehicles and prevent soil erosion, ensuring safe and efficient access for construction activities.
- Q: How much investment is needed for the grid cloth on the production site
- The application of the grid is more linked to the advertising industry, which is involved in the basic use of high-rise building wall advertising, due to the special characteristics of grid cloth material, more durable and more durable than the general fabric.
- Q: How do geogrids improve the performance of geotextile sediment retention systems?
- Geogrids improve the performance of geotextile sediment retention systems by providing additional reinforcement and stability to the system. They enhance the overall strength and load-bearing capacity of the geotextile, preventing soil erosion and retaining sediments more effectively. Geogrids also help distribute stress and load forces evenly, reducing the potential for geotextile failure or displacement. Ultimately, the inclusion of geogrids in sediment retention systems enhances their long-term performance and increases their effectiveness in controlling soil erosion and sediment migration.
- Q: What is the recommended geogrid aperture size?
- The recommended geogrid aperture size depends on various factors such as the specific application, soil conditions, and engineering requirements. It is best to consult with a geotechnical engineer or a specialist in geogrid design to determine the appropriate aperture size for a particular project.
- Q: How do geogrids improve the performance of geosynthetic-reinforced slopes in seismic zones?
- Geogrids improve the performance of geosynthetic-reinforced slopes in seismic zones by providing increased stability and reducing the potential for slope failure. These geosynthetic materials act as a reinforcement layer within the slope, distributing and dissipating the seismic forces more effectively. By enhancing the tensile strength and shear resistance of the slope, geogrids minimize the displacement and deformation during seismic events, thereby enhancing the overall stability and safety of the slope in seismic zones.
- Q: How do geogrids improve the performance of reinforced soil slopes in expansive soils?
- Geogrids improve the performance of reinforced soil slopes in expansive soils by providing additional tensile strength and stability. They act as a reinforcement layer, preventing soil movement and reducing the potential for slope failure. The geogrids distribute the loads evenly, minimizing stress concentration and enhancing the overall stability of the slope. Additionally, they help to control soil erosion and provide long-term durability, making reinforced soil slopes more resistant to the detrimental effects of expansive soils.
- Q: Building houses and roads require pipes and geotextile, grille?
- By stretching, the chain shaped molecules which are scattered in the original distribution are in a linear state, which improves the tensile strength and rigidity of the grid. Laying in the soil, through the mesh grille and soil interlock and interlock function, constitute an efficient stress transfer mechanism, so that local load can be quickly and effectively spread to a large area of soil, to reduce the local failure stress, to achieve the purpose of improving life.
- Q: Fiberglass grille price?
- Fiberglass geogrid 50KN, 2 yuan per squareFiberglass geogrid 80KN, 3.5 yuan per squareFiberglass geogrid 100KN, 4.5 yuan per squareFiberglass geogrid 30KN, 1.7 yuan per squareFiberglass geogrid 40KN, 1.9 yuan per square
- Q: What are the different types of geogrids?
- There are several types of geogrids, including uniaxial geogrids, biaxial geogrids, and triaxial geogrids. Uniaxial geogrids are designed to provide strength in one direction, typically used for reinforcement applications. Biaxial geogrids offer strength in both directions, making them suitable for applications such as soil stabilization and slope reinforcement. Triaxial geogrids have additional strength in the third dimension, making them ideal for applications involving heavy loads or high tensile forces.
Send your message to us
Geogrids Nptel Permeable Hard Geotube Drain Pipe for Drainage Ditch
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m
- Supply Capability:
- 150000 m/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords