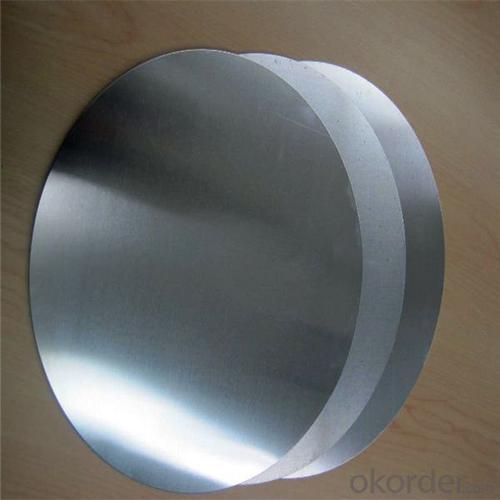
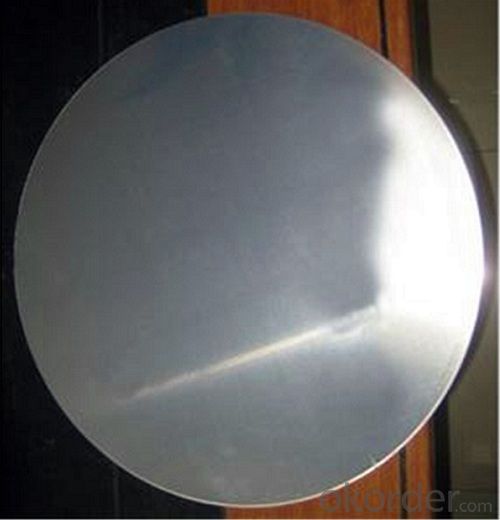
Aluminum Cookware Material Circle/Disc
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2.5
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Cookware Material Aluminium Circle/ Disc
l Product Introduction
Aluminum Circle is mainly used for general commercial and industrial uses, like the capacitor case, toothpaste case, medical tubes, kitchen ware, spray bottle, cosmetic case. With high quality casting and rolling coils or hot-rolled coils as raw meterials, it goes through different cold rolling deformation, slitting, annealing and finally stamping into an aluminum disc, then packaging for delivery.
l Product Description
Certificate | ISO9001:2008 ISO 14001:2004 OHSAS 18001:2007 | ||||||||
Product Name | Cookware Material Aluminium Circle/ Disc | ||||||||
Hardness state | H14, H16, H18, H22, H24, H26, H22, H32,H34 and “O”. | ||||||||
Product Size | Thickness: 0.3-68.0mm, Diameter: 20-1030mm | ||||||||
Surface Treatment | mill finished | ||||||||
Processed | Deep drawings | ||||||||
Min order quantity | 5 tons | ||||||||
Short lead time | 20 days | ||||||||
Application | Cookware, Electrical Appliances | ||||||||
Month Capacity | 5000 tons | ||||||||
Chemical Composition (WT.%) | |||||||||
Alloy | Min.AL | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Ni | |
1050 | 99.5 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | --- | --- | |
1060 | 99.6 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | --- | --- | |
1070 | 99.7 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | -- | --- | |
1100 | 99 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.05 | --- | -- | --- | |
Mechanical Properties | |||||||||
TEMPER | THICKNESS(mm) | TENSILE STRENGTH | |||||||
HO | 0.55-5.50 | 60-100 | |||||||
H12 | 0.55-5.50 | 70-120 | |||||||
H14 | 0.55-5.50 | 85-120 | |||||||
l Packaging & Delivery
Packaging detail: Seaworthy Export Standard Wooden Pallet
Delivery detail: About 25 days

l Company Profile
CNBM International Corporation, China National Building Materials (Group) Corporation, is one of the largest companies in China building material & equipment industry, with 42,800 employees and sales in 2005 of US Dollar 4.395 billion. In 2006, China National Building Material Company Limited was listed on Hong Kong Stock Market with the stock code as 3323. |

l CNBM World Wide
l Products Images
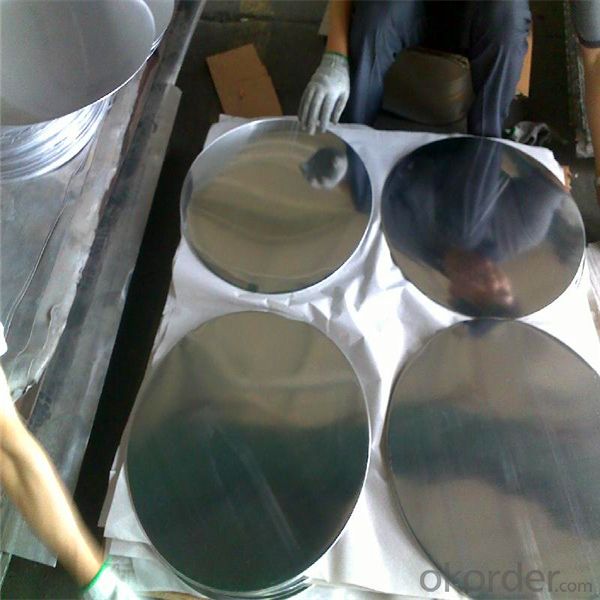



l Certificates



l FAQ
Q: Do you provide free samples?
A: Yes, free samples will be sent to you on freight at destination.
Q: Can I get your latest products catalogue?
A: Yes, it will be sent to you in no time.
Q: What is the MOQ?
A: 2.5 tons
Q: What are your payment terms?
A: We accept L/C, T/T
- Q: This question asks for a list of typical metal alloys that are utilized in the production of cars.
- <p>Common alloys used in automobile manufacturing include steel alloys such as low carbon steel, high-strength steel, and stainless steel for body and frame construction. Aluminum alloys are also widely used for their lightweight properties, especially in engine components and body panels. Magnesium alloys are employed for parts requiring high strength-to-weight ratios. Additionally, cast iron is used for engine blocks and cylinder heads, while copper alloys are utilized in radiators and electrical wiring. Titanium alloys find use in high-performance or luxury vehicles for their exceptional strength and low weight.</p>
- Q: Is the accumulation of aluminum in the body harmful to health?
- <p>Aluminum buildup in the body has been a subject of concern, particularly in relation to Alzheimer's disease. While aluminum is naturally present in the environment and is used in various products, including food packaging and cookware, there is no strong scientific evidence to support the claim that aluminum exposure or accumulation causes health problems in humans. The World Health Organization and other health authorities have stated that aluminum intake from food and drinking water is not a significant health risk for the general population. However, it is always recommended to follow good hygiene practices and use cookware that is known to be safe for food preparation to minimize any potential risks.</p>
- Q: This question asks whether it is safe to use aluminum cookware for pregnant women or individuals with health conditions.
- <p>While aluminum cookware is generally safe for most people, there are concerns about its potential health effects. Aluminum has been linked to cognitive issues and Alzheimer's disease, although the evidence is not conclusive. For pregnant women and those with health conditions, it is advisable to err on the side of caution. Opt for cookware made from stainless steel, cast iron, or non-stick materials without aluminum. If you must use aluminum cookware, avoid acidic or alkaline foods and ensure the cookware is not scratched, as this can increase aluminum leaching into food.</p>
- Q: Is aluminum a suitable material for use in nuclear power plants?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be used in nuclear power plants, but its application is limited due to its reactivity with neutrons. Aluminum is used in non-nuclear grade components such as cooling systems, electrical equipment, and structural supports. However, it is not used in the core or in high-radiation areas due to its tendency to absorb neutrons, which can lead to transmutation and the production of radioactive isotopes. Materials like stainless steel, zirconium alloys, and other neutron-resistant materials are preferred for core components and high-radiation environments.</p>
- Q: What are the positive environmental impacts of utilizing recycled aluminum over newly produced aluminum?
- <p>Using recycled aluminum has several environmental benefits. It conserves natural resources by reducing the need for bauxite mining, which is the primary source of aluminum. Recycling aluminum requires significantly less energy compared to producing new aluminum from raw materials, which can lead to a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, recycling aluminum helps in reducing landfill waste, as it diverts used aluminum products from landfills. Moreover, it decreases the environmental impact associated with the production process, such as water pollution and habitat destruction. Overall, recycling aluminum is a more sustainable practice that contributes to a lower carbon footprint and a healthier environment.</p>
- Q: This question asks about the methods and steps involved in processing aluminum.
- <p>Aluminum processing involves several key steps: extraction from bauxite ore, refining, and fabrication. Initially, bauxite is mined and then processed to remove impurities. The Bayer process is commonly used to extract alumina (aluminum oxide) from bauxite by dissolving it in a caustic soda solution. The alumina is then smelted in a reduction furnace using the Hall-H茅roult process, where it is dissolved in molten cryolite and electrolyzed to produce pure aluminum. Finally, the aluminum is shaped and fabricated into various products through methods such as casting, extrusion, or rolling.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to utilize recycled aluminum to manufacture new items?
- <p>Yes, recycled aluminum can be used to make new products. It is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective process. Recycling aluminum conserves energy, as it requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum from raw materials. Recycled aluminum maintains its properties, making it suitable for various applications, including automotive parts, construction materials, and consumer goods. The process also reduces waste and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to sustainability efforts.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to recycle aluminum from old products to create new ones?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be recycled to make new products from old ones. Recycling aluminum is a highly efficient process that requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum from raw materials. This process is not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable. Recycled aluminum maintains its quality and can be used to create a wide range of new products, from cans and packaging to automotive parts and construction materials.</p>
- Q: Is it safe to use aluminum for making containers for food and beverages?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be used to make containers for food and drink. Aluminum is a common material for food packaging due to its lightweight, durability, and resistance to corrosion. It forms a protective oxide layer that prevents the metal from interacting with the food, ensuring safety. However, it's important to note that aluminum containers should not be used for storing acidic foods or beverages for extended periods, as this can lead to leaching of aluminum into the food. Additionally, some studies suggest a potential link between aluminum and neurological disorders, though this is still a subject of debate.</p>
- Q: Is there a more environmentally friendly method for recycling aluminum?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be recycled in a more environmentally friendly way. The process of recycling aluminum is already quite efficient, as it requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum from raw materials. However, further improvements can be made by optimizing recycling processes, reducing transportation emissions, and increasing the use of recycled aluminum in new products. Additionally, implementing closed-loop recycling systems where aluminum is continuously recycled without loss in quality can minimize waste and environmental impact. Educating consumers about the importance of recycling and improving collection systems can also contribute to more sustainable aluminum recycling practices.</p>
Send your message to us
Aluminum Cookware Material Circle/Disc
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2.5
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























