Carbon Steel Hot Rolled Wire Rod SAE1008
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
OKorder is offering Wire Rod at great prices with worldwide shipping. Our supplier is a world-class manufacturer of steel, with our products utilized the world over. OKorder annually supplies products to European, North American and Asian markets. We provide quotations within 24 hours of receiving an inquiry and guarantee competitive prices.
Product Applications:
After hot-rolled the products shaped into coil and delivery as finished product, including round, square, rectangular, hexagonal and so on. Since most of the products are round, it is generally called wire rod. Carbon steel wire rod is widely used in construction and manufacturing. Carbon steel wire rod is mainly used for reinforcement of reinforced concrete and welded structure or reprocessed (roberts , nail, etc.) materials, especially used to produce wire drawing, welding electrode, nails, spring, electronic, precise machinery parts and so on.
Product Advantages:
OKorder's Wire Rod are durable, strong, and resist corrosion.
Main Product Features:
· Premium quality
· Prompt delivery & seaworthy packing (30 days after receiving deposit)
· Corrosion resistance
· Can be recycled and reused
· Mill test certification
· Professional Service
· Competitive pricing
Product Specifications:
Steel Grade: Q195/235, SAE1006-1018B Standard: ASTM, GB
Diameter: 5.5mm, 6.5mm, 7mm,8mm,9mm,10mm,12mm,14mm
Type: in coil, coil weight around 2MT Alloy or Not: Alloy
Surface: round, no twisted, light and smooth Chemical Composition: (Please kindly find our chemistry of our material based on Q195、Q235A and Q235B as below for your information)
Grade | Chemical Composition (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | B | |
SAE1008B | 0.10max | 0.32max | 0.045max | 0.040max | 0.30max | 0.0008min |
Mechanical properties | ||||||
Yield strength(N/mm2) | Tensile strength(N/mm2) | Elongation (%) | ||||
≥195 | 350-380 | ≥32 | ||||
Packaging & Delivery of Wire Rod SAE1008B:
Packaging Detail: products are packed in coil and then shipped by container or bulk vessel
Each coil weight: 2-3MT
Delivery Detail: within 45 days after received deposit or LC.
Label: to be specified by customer, generally, each bundle has 1-2 labels
Trade terms: CFR, CIF
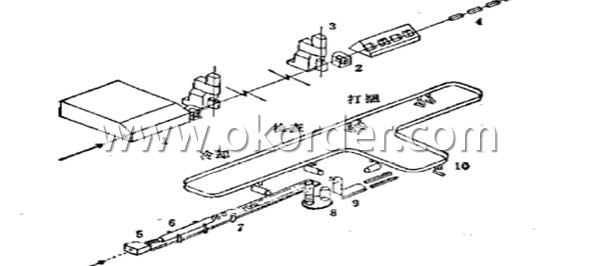
1-Furnace 2-Roughing Mill 3-High-speed Finishing Mill 4-Water-cooled Device 5-Coiling Device
6-Cooling Device 7-Chain Conveyer 8-Spool Collecting Device 9-Spool Down Device 10-Hook Conveyer
FAQ:
Q1: How soon can we receive the product after purchase?
A1: Within three days of placing an order, we will begin production. The specific shipping date is dependent upon international and government factors, but is typically 7 to 10 workdays.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q3: Can stainless steel rust?
A3: Stainless does not "rust" as you think of regular steel rusting with a red oxide on the surface that flakes off. If you see red rust it is probably due to some iron particles that have contaminated the surface of the stainless steel and it is these iron particles that are rusting. Look at the source of the rusting and see if you can remove it from the surface.
Images:


- Q: What are the different mechanical testing methods used for steel wire rod?
- The quality and performance of steel wire rod can be assessed through several commonly used mechanical testing methods. These methods include: 1. Tensile testing, which measures the ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation of the wire rod by applying a pulling force until it breaks. This test helps determine the wire rod's ability to withstand stretching or pulling forces without breaking. 2. Hardness testing, which evaluates the wire rod's resistance to indentation or penetration by a hard object. Different hardness testing methods, such as Brinell, Rockwell, and Vickers, can be used to measure the wire rod's strength and durability. 3. Bend testing assesses the wire rod's ability to withstand bending forces without failure by bending it to a specified angle and examining it for cracks or fractures. This is important for applications requiring flexibility or resistance to deformation. 4. Fatigue testing evaluates the wire rod's resistance to repeated loading and unloading cycles, which it often experiences during its service life. This test helps determine its endurance limit, fatigue strength, and fatigue life, ensuring its reliability in applications with dynamic or cyclic loads. 5. Impact testing measures the wire rod's ability to absorb energy and resist fracture under high-velocity loading. This is crucial for applications involving machinery or structural components that may encounter sudden impact or shock loads. By utilizing these various mechanical testing methods, manufacturers and users of steel wire rod can guarantee its quality, performance, and suitability for specific applications.
- Q: What are the different production processes involved in steel wire rod manufacturing?
- The manufacturing of steel wire rods involves several production processes. These processes are crucial in transforming raw materials into the final product. Here are the different production processes involved in steel wire rod manufacturing: 1. Ironmaking: The steel wire rod manufacturing process begins with ironmaking. Iron ore is extracted and processed in a blast furnace to produce pig iron. The pig iron is then further refined to remove impurities and create steel. 2. Steelmaking: In the steelmaking process, the pig iron is melted in a furnace and alloyed with various elements such as carbon, manganese, and silicon to achieve the desired steel properties. This process ensures that the steel meets the specific requirements of wire rod production. 3. Continuous Casting: After steelmaking, the molten steel is cast into billets or blooms using continuous casting technology. This process involves pouring the molten steel into a water-cooled mold to solidify it into a specific shape. For wire rod production, the billets are typically cast in a square cross-section. 4. Hot Rolling: The next step is hot rolling, where the billets are reheated and passed through a series of rolling mills. These rolling mills reduce the billets' cross-sectional area and elongate them into wire rod form. The hot rolling process improves the mechanical properties and surface finish of the wire rods. 5. Cooling: Once the wire rods are hot rolled, they undergo a cooling process to achieve the desired properties. Cooling can be done through air cooling or water spray cooling, depending on the specific requirements of the wire rods. 6. Surface Treatment: After cooling, the wire rods undergo surface treatment processes such as pickling or coating. Pickling involves removing any scale or oxide on the surface of the wire rods using acid solutions. Coating may involve applying a protective layer to prevent corrosion or improve the wire rods' performance in specific applications. 7. Inspection and Quality Control: Throughout the manufacturing process, the wire rods undergo rigorous inspection and quality control measures. This ensures that the wire rods meet the required standards and specifications. Various tests, such as tensile strength, elongation, and dimensional checks, are conducted to ensure the quality of the wire rods. 8. Packaging and Delivery: Finally, the wire rods are packaged according to customer requirements and prepared for delivery. They may be bundled, coil-wound, or packaged in other forms, depending on the customer's needs. The wire rods are then transported to the customers, where they can be further processed or used in various applications. These production processes play a vital role in the manufacturing of steel wire rods, ensuring that they meet the required specifications and are suitable for different applications in industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
- Q: How is steel wire rod used in the manufacturing of wire for agricultural fencing?
- Steel wire rod is used in the manufacturing of wire for agricultural fencing by being drawn through a series of dies to reduce its diameter and increase its length. This process, known as wire drawing, results in a strong and durable wire that is then woven or welded into the desired fencing shape. The high tensile strength of steel wire rod ensures that the agricultural fencing can withstand the pressure and stress it may encounter in outdoor environments, making it an ideal material for securing livestock and crops.
- Q: What are the advantages of using steel wire rods in construction?
- There are several advantages of using steel wire rods in construction. Firstly, steel wire rods are incredibly strong and durable. They have a high tensile strength, which means they can withstand heavy loads and resist deformation, making them ideal for structural applications. This strength also ensures the longevity of the construction, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Secondly, steel wire rods are highly flexible, allowing them to be easily shaped and bent to fit various construction designs and requirements. This flexibility enables architects and engineers to create intricate and innovative structures while ensuring structural integrity. Furthermore, steel wire rods have excellent corrosion resistance properties. They are often galvanized or coated with protective layers to prevent rust and corrosion, enhancing their lifespan and reliability in harsh environmental conditions. This resistance to corrosion also makes them suitable for use in coastal or high-humidity areas where other materials may deteriorate over time. In addition, steel wire rods are cost-effective. They are readily available, making them cost-efficient compared to other construction materials. Their versatility and ease of installation also contribute to reducing labor and construction costs. Another advantage of steel wire rods is their eco-friendliness. Steel is a highly recyclable material, and using steel wire rods in construction helps conserve natural resources and reduce waste. Additionally, steel structures can be disassembled and reused, reducing the environmental impact associated with construction activities. Lastly, steel wire rods are fire-resistant, providing an added layer of safety in buildings. Steel does not burn or contribute to the spread of fire, which is crucial in preventing the loss of life and property during fire incidents. Overall, the advantages of using steel wire rods in construction are their strength, flexibility, corrosion resistance, cost-effectiveness, sustainability, and fire resistance. These qualities make them a preferred choice for various construction applications and contribute to the overall quality and longevity of the structures.
- Q: What are the different types of steel wire rod coatings used for lubrication?
- Different types of coatings are utilized to lubricate steel wire rods, each possessing distinct properties and advantages. Some commonly employed coatings are as follows: 1. Zinc Coating: Zinc coatings are extensively used for lubrication due to their exceptional corrosion resistance. Acting as a sacrificial layer, they shield the underlying steel wire rod from rust and other forms of corrosion. Moreover, zinc coatings can also serve as lubricants, reducing friction between the wire rod and other surfaces. 2. Phosphate Coating: Prior to applying other lubricant coatings, phosphate coatings are frequently utilized as pre-treatments. These coatings generate a layer of phosphate crystals on the wire rod's surface, enhancing the adhesion of subsequent lubricant coatings. Phosphate coatings also enhance the wire rod's resistance to wear and provide a smooth surface for superior lubrication. 3. Polymer Coating: Polymer coatings, composed primarily of synthetic polymers like polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or polyamide, are commonly employed for lubrication purposes. These coatings possess excellent friction-reducing properties. They establish a low-friction surface that diminishes wear and tear, prolongs the wire rod's lifespan, and enhances its performance in various applications. 4. Wax Coating: Wax coatings are a favored choice for lubricating steel wire rods. Typically formulated with natural or synthetic waxes, they are applied through dipping or spraying methods. Wax coatings furnish a protective layer that reduces friction, prevents rust, and enhances the wire rod's handling during manufacturing and processing. 5. Oil Coating: Oil coatings are frequently used to temporarily lubricate steel wire rods during storage and transportation. These coatings are usually applied as a thin layer of oil, offering immediate lubrication and corrosion protection. Oil coatings are easily applied and can be effortlessly removed prior to further processing or use. It is crucial to note that the selection of a specific coating depends on various factors, including the desired level of lubrication, corrosion resistance, and the specific application of the wire rod. Manufacturers take into account considerations such as cost, performance requirements, and environmental factors when deciding on the appropriate coating for steel wire rods.
- Q: What are the different alloys used in steel wire rod production?
- There are several different alloys that are commonly used in steel wire rod production, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. Each alloy has its own unique properties and characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications. Carbon steel is the most common alloy used and offers excellent strength and durability. Stainless steel is corrosion-resistant and often used in environments where rusting is a concern. Alloy steel, on the other hand, is a combination of different metals and offers enhanced strength and wear resistance.
- Q: What are the common industry associations for steel wire rod?
- The common industry associations for steel wire rod include the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI), the Steel Manufacturers Association (SMA), and the International Wire & Machinery Association (IWMA).
- Q: How does the dimensional accuracy of steel wire rod vary with different heat treatment processes?
- Different heat treatment processes can result in varying dimensional accuracy for steel wire rods. Heat treatment involves subjecting the wire rod to controlled heating and cooling procedures that alter its physical and mechanical properties. One commonly used heat treatment process for steel wire rods is annealing. Annealing involves heating the wire rod to a specific temperature and then gradually cooling it. This process helps alleviate internal stresses, enhance ductility, and refine the grain structure of the steel. In terms of dimensional accuracy, annealing can minimize internal stresses that may lead to distortion or warping in the wire rod, resulting in improved dimensional stability. Another heat treatment process is quenching and tempering. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the wire rod after heating it to a high temperature, typically using a liquid like oil or water. This rapid cooling hardens the steel, making it stronger but also more brittle. To enhance toughness and reduce brittleness, the wire rod is then tempered by reheating it to a lower temperature and slowly cooling it. The quenching process can affect dimensional accuracy due to the rapid cooling, which may cause distortion or warping. However, tempering helps decrease brittleness and minimize distortion, leading to improved dimensional accuracy. Additionally, other heat treatment processes such as normalizing and stress relieving can also impact the dimensional accuracy of steel wire rods. Normalizing involves heating the wire rod to a specific temperature and allowing it to cool in still air. This process refines the grain structure and improves the mechanical properties of the steel. On the other hand, stress relieving involves heating the wire rod to a temperature below the critical range and gradually cooling it, which reduces internal stresses. Both normalizing and stress relieving can contribute to improved dimensional accuracy by minimizing distortions or warping. To summarize, the dimensional accuracy of steel wire rods can vary depending on the heat treatment process used. Annealing, quenching and tempering, normalizing, and stress relieving are some commonly employed heat treatment processes that can affect dimensional accuracy. Careful consideration should be given to the choice of heat treatment process in order to achieve the desired dimensional accuracy while also meeting the required mechanical properties of the steel wire rod.
- Q: What are the different types of steel wire rod surface finishing processes?
- There are several types of steel wire rod surface finishing processes, including pickling and phosphating, galvanizing, coating with zinc-rich paint, and powder coating. These processes help to enhance the appearance, corrosion resistance, and durability of the steel wire rod.
- Q: What are the different types of steel wire rod surface treatment methods?
- Various industries commonly use several different methods to treat the surface of steel wire rods. These methods aim to improve the wire rods' properties, durability, and longevity. Some of the most frequently used surface treatment methods for steel wire rods include: 1. Pickling: In this method, the steel wire rods are immersed in an acid solution, usually hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. This process eliminates scale, rust, and other impurities from the surface, enhancing the wire rods' appearance and cleanliness. 2. Coating: Another popular surface treatment method is applying a protective layer to the steel wire rods. This can be achieved through processes like galvanizing, which coats the wire rods with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion and increase resistance to wear and tear. Other coating methods include epoxy, polymer, or ceramic coatings, offering additional protection against environmental factors. 3. Heat treatment: Heat treatment involves subjecting the steel wire rods to controlled heating and cooling cycles to modify their microstructure and enhance mechanical properties. This treatment method includes processes like annealing, normalizing, or quenching and tempering, which improve the wire rods' strength, hardness, and ductility. 4. Surface passivation: Passivation is a chemical process that eliminates free iron and other contaminants from the surface of the steel wire rods. This method promotes the formation of a passive oxide layer, acting as a protective barrier against corrosion. 5. Shot peening: Shot peening is a mechanical surface treatment method where small spherical particles, known as shot, are bombarded onto the steel wire rods at high velocities. This process induces compressive stresses in the surface layer of the wire rods, enhancing their fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. In conclusion, these various surface treatment methods for steel wire rods are essential for improving their performance, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. The choice of treatment method depends on the specific requirements of the industry and the intended application of the wire rods.
Send your message to us
Carbon Steel Hot Rolled Wire Rod SAE1008
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























