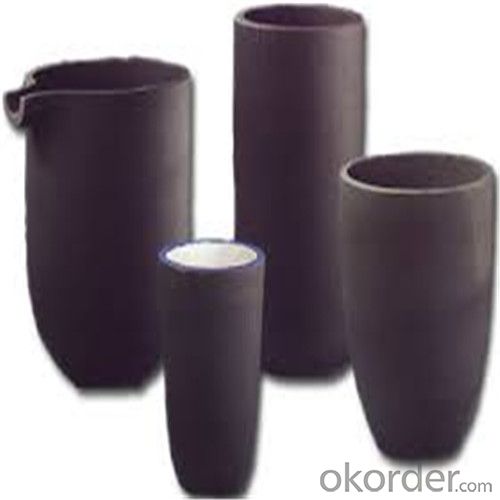
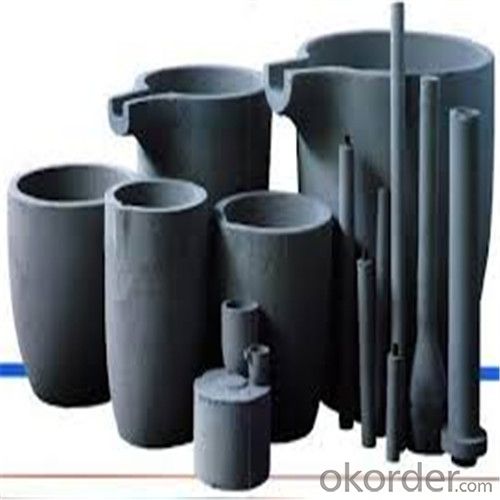
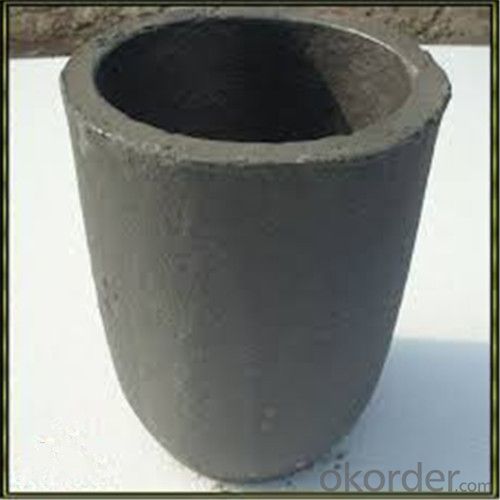
Graphite Crucible for Sale Near Me - SIC Crucibles for Melting Aluminium, Copper, and Brass with High Heat Resistance
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles
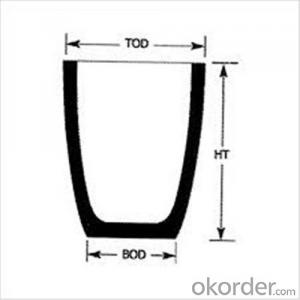
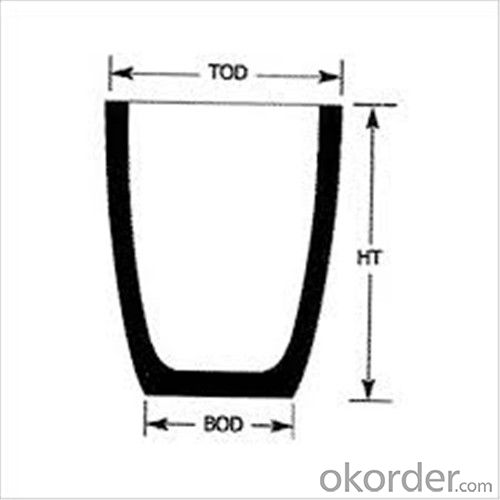
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
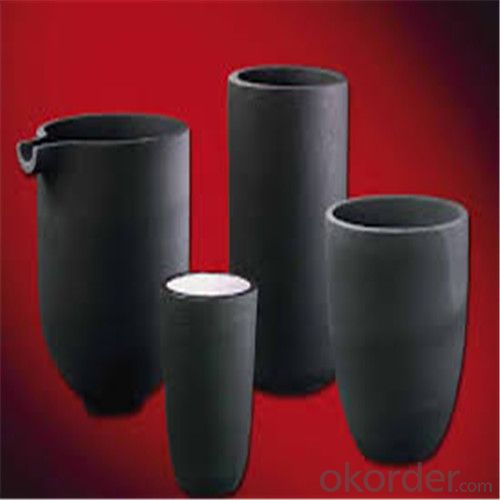

Features of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
1. resistance to deformation at high temperature,
2. thermal shock resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance.
3. anti-oxidation, anti- erosion.
Usage of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
electricity and steel slag trench,
coal chemical and mining transport pipeline.
- Q: How is a graphite crucible disposed of at the end of its life?
- At the end of its life, a graphite crucible can be disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner. Since graphite is a non-toxic material, it can be recycled or reused rather than being sent to a landfill. There are several options for disposing of a graphite crucible: 1. Recycling: Graphite crucibles can be recycled by specialized recycling facilities. The graphite is typically melted down and purified to be used in the production of new graphite products. This helps conserve natural resources and reduces the need for new graphite extraction. 2. Reuse: If the crucible is still in good condition, it can be reused for its original purpose or repurposed for other applications. Many industries, such as metallurgy, ceramics, and jewelry making, can benefit from using second-hand graphite crucibles. This not only saves money but also reduces waste. 3. Donation: Another option is to donate the graphite crucible to educational institutions or research facilities. These organizations often require such equipment for experiments and studies. By donating, you extend the life of the crucible and contribute to scientific advancements. 4. Local regulations: It is essential to adhere to local regulations regarding the disposal of graphite crucibles. Some areas may have specific rules for the disposal of industrial equipment. It is advisable to consult with local waste management authorities or recycling centers to ensure compliance with regulations. Regardless of the disposal method chosen, it is crucial to handle the graphite crucible safely. Clean any residue or contaminants from the crucible before disposal, and follow any specific instructions provided by the manufacturer. By responsibly disposing of graphite crucibles, we can minimize environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
- Q: What are the different methods of controlling temperature in a graphite crucible?
- There are several methods of controlling temperature in a graphite crucible, including the use of external heating sources such as gas burners or electric heaters, the addition of insulating materials to regulate heat transfer, and the implementation of temperature sensors and controllers to maintain a specific temperature range. Additionally, techniques like preheating the crucible or adjusting the gas flow rate can also impact and control the temperature inside the crucible.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for semiconductor manufacturing?
- No, graphite crucibles cannot be used for semiconductor manufacturing. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in industries such as metallurgy and foundries for melting and casting metals due to their high thermal conductivity and resistance to high temperatures. However, in semiconductor manufacturing, the requirements are quite different. Semiconductor manufacturing involves highly controlled and precise processes, where contamination is a major concern. Graphite crucibles release carbon particles that can contaminate the semiconductor materials and affect their performance. Therefore, semiconductor manufacturing typically requires crucibles made from materials such as quartz or ceramic, which have low contamination levels and can withstand the high temperatures and chemical environments involved in the fabrication processes.
- Q: What are the main changes in graphene supercapacitors?
- What are the main changes in graphene supercapacitors?"
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for carbon and graphite production?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for carbon and graphite production. Graphite crucibles are specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and are commonly used in various industries, including carbon and graphite production. They provide a stable and reliable container for melting and refining carbon and graphite materials.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for melting steel?
- No, a graphite crucible cannot be used for melting steel. Graphite has a relatively low melting point (around 3,600 degrees Fahrenheit or 2,000 degrees Celsius), while steel requires much higher temperatures to melt (around 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit or 1,370 degrees Celsius). Thus, using a graphite crucible would result in the crucible itself melting before achieving the desired temperature to melt the steel. For melting steel, a crucible made of materials with higher melting points, such as clay-graphite or silicon carbide, would be more suitable.
- Q: Are there any alternative materials to graphite for crucibles?
- Yes, there are alternative materials to graphite for crucibles. Some common alternatives include silicon carbide, alumina, zirconia, and boron nitride. These materials are often preferred for their specific properties and applications. For example, silicon carbide exhibits excellent thermal conductivity and high mechanical strength, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Alumina, on the other hand, is known for its chemical inertness and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for handling reactive materials. Zirconia offers good thermal shock resistance and is often used in applications requiring rapid temperature changes. Lastly, boron nitride is preferred for its excellent thermal stability and lubricity. Each of these alternative materials has its own advantages and specific uses, making them viable options for crucibles depending on the specific requirements of the application.
- Q: How do you prevent graphite crucibles from thermal expansion-related issues?
- To prevent graphite crucibles from thermal expansion-related issues, one can use a technique called preheating. By gradually heating the crucible to the desired temperature before adding any material, the expansion is minimized, reducing the risk of cracking or warping. Additionally, proper cooling methods, such as controlled cooling or using an annealing process, can help alleviate thermal stress and extend the lifespan of the crucible.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for melting nickel?
- Indeed, nickel can be melted using graphite crucibles. These crucibles find widespread usage in high-temperature scenarios, such as the melting of different metals and alloys. Graphite boasts exceptional thermal conductivity and can endure extreme temperatures, rendering it an apt choice for melting nickel, which liquefies at approximately 1,455 degrees Celsius (2,651 degrees Fahrenheit). Furthermore, graphite crucibles exhibit commendable chemical resistance and do not undergo any reaction with nickel, thus facilitating a pristine and productive melting operation.
- Q: What material of graphite is used in arc furnace production?
- Today, large diameter semi graphitic carbon electrodes have been adopted in industrial silicon electric furnaces. Can effectively save production costs, and the technology is relatively mature.
Send your message to us
Graphite Crucible for Sale Near Me - SIC Crucibles for Melting Aluminium, Copper, and Brass with High Heat Resistance
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords