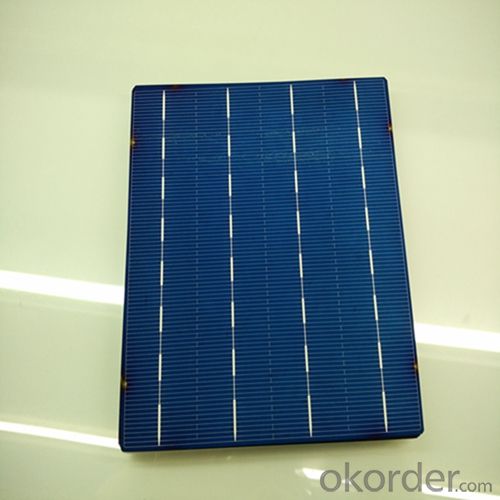
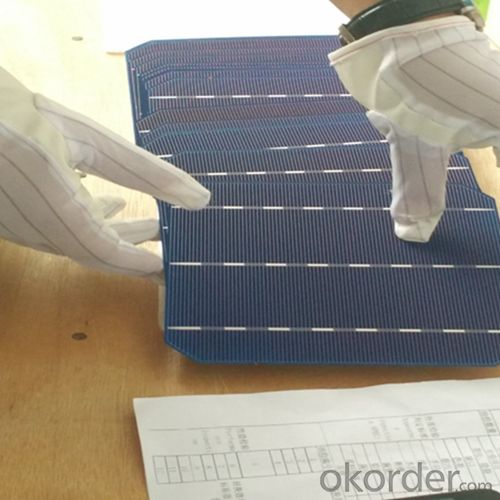
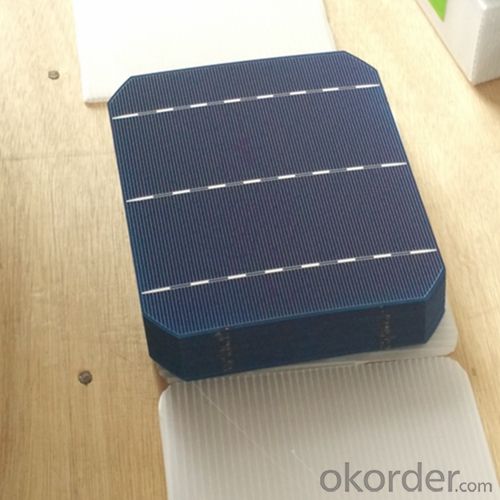
Lightest Solar Cells - Poly 156x156mm2 Solar Cells Made in Panels
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2999 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 6000000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
The operation of a photovoltaic (PV) cell requires 3 basic attributes:
The absorption of light, generating either electron-hole pairs or excitons.
The separation of charge carriers of opposite types.
The separate extraction of those carriers to an external circuit.
In contrast, a solar thermal collector supplies heat by absorbing sunlight, for the purpose of either direct heating or indirect electrical power generation from heat. A "photoelectrolytic cell" (photoelectrochemical cell), on the other hand, refers either to a type of photovoltaic cell (like that developed by Edmond Becquerel and modern dye-sensitized solar cells), or to a device that splits water directly into hydrogen and oxygen using only solar illumination.Characteristic of Mono 156X156MM2 Solar Cells
You are gaining energy independence - add battery backup power for even greater energy security
The cost of electricity is only going to rise – insure against that rising cost
Adaptive cells change their absorption/reflection characteristics depending to respond to environmental conditions. An adaptive material responds to the intensity and angle of incident light. At the part of the cell where the light is most intense, the cell surface changes from reflective to adaptive, allowing the light to penetrate the cell. The other parts of the cell remain reflective increasing the retention of the absorbed light within the cell.[67]
In 2014 a system that combined an adaptive surface with a glass substrate that redirect the absorbed to a light absorber on the edges of the sheet. The system also included an array of fixed lenses/mirrors to concentrate light onto the adaptive surface. As the day continues, the concentrated light moves along the surface of the cell. That surface switches from reflective to adaptive when the light is most concentrated and back to reflective after the light moves along
Mechanical data and design
Format | 156mm x 156mm±0.5mm |
Thickness | 210μm±40μm |
Front(-) | 1.5mm bus bar (silver),blue anti-reflection coating (silicon nitride) |
Back (+) | 2.5mm wide soldering pads (sliver) back surface field (aluminium) |
Temperature Coefficient of Cells
Voc. Temp.coef.%/K | -0.35% |
Isc. Temp.coef .%/K | +0.024%/K |
Pm.Temp.coef. %/K | -0.47%/K |
Electrical Characteristic
Effiency(%) | Pmpp(W) | Umpp(V) | Impp(A) | Uoc(V) | Isc(A) | FF(%) |
18.35 | 4.384 | 0.526 | 8.333 | 0.63 | 8.877 | 78.39% |
18.20 | 4.349 | 0.526 | 8.263 | 0.63 | 8.789 | 78.54% |
18.05 | 4.313 | 0.525 | 8.216 | 0.63 | 8.741 | 78.32% |
17.90 | 4.277 | 0.524 | 8.161 | 0.625 | 8.713 | 78.04% |
17.75 | 4.241 | 0.523 | 8.116 | 0.625 | 8.678 | 77.70% |
17.60 | 4.206 | 0.521 | 8.073 | 0.625 | 8.657 | 77.36% |
17.45 | 4.170 | 0.519 | 8.039 | 0.625 | 8.633 | 76.92% |
17.30 | 4.134 | 0.517 | 8.004 | 0.625 | 8.622 | 76.59% |
17.15 | 4.096 | 0.516 | 7.938 | 0.625 | 8.537 | 76.80% |
17.00 | 4.062 | 0.512 | 7.933 | 0.625 | 8.531 | 76.18% |
16.75 | 4.002 | 0.511 | 7.828 | 0.625 | 8.499 | 75.34% |
16.50 | 3.940 | 0.510 | 7.731 | 0.625 | 8.484 | 74.36% |



 FAQ
FAQ
Q: What price for each watt?
A: It depends on the quantity, delivery date and payment terms, generally Large Quantity and Low Price
Q: What is your size for each module? Can you tell me the Parameter of your module?
A: We have different series of panels in different output, both c-Si and a-Si. Please take the specification sheet for your reference.
Q: What is your size for each module? Can you tell me the Parameter of your module?
A: We have different series of panels in different output, both c-Si and a-Si. Please take the specification sheet for your reference.
- Q: Can solar cells be used for powering concert venues?
- Yes, solar cells can be used for powering concert venues. Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, convert sunlight into electricity. Concert venues typically require a significant amount of energy for lighting, sound systems, and other equipment. By installing solar panels on the venue's roof or in nearby open spaces, the electricity generated can be used to power the venue. This not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also helps to lower energy costs and minimize the venue's carbon footprint.
- Q: How to define the poly solar cells as the A Grade one?
- You can check with the manufacturers first and they will tell you if the poly solar cells they are selling is the A grade level.
- Q: Can solar cells be used to power electric vehicle charging stations?
- Yes, solar cells can be used to power electric vehicle charging stations. Solar panels can generate electricity from sunlight, which can be stored in batteries or directly used to charge electric vehicles. This renewable energy source can reduce reliance on the grid and contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly charging infrastructure.
- Q: Can solar cells be used for heating?
- Yes, solar cells can be used for heating through the use of solar thermal collectors. These collectors capture the sun's energy and convert it into heat, which can then be used for various heating purposes such as heating water or indoor spaces.
- Q: How do solar cells perform in different temperature ranges?
- Solar cells generally perform less efficiently at high temperatures. This is because the increase in temperature can lead to an increase in electron-hole recombination, reducing the overall photoelectric conversion efficiency. On the other hand, solar cells can also experience a decrease in performance at extremely low temperatures, although this effect is usually less significant. Overall, the efficiency of solar cells varies with temperature, with a decline at high temperatures and a smaller impact at low temperatures.
- Q: Are solar cells affected by electromagnetic radiation?
- Yes, solar cells are affected by electromagnetic radiation. Solar cells convert sunlight, which is a form of electromagnetic radiation, into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. However, it's important to note that certain types of electromagnetic radiation, such as infrared or ultraviolet radiation, can have varying effects on solar cell efficiency.
- Q: What is the role of anti-reflective coatings on solar cells?
- The role of anti-reflective coatings on solar cells is to minimize the amount of light that is reflected away from the surface of the cell. By reducing reflection, these coatings allow more light to be absorbed by the solar cell, increasing its efficiency and overall power output.
- Q: Can solar cells be used in desert environments?
- Yes, solar cells can definitely be used in desert environments. In fact, solar energy is particularly well-suited for such locations due to the high levels of solar radiation and clear skies typically found in deserts. The arid climate and ample sunlight make desert regions ideal for harnessing solar power, allowing solar cells to generate a significant amount of electricity.
- Q: How do solar cells perform in snowy conditions?
- Solar cells do not perform as efficiently in snowy conditions because the snow cover blocks sunlight from reaching the cells. However, modern solar panels are designed to be durable and can still generate some electricity even in snowy conditions. Additionally, when the snow melts or is removed from the panels, they can resume their normal performance.
- Q: What is the lifespan of a solar cell battery?
- The lifespan of a solar cell battery can vary depending on various factors such as the quality of the battery, usage patterns, and maintenance. On average, a well-maintained solar cell battery can last anywhere between 5 to 20 years.
Send your message to us
Lightest Solar Cells - Poly 156x156mm2 Solar Cells Made in Panels
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2999 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 6000000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords