Siemens Solar Inverter GW4200D-DI (High Frequency Isolated)
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
GW3000/3600/4200D-DI (High Frequency Isolated) is the new on-grid PV inverter which integrated with most advanced technology, come with 10 years warranty,
and are designed to meet the new IEE1547 requirements for the North American market. Also it’s suitable for thick-film modules.
Easy installation and simple operation make them ideal for residential and small-to-medium commercial applications.
GoodWe inverters, with ever-increasing efficiency and high stability,
could ensure you better overall performance of solar power systems and shorter payback periods.
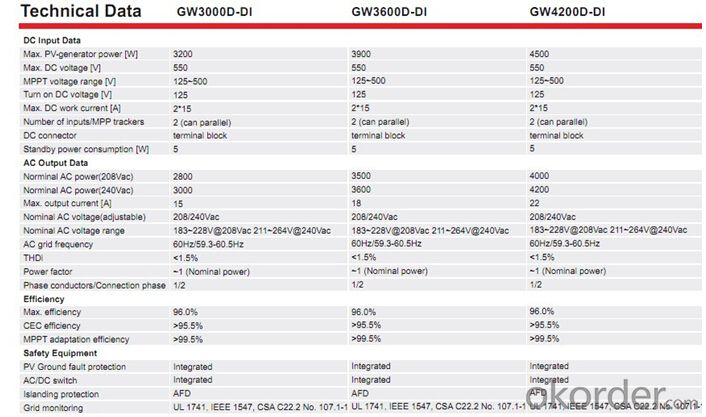
Datasheet
- Q: Can I connect solar panels directly to the grid without an inverter?
- No, you cannot connect solar panels directly to the grid without an inverter. An inverter is necessary to convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used by the electrical grid.
- Q: Are there any limitations on the number of solar panels that can be connected to a single inverter?
- The number of solar panels that can be connected to a single inverter is limited. Various factors, such as the inverter's power rating, the voltage and current ratings of the panels, and the system's configuration, determine the maximum number of panels that can be connected. In general, the inverter should be able to handle the combined power output of all the connected panels. If the panels generate more power than the inverter can handle, it can lead to inefficiencies, reduced performance, or damage to the inverter. Moreover, the panels' voltage and current ratings should be within the acceptable range of the inverter. If the panels exceed the inverter's safe limits, it can lead to overloading or malfunctioning. Furthermore, the configuration of the panels is also important in determining the limitations. Panels can be connected in series or parallel, each with its own requirements and limitations. The inverter must be compatible with the specific configuration used. To ensure proper functioning and optimal performance, it is advisable to refer to the manufacturer's guidelines and specifications for both the solar panels and the inverter. These guidelines provide information on the maximum number of panels that can be connected to a single inverter, as well as any other specific limitations or requirements to consider.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a solar-powered swimming pool heater?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a solar-powered swimming pool heater. A solar inverter is responsible for converting the direct current (DC) energy produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) energy that can be used to power appliances and devices. In the case of a solar-powered swimming pool heater, the solar panels generate DC energy from sunlight, which is then converted into AC energy by the solar inverter. This AC energy can be used to power the swimming pool heater and heat the pool water using solar energy.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different tracking algorithms?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different tracking algorithms. Inverters are designed to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for use in homes and businesses. They typically have the ability to integrate with various tracking algorithms that optimize solar panel performance by adjusting their position and angle according to the sun's movement. This flexibility allows for increased energy production and efficiency based on the specific tracking algorithm used.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle variations in solar irradiation?
- A solar inverter handles variations in solar irradiation by continuously monitoring the amount of sunlight received and adjusting the conversion of direct current (DC) power generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) power accordingly. It does this by employing maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms that optimize the power output from the panels, ensuring maximum efficiency regardless of the fluctuations in solar irradiation.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different solar panel brands?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different solar panel brands as long as they have compatible voltage and current ratings. However, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be installed indoors or outdoors?
- A solar inverter can be installed both indoors and outdoors. However, it is generally recommended to install it indoors to protect it from harsh weather conditions and extend its lifespan.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle voltage flicker?
- A solar inverter handles voltage flicker by regulating and stabilizing the voltage output. It detects any fluctuations in the grid voltage caused by flicker and adjusts the output accordingly to maintain a consistent and stable voltage for the connected solar panels or other electrical devices.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle voltage regulation?
- A solar inverter handles voltage regulation by converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that is suitable for use in our homes and businesses. It ensures that the voltage produced by the solar panels matches the voltage requirements of the electrical grid or the appliances connected to it. This is achieved through advanced electronics that monitor and adjust the voltage levels to maintain stability and efficiency in the power generation process.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with thin-film solar panels?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with thin-film solar panels. Thin-film solar panels have a different structure and composition compared to traditional crystalline silicon panels, but they still generate DC electricity that needs to be converted into AC for use in homes or businesses. A solar inverter is responsible for this conversion process, regardless of the type of solar panels used.
Send your message to us
Siemens Solar Inverter GW4200D-DI (High Frequency Isolated)
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























