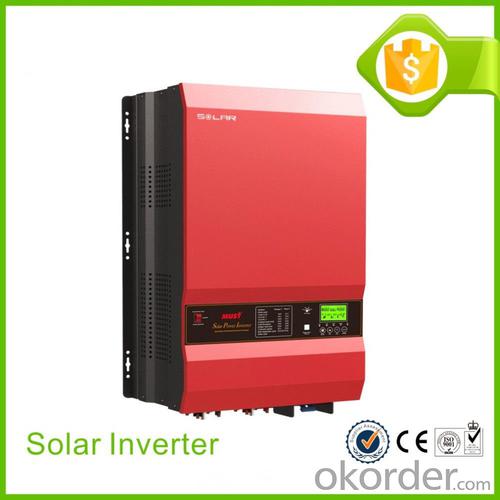
3200 watt Off-Grid Hybrid Solar Power Inverter 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000VA
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description
What is Solar inverter?
Solar pv inverters is an electronic system that operates the photovoltaic(PV) modules in a manner that allows the modules to produce all the power they are capable of. The solar mate charge controller is a microprocessor-based system designed to implement the MPPT. It can increase charge current up to 30% or more compared to traditional charge controllers.
Features
. Pure sine wave inverter
. Selectable input voltage range for home appliances and personal computers
. Selectable charging current based on applications
. Configurable AC/Solar input priority via LCD setting
. Compatible to mains voltage or generator power
. Parallel operation with up to 6 units only available for PV1800 4KVA/5KVA
. Auto restart while AC is recovering
. Overload and short circuit protection
. Smart battery charger design for optimized battery performance
. Cold start function
Specification
RATED POWER | 1000VA / 800W | 2000VA/ | 3000VA / 2400W | 4000VA / 3200W | 5000VA / 4000W | |||||
INPUT | ||||||||||
Voltage | 230 VAC | |||||||||
Selectable Voltage Range | 170-280 VAC (For Personal Computers) ; 90-280 VAC (For Home Appliances) | |||||||||
Frequency Range | 50 Hz/60 Hz (Auto sensing) | |||||||||
OUTPUT | ||||||||||
AC Voltage Regulation | 230 VAC ± 5% | |||||||||
Surge Power | 2000VA | 4000VA | 6000VA | 8000VA | 10000VA | |||||
Efficiency (Peak) | 90% | 93% | ||||||||
Transfer Time | 10 ms (For Personal Computers) ; 20 ms (For Home Appliances) | |||||||||
Waveform | Pure sine wave | |||||||||
BATTERY | ||||||||||
Battery Voltage | 12 VDC | 24 VDC | 48 VDC | |||||||
Floating Charge Voltage | 13.5 VDC | 27 VDC | 54 VDC | |||||||
Overcharge Protection | 15 VDC | 30 VDC | 60 VDC | |||||||
Maximum Charge Current | 10 A or 20 A | 20 A or 30 A | 60 A | |||||||
SOLAR CHARGER (OPTION) | ||||||||||
Charging Current | 50 A | |||||||||
Maximum PV Array Open Circuit Voltage | 30 VDC | 60 VDC | 105 VDC | |||||||
Standby power Consumption | 1 W | 2 W | 2 W | |||||||
PHYSICAL | ||||||||||
Dimension, D x W x H (mm) | 95 x 240 x 316 | 100 x 272 x 355 | 125 x 297.5 x 468 | |||||||
Net Weight (kgs) | 5.0 | 6.4 | 6.9 | 9.8 | 9.8 | |||||
OPERATING ENVIRONMENT | ||||||||||
Humidity | 5% to 95% Relative Humidity(Non-condensing) | |||||||||
Operating Temperature | 0°C - 55°C | |||||||||
Storage Temperature | -15°C - 60°C | |||||||||
Images
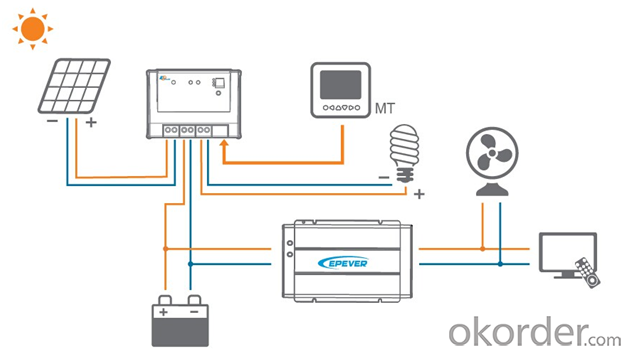
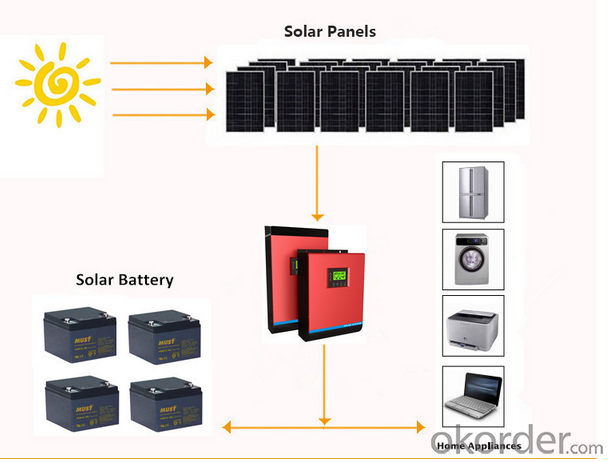
Packaging & Shipping
What is the packing?
1.Package: Carton Box for packaging, or Wooden Box advised for Samples to protect in transportations. Package designed by Clients is welcomed.
2.Shipping: DHL,FEDEX,UPS,EMS,AirWay and By Sea.
3.Payment: T/T( telegraphic transfer (T/T) and Western Union
4.Welcome to your Sample Order to test First.
FAQ
Q1: How to choose a right inverter?
A1:Tell us your demand, then our sales will recommend a suitable inverter to you.
Q2: What's the different between inverter and solar inverter?
A2: Inverter is only accept AC input, but solar inverter not only accept AC input but also can connect with solar panel to accept PV input, it more save power.
Q3: How about the delivery time?
A3: 7 days for sample; 25 days for bulk order.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different types of grounding configurations?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different types of grounding configurations. However, it is important to ensure that the grounding configuration of the inverter is compatible with the specific electrical system it is being connected to. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer's guidelines and local electrical codes to determine the appropriate grounding configuration for safe and efficient operation.
- Q: What is the role of a solar inverter in preventing system downtime?
- The role of a solar inverter in preventing system downtime is to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power electrical devices and to feed excess energy back into the grid. By maintaining a stable and reliable flow of electricity, solar inverters help prevent disruptions and downtime in the solar energy system, ensuring continuous operation and maximizing energy efficiency.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle voltage sags or swells in the grid?
- A solar inverter handles voltage sags or swells in the grid by continuously monitoring the voltage levels. When it detects a sag or swell, it adjusts its internal circuitry to regulate the output voltage accordingly. This ensures that the connected solar panels continue to operate within their optimal voltage range, minimizing any negative impact on the overall power generation system.
- Q: What is the importance of insulation resistance measurement in a solar inverter?
- Insulation resistance measurement in a solar inverter is crucial as it helps ensure the safety and efficiency of the electrical system. By measuring the insulation resistance, any potential faults or deteriorations in the insulation can be detected, preventing electrical leakage or short circuits. This measurement also helps identify any insulation breakdowns that may compromise the performance and reliability of the solar inverter. Ultimately, insulation resistance measurement is essential for maintaining the integrity of the solar inverter and ensuring the safety of both the electrical system and the people using it.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle frequency variations?
- A solar inverter handles frequency variations by continuously monitoring the grid frequency and adjusting its own output accordingly. It uses advanced control algorithms to maintain a stable output frequency, ensuring the smooth and synchronized integration of solar power into the grid.
- Q: What are the safety certifications for a solar inverter?
- Some common safety certifications for a solar inverter include UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification, IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) certification, and CE (Conformité Européene) marking. These certifications ensure that the solar inverter meets specific safety standards and regulations to protect users from potential hazards.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a solar-powered security camera system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a solar-powered security camera system. A solar inverter is responsible for converting the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power electrical devices. In the case of a solar-powered security camera system, the solar panels generate DC power, which is then converted by the solar inverter into AC power that can be used to operate the cameras and other components of the system.
- Q: What are the key features to consider when choosing a solar inverter?
- When choosing a solar inverter, some key features to consider are the power rating, efficiency, warranty, monitoring capabilities, and compatibility with your solar panels and battery storage system.
- Q: What is the role of galvanic isolation in a solar inverter?
- The role of galvanic isolation in a solar inverter is to provide electrical safety and prevent potential hazards. It separates the input and output circuits electrically, using transformers or optocouplers, to eliminate any potential voltage differences, ground loops, or electrical noise that could cause damage to the inverter or connected devices. Additionally, galvanic isolation helps to protect against electric shocks and ensures the safety of both the system and individuals working with or around the solar inverter.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a solar-powered cooling system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a solar-powered cooling system. The solar inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various electrical devices, including the cooling system. This allows for the efficient use of solar energy to run the cooling system, reducing reliance on grid electricity and promoting sustainability.
Send your message to us
3200 watt Off-Grid Hybrid Solar Power Inverter 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000VA
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























