H beam; structural steel;
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Product Description:
Specifications of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
1. Standard: GB700-88, Q235B2.
2. Grade: Q235, SS400 or Equivalent
3. Length: 6m,10m, 12m as following table
4. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
5.Payment: TT or L/C
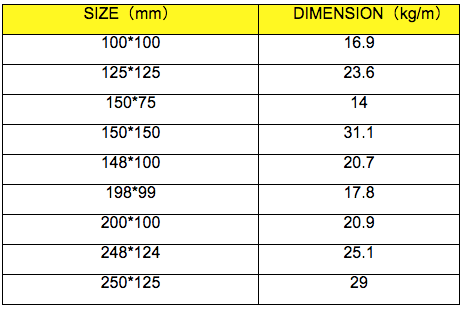
6. Sizes:
Usage & Applications of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
Commercial building structure ;Pre-engineered buildings; Machinery support structure; Prefabricated structure; Medium scale bridges; Ship-building structure. etc.
Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel
Production flow of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
- Q: What are the different types of coatings available for fire protection of steel H-beams?
- There are several types of coatings available for fire protection of steel H-beams, including intumescent coatings, cementitious coatings, and epoxy-based coatings. Intumescent coatings are often used as a passive fire protection measure, as they expand when exposed to high temperatures, forming a layer of insulating char that slows down the transfer of heat to the steel. Cementitious coatings, on the other hand, are typically applied in multiple layers and provide fire resistance by releasing water vapor when exposed to heat, creating a cooling effect. Epoxy-based coatings offer a combination of fire resistance and corrosion protection, as they form a protective film on the surface of the steel, reducing the risk of fire and preventing corrosion. The selection of the appropriate coating depends on factors such as the desired fire rating, environmental conditions, and aesthetic considerations.
- Q: Can steel H-beams be used in museum storage or archive facilities?
- Yes, steel H-beams can be used in museum storage or archive facilities. These beams are commonly used in construction due to their strength and durability. In museum storage or archive facilities, where heavy loads need to be supported, steel H-beams can provide the necessary structural strength and stability. Additionally, they can be easily integrated into the facility's infrastructure to create storage systems and shelving units.
- Q: What are the cost implications of using steel H-beams?
- The cost implications of using steel H-beams can vary depending on various factors. Firstly, the cost of steel H-beams themselves can significantly impact the overall project budget. Steel is a widely used construction material due to its strength and durability, but it can be more expensive compared to other materials like wood or concrete. The price of steel H-beams is influenced by factors such as market demand, supply chain dynamics, and global economic conditions. Additionally, the size and dimensions of the H-beams can affect their cost. Larger and heavier H-beams will generally be more expensive as they require more steel material and may require specialized handling and transportation. Furthermore, the cost implications of using steel H-beams extend beyond the material itself. Considerations such as fabrication, installation, and maintenance expenses should also be taken into account. Fabrication costs usually include cutting, welding, and shaping the steel beams according to the project's specifications. Installation costs involve labor, equipment, and any necessary support structures. Finally, ongoing maintenance costs should be factored in, as steel requires periodic inspections, painting, and potential repairs to ensure its longevity. However, it's essential to consider the long-term benefits of using steel H-beams. Their high strength-to-weight ratio and durability make them a reliable choice for structural applications. Steel H-beams have a longer lifespan compared to other materials, reducing the need for frequent replacements or repairs. This can result in cost savings over time, as the initial investment in steel H-beams can offset the expenses associated with maintenance and replacement in the future. Ultimately, the cost implications of using steel H-beams should be evaluated in the context of the specific project requirements, budget constraints, and long-term considerations. Consulting with professionals in the construction industry, such as engineers or contractors, can provide a more accurate assessment of the cost implications and help make informed decisions.
- Q: What are the typical applications of steel H-beams?
- Steel H-beams are commonly used in construction and structural engineering for various applications. They are widely used in building frameworks, bridges, and platforms, providing support and stability in heavy load-bearing structures. H-beams are also utilized in the construction of industrial buildings and warehouses, as well as in the manufacturing and automotive industries for the fabrication of machinery and equipment. Additionally, they find application in the construction of high-rise buildings, stadiums, and infrastructure projects, where their strength and durability are essential for withstanding heavy loads and structural integrity.
- Q: Can steel H-beams be used for residential garages?
- Yes, steel H-beams can be used for residential garages. They are commonly used in construction for their strength and durability, making them suitable for supporting the weight of a garage structure.
- Q: What are the dimensions of a steel H-beam?
- The dimensions of a steel H-beam can vary depending on the specific design and manufacturer. However, in general, H-beams are characterized by their height, width, and weight per foot. The height of an H-beam refers to the vertical distance from the top to the bottom flange, while the width is the horizontal distance between the two flanges. The weight per foot indicates the amount of steel used in a linear foot of the beam. These dimensions can vary widely depending on the intended use and load-bearing requirements.
- Q: What is the weight of a steel H-beam?
- The size and dimensions of a steel H-beam can cause variations in its weight. Typically, standard H-beams weigh between 33 pounds per foot and 330 pounds per foot. The weight is influenced by the beam's height, width, and thickness. To obtain an accurate weight measurement, knowledge of the precise dimensions of the H-beam under consideration is essential.
- Q: How do steel H-beams perform in vibration-prone environments?
- Steel H-beams perform well in vibration-prone environments due to their high structural integrity and stiffness. The unique H-shape design offers excellent resistance against bending and torsional forces, minimizing the risk of structural failure or excessive vibrations. Additionally, steel beams have a high natural frequency, which helps absorb and dissipate vibrations, ensuring a stable and safe structure in such environments.
- Q: How do steel H-beams perform in areas with high levels of wind or hurricane force?
- Steel H-beams perform exceptionally well in areas with high levels of wind or hurricane force. Due to their robust structural design, they offer superior strength and resistance against strong winds and extreme weather conditions. The H-shape of the beams allows for efficient distribution of forces, making them highly reliable in maintaining structural integrity during severe storms. As a result, steel H-beams are widely used in construction projects located in hurricane-prone regions to ensure the safety and durability of buildings.
- Q: How do steel H-beams contribute to the overall cost-effectiveness of a project?
- Steel H-beams provide several benefits that contribute to the cost-effectiveness of a project. Firstly, they possess exceptional strength and durability, resulting in minimal maintenance and a long lifespan. This decreases the need for frequent repairs or replacements, leading to cost savings over time. Furthermore, steel H-beams are significantly lighter compared to alternative construction materials like concrete or timber, making transportation and on-site handling easier and cheaper. Consequently, this can reduce labor costs and shorten construction times, ultimately saving money in the overall project budget. In addition, steel H-beams can be prefabricated off-site, enhancing precision and efficiency during the construction process. This reduces the likelihood of errors and wastage, resulting in cost savings in terms of materials and labor. Moreover, steel is an environmentally sustainable material. It can be fully recycled, allowing for repurposing or recycling at the end of its lifespan. This reduces waste and minimizes the project's environmental impact, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable construction practices. It can also lead to potential cost savings through incentives or tax benefits. Overall, incorporating steel H-beams into a construction project offers various cost-effective advantages. Their strength, durability, and low maintenance requirements ensure long-term cost savings, while their lightweight nature and prefabrication capabilities reduce transportation and labor costs. Additionally, the sustainability of steel contributes to potential financial benefits.
Send your message to us
H beam; structural steel;
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























