Cyanuric Acid 98.5% Granular High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 17 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1800 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Cyanuric Acid
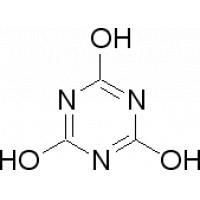
Structure of Cyanuric Aicd Descriptions:
Trade Name: Isocyanuric Acid
Other name: Cyanuric Acid; 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triol
Uses: Bleaches and sanitisers.
Formula: C3H3N3O3
Molecular Weight: 129.07
CAS NO.: 108-80-7
Main Feautrues of Cyanuric Acid
White powder, granular or colored tablet form, non-toxic and odorless
Cyanuric Acid Image:

Cyanuric Acid Specification:
| ITEM | SPECIFICATION | RESULT | |||
| Content | ≥98.5% | 98.64% | |||
| Moisture | ≤0.5% | 0.11% | |||
| PH value | 4.0-4.5 | 4.26 | |||
| Fe2+ | ≤15ppm | 7.5ppm | |||
| NH4+ | ≤200ppm | 97ppm | |||
| Ash | ≤0.1% | 0.05% | |||
| Insoluble matter in DMF | ≤0.3% | 0.25% | |||
| Appearance | White crystalline power | White crystalline power | |||
| Mesh number | 95% pass 80 mesh | 95% pass 80 mesh | |||
| White degree | ≥89 | 90.5 | |||
| Conclusion: | The product complies with the standard above. | ||||
Packing:
in 25kg, 1000kg bag for powder
in 25kg plastic bag or 50kg PE drums for granular


Storage:
kept in a light-proof,well-colsed,dry and cool place.
- Q: What is the superiority of the catalyst compared to the stoichiometric reagent?
- Specificity: an enzyme can only catalyze one or a class of substrates, such as proteases that catalyze the hydrolysis of proteins into polypeptides;
- Q: Chemical production of iodine and magnesium with water as catalyst!
- In the 250mL three bottles were equipped with spherical condenser and constant pressure dropping funnel, in the condensate tube connected to the anhydrous calcium chloride drying tube. The flask was placed with 1.5 g of magnesium chip and a small tablet of iodine, 10 g of bromobenzene and 30 mL of anhydrous ether were mixed in a constant pressure dropping funnel. First 1/4 of the mixture into the flask, a few minutes later see the magnesium surface of the bubble generated, the solution was slightly cloudy, iodine color began to disappear. If no reaction occurs, use a hot water bath. After the start of the reaction, stir, slowly dropping the remaining bromophene ether solution, dropping the rate to keep the solution was slightly boiling state, after adding, in the water bath to continue reflow 0.5h, magnesium tablets full effect.
- Q: How does catalyst aid a chemical reaction?
- A catalyst will change the activation time; in a faster way. Hence the reaction will worke quicker. It is kind of like Nitrous in a car. It speeds up the engine, which would be kind of comparabale to two substances.
- Q: Chemical equation if there is a catalyst and heating, which write in the equal sign above, which written in the following? Tomorrow academic level test, solution
- At the same time, the catalyst is heated
- Q: What is chemical adsorption and its relationship with heterogeneous catalysis
- The catalytic cycle includes five steps: diffusion, chemical adsorption, surface reaction, desorption and reverse diffusion.The chemical adsorption is an important part of the heterogeneous catalysis process, and the adsorption of the reactants on the catalyst surface,
- Q: What is the quality of the catalyst in the chemical reaction, for example, 34.3 g before the hydrogen peroxide reaction, 32.7 g after the reaction, and how much is the catalyst mass?
- You can not calculate this question, the quality of the catalyst before and after the same reaction, how much reaction before the reaction on how much
- Q: Where are they good catalysts and why?? THanks!
- A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by providing an alternate reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Catalysts appear not to take part in the reaction. Frequently, catalysts are not very reactive. Acids and bases, on the other hand, are very reactive. Acids (as H+) and bases ( as OH-) sometimes function as catalysts in some organic reactions. They appear to be catalysts because in the course of the mechanism H+ or OH- is regenerated.
- Q: what is a catalyst?
- A catalyst is a substance that increase the rate of chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical changeb
- Q: What are the catalysts?
- The catalyst is a substance that can change the rate of the reaction without changing the standard of the reaction Gibbs free, according to the definition of the International Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) in 1981, Enthalpy change. This action is called catalysis. The reaction involving the catalyst is a catalytic reaction. The catalyst will induce a chemical reaction to change, causing the chemical reaction to become faster or slower or to undergo a chemical reaction at a lower temperature The catalyst is also known as a catalyst in industry, and the composition, chemical properties and quality of the catalyst itself do not change before and after the reaction;
- Q: Nitrogen and hydrogen in the role of high temperature and pressure catalyst to generate ammonia chemical equation
- N2 + 3H2 = catalyst, high temperature and high pressure = 2NH3
Send your message to us
Cyanuric Acid 98.5% Granular High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 17 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1800 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches