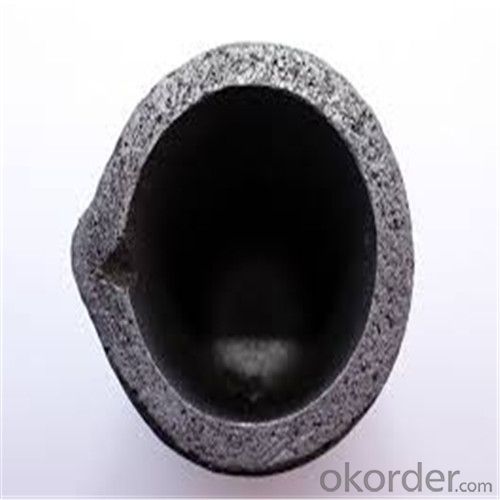
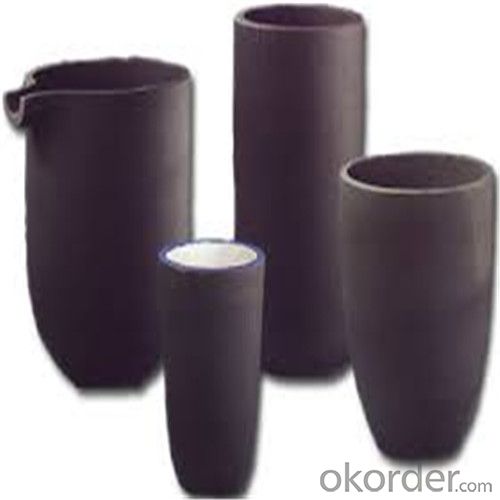
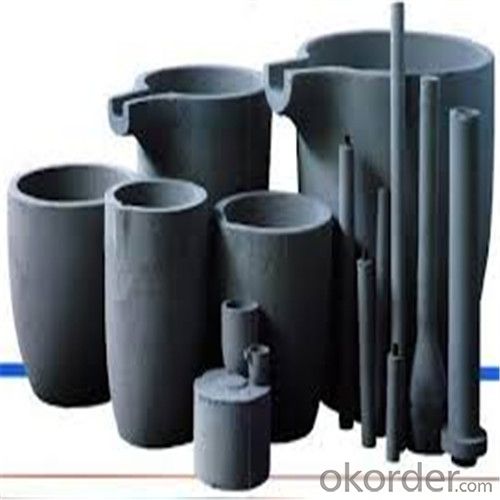
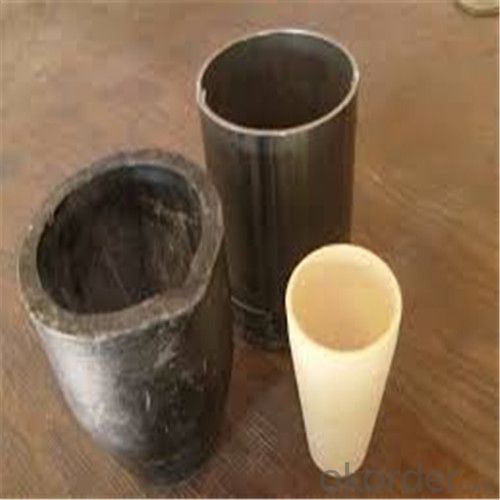
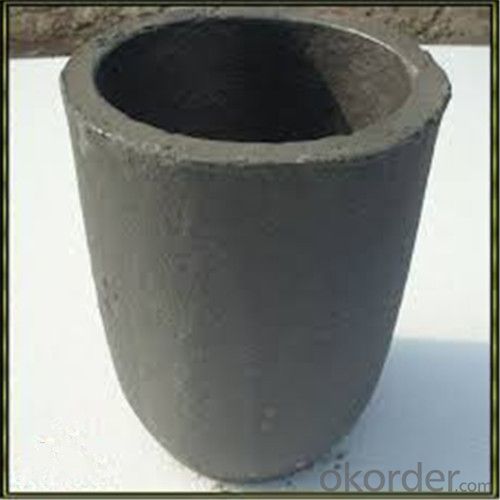
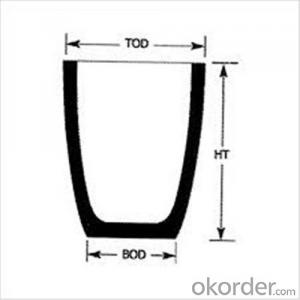
Graphite Crucible Price for SIC Crucibles Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass, Clay Graphite Crucible
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
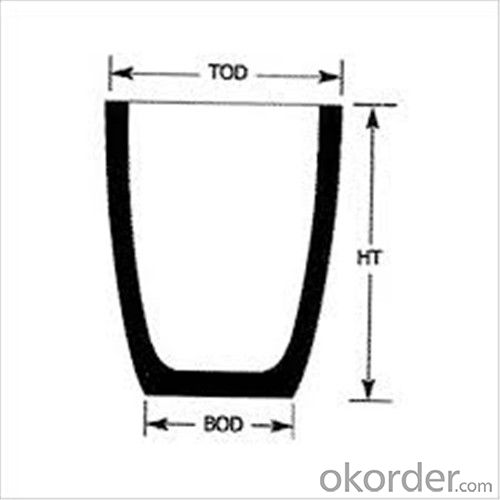

Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
- Q: Are graphite crucibles suitable for melting composite propellants?
- Yes, graphite crucibles are suitable for melting composite propellants. Graphite is known for its high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical reactions, making it an ideal material for containing and heating composite propellants during the melting process.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting refractory metals?
- Absolutely! When it comes to melting refractory metals, graphite crucibles are the way to go. The reason being is that graphite possesses exceptional thermal conductivity and a remarkably high melting point, which renders it ideal for applications involving high temperatures. Take refractory metals like tungsten, molybdenum, and niobium for instance; these metals boast extraordinary melting points and can effortlessly withstand the temperatures achieved within a graphite crucible. Moreover, graphite exhibits minimal reactivity with most metals, thereby making it a suitable material for securely housing and melting refractory metals without any risk of contamination. However, it is of utmost importance to select a top-notch graphite crucible that is specifically engineered for melting refractory metals in order to ensure optimal performance and durability.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting and casting of non-ferrous metals?
- Graphite crucibles are capable of being utilized in the process of melting and casting non-ferrous metals. Within various industries, including foundries and metalworking, graphite crucibles are highly prevalent due to their exceptional thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high temperatures. Non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum, copper, zinc, and gold, possess lower melting points when compared to iron and steel, thus rendering them appropriate for melting within graphite crucibles. The superior thermal conductivity of graphite ensures the even distribution of heat throughout the crucible, thereby facilitating the efficient melting and casting of non-ferrous metals. Furthermore, graphite crucibles exhibit commendable chemical resistance and minimal reactivity with non-ferrous metals, thereby further enhancing their suitability for this particular application. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that graphite crucibles may not be suitable for certain metals that are reactive or corrosive, as they have the potential to react with graphite and adversely impact the quality of the casting.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for powder metallurgy?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for powder metallurgy. Graphite is an excellent material for high-temperature applications and is commonly used in powder metallurgy processes. Graphite crucibles have a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity, making them ideal for melting and holding metal powders during sintering or melting processes. Additionally, graphite crucibles have good chemical resistance, allowing them to withstand the corrosive effects of certain metal powders. Overall, graphite crucibles are a reliable and efficient choice for powder metallurgy applications.
- Q: You solved it. What happens if a quartz crucible is coated with a graphite crucible?
- The graphite crucible will burn on an alcohol burner, and the quartz crucible may cause cracks due to uneven heat.
- Q: Are graphite crucibles suitable for melting alloys with low melting points?
- Yes, graphite crucibles are suitable for melting alloys with low melting points. Graphite has a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to withstand high temperatures and efficiently transfer heat to the alloy. Additionally, graphite is chemically inert and does not react with most metals, making it an ideal choice for melting low melting point alloys.
- Q: What are the different methods of preventing graphite crucible leakage?
- To prevent graphite crucible leakage, there are various approaches that can be utilized. To begin with, ensuring the crucible is properly prepared and installed is essential. This involves thoroughly cleaning the surfaces of the crucible and the lid or cover that it mates with. By eliminating any dirt or debris, a tighter seal can be achieved. Additionally, applying a thin layer of graphite lubricant or a high-temperature sealant to the mating surfaces can aid in creating a more secure seal, thus preventing leakage. Another effective method is the utilization of gaskets or O-rings between the crucible and the lid. These gaskets, typically composed of materials like graphite, ceramic fiber, or metal, are designed to provide a reliable seal. Placing the gasket between the crucible and the lid establishes a barrier, effectively preventing any molten metal or other substances from escaping. Proper tightening of the crucible lid or cover is also crucial in preventing leakage. Excessive tightening can lead to damage and subsequent leaks, while insufficient tightening can result in a loose seal. Adhering to the manufacturer's recommended torque specifications for the lid or cover is imperative to ensure a proper seal. In addition, regular inspection and maintenance of the crucible play a vital role in preventing leakage. Promptly addressing any signs of cracks, chips, or deterioration is essential, as these issues can compromise the crucible's integrity. By either replacing damaged crucibles or carrying out timely repairs, the risk of leakage can be minimized. Furthermore, proper handling and usage of the crucible contribute significantly to leakage prevention. Avoiding sudden temperature changes, thermal shocks, and excessive mechanical stresses can help prolong the crucible's lifespan and maintain its integrity. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's recommended operating procedures and guidelines to ensure the crucible remains intact and leakage-free. In conclusion, by implementing these methods - proper preparation and installation, utilization of gaskets or O-rings, correct lid tightening, regular inspection and maintenance, and appropriate handling - leakage in graphite crucibles can be effectively prevented, guaranteeing a safe and efficient operation.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for ceramic glazing?
- No, a graphite crucible is not suitable for ceramic glazing. Ceramic glazes require high firing temperatures that can cause the graphite crucible to degrade or react with the glaze materials, leading to contamination and poor results. It is recommended to use a crucible made from materials like alumina or porcelain for ceramic glazing.
- Q: Why graphite and diamond is composed of carbon graphite, but not light, is black, and the diamond is urgently in light!
- Simply speaking, the structure is different, so the nature of the expression is different
- Q: Will a graphite crucible conduct electricity?Soluble aluminum material with electric iron stove appearance
- High temperature resistance: Graphite resistance to high temperature about 2300, even after the ultra-high temperature arc ignition, the weight loss is very small, the thermal expansion coefficient is very small. The strength of graphite increases with the temperature, and at 2000 degrees, the graphite strength doubled
Send your message to us
Graphite Crucible Price for SIC Crucibles Melting Aluminium, Copper, Brass, Clay Graphite Crucible
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords