Low Ash and Low Sulphur Calcined Petroleum Coke
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1.Structure of Calcined Petroleum Coke Description
Calcined Petroleum Coke is made from raw petroleum coke,which is calcined in furnace at a high temperature(1200-1300℃).CPC/Calcined Petroleum Coke is widely used in steelmaking,castings manufacture and other metallurgical industry as a kind of recarburizer because of its high fixed carbon content,low sulfur content and high absorb rate.Besides,it is also a best kind of raw materials for producing artifical graphite(GPC/Graphitized Petroleum Coke) under the graphitizing temperature(2800℃).
2.Main Features of the Calcined Petroleum Coke
High-purity graphitized petroleum coke is made from high quality petroleum coke under a temperature of 2,500-3,500°C. As a high-purity carbon material, it has characteristics of high fixed carbon content, low sulfur, low ash, low porosity etc.It can be used as carbon raiser (Recarburizer) to produce high quality steel,cast iron and alloy.It can also be used in plastic and rubber as an additive.
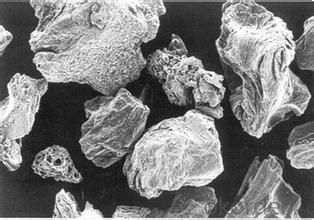
3. Calcined Petroleum Coke Images
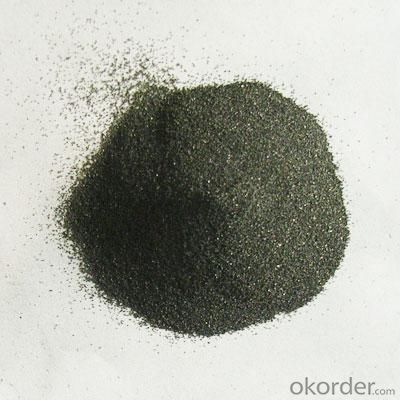


4. Calcined Petroleum Coke Specification
| Place of Origin: | Henan, China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | CNBM | Model Number: | YY-CPC-A |
| Application: | as fuel, electrodes | Dimensions: | 3-8cm | Chemical Composition: | F.C |
| Ash: | 0.8% | V.M: | 0.5% | water: | 0.3% |
| sulfur: | 0.8% | Size: | 3-8cm |
5.FAQ of Calcined Petroleum Coke
1). Q: Are you a factory or trading company?
A: We are a factory.
2). Q: Where is your factory located? How can I visit there?
A: Our factory is located in ShanXi, HeNan, China. You are warmly welcomed to visit us!
3). Q: How can I get some samples?
A: Please connect me for samples
4). Q: Can the price be cheaper?
A: Of course, you will be offered a good discount for big amount.
- Q: I don't know the battery. Although I know the former is chemical energy, I want to know if the 1 grain size 5 can compare the charge capacity with the 1 grain 5 1ANot much of a fortune, but thank you very much for the enthusiastic friend who gave me the answer. Thank you!
- The typical capacity of a AA carbon cell is 500maH, the voltage is 1.4V (average discharge platform) and the power is 0.7WHA typical capacity of AA alkaline battery is 2800maH, the voltage is 1.4V (average discharge platform) and the power is 3.9WHA AA disposable lithium iron battery, the typical capacity is 3000maH, voltage is 1.5V (discharge platform average), power is: 4.5WHA AA nickel hydrogen rechargeable battery, the maximum capacity is 2700maH, voltage is 1.2V (average discharge platform), power is: 3.2WHA AA lithium rechargeable battery, the maximum capacity is 800maH, the voltage is 3.7V (average discharge platform), power is: 2.9WHA AA lithium iron phosphate battery has a maximum capacity of 700maH, a voltage of 3.2V, and a power of 2.2WhBased on the above data, it is concluded that AA single iron lithium battery and disposable alkaline battery are the most durable, and their capacity (no matter size, current, discharge) is more than 6 times of that of carbon battery
- Q: How many points can Yongan change for 1 carbon coins?
- Yongan APP one hundred carbon points, change a carbon coin
- Q: Which is better, 13 and 14 carbon breath tests?
- According to your case, carbon 14 is cheaper than 13, and the accuracy is the same
- Q: What is the role of carbonation in carbonated drinks?
- The purpose of carbonation in carbonated drinks is to give them their characteristic refreshing and bubbly sensation. Carbonation occurs when carbon dioxide gas is dissolved into a liquid, usually water, under pressure. This process produces carbonic acid, which adds a tangy taste to the drink. Carbonation serves multiple functions in carbonated beverages. Firstly, it enhances the flavor by creating a unique bubbly sensation that delights the taste buds and provides a refreshing feeling in the mouth. The effervescence resulting from carbonation also adds to the overall sensory experience, making the drink more enjoyable to consume. Additionally, carbonation acts as a natural preservative in carbonated drinks. The presence of carbon dioxide gas inhibits the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms, thus extending the shelf life of the beverage. This is especially important for soft drinks that are often stored for long periods before being consumed. Furthermore, carbonation plays a role in the presentation of carbonated drinks. The release of carbon dioxide gas creates bubbles and fizz, making the beverage visually appealing and enticing. This visual appeal is often associated with a sense of luxury and indulgence. In summary, carbonation is a vital element of carbonated drinks as it contributes to their taste, preservation, and visual appeal. It enhances the sensory experience and adds to the overall enjoyment of these beverages.
- Q: What are the impacts of carbon emissions on coral reefs?
- The impacts of carbon emissions on coral reefs are significant and detrimental. Increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere lead to ocean acidification, which disrupts the delicate balance of the reef ecosystem. Acidic conditions hinder the ability of corals to build their calcium carbonate skeletons, making them more vulnerable to erosion and bleaching. Additionally, rising temperatures caused by carbon emissions contribute to coral bleaching events, where corals expel their symbiotic algae, leading to their eventual death. Overall, carbon emissions pose a major threat to coral reefs, jeopardizing their biodiversity and ecological functions.
- Q: What are the impacts of carbon emissions on human respiratory diseases?
- Carbon emissions have significant impacts on human respiratory diseases. The release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases from various sources, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, contributes to air pollution. This pollution can lead to the exacerbation of respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and respiratory infections. Additionally, exposure to particulate matter and toxic chemicals emitted from carbon-based industries can increase the risk of developing respiratory diseases and worsen existing conditions. Overall, reducing carbon emissions is crucial to mitigate the adverse effects on human respiratory health.
- Q: What are the properties of carbon-based adhesives?
- Carbon-based adhesives are extensively used in various industries due to their versatility and several desirable properties. One of their notable features is their exceptional bonding strength, enabling the creation of durable bonds between different materials like metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Consequently, they find suitability in applications that require reliable and long-lasting bonding solutions. Another significant property of carbon-based adhesives is their capacity to withstand high temperatures without compromising their adhesive properties. This makes them ideal for deployment in environments with extreme temperatures, such as the aerospace and automotive industries, where components are often exposed to elevated temperatures. Furthermore, carbon-based adhesives exhibit remarkable resistance to chemicals, enabling them to endure exposure to various substances without degradation. As a result, they are well-suited for industries where adhesives may come into contact with solvents, fuels, or harsh chemicals. Moreover, carbon-based adhesives possess excellent electrical conductivity, making them valuable in applications that require electrical or thermal conductivity, particularly in the electronics industry. Additionally, these adhesives typically have minimal shrinkage and outgassing characteristics. This implies that they undergo negligible size changes or release volatile substances during the curing process, thereby minimizing the risk of damage or contamination to surrounding materials. In conclusion, carbon-based adhesives offer a combination of high bonding strength, temperature resistance, chemical resistance, electrical conductivity, and dimensional stability. Consequently, they are highly preferred in various industries where reliable and durable bonding solutions are essential.
- Q: What is carbon nanomembrane?
- A carbon nanomembrane (CNM) refers to an ultra-thin layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional lattice structure. It is typically just a single atom thick, making it one of the thinnest materials known to exist. CNMs are created by depositing a precursor material onto a substrate and then using heat or chemical processes to transform it into a pure carbon layer. Due to its unique properties, carbon nanomembranes have garnered significant interest in various fields of science and technology. CNMs are highly impermeable to gases and liquids, making them ideal for applications such as gas separation and filtration. They also possess exceptional electrical conductivity, making them suitable for electronic devices and sensors. Furthermore, carbon nanomembranes can be engineered with tailored pore sizes and chemical functionalities, enabling their use in molecular sieving and biological applications. They have shown promise in areas such as drug delivery, water purification, and tissue engineering. Additionally, CNMs have demonstrated excellent mechanical strength and flexibility, which opens up opportunities for their use in lightweight and flexible electronics. Overall, carbon nanomembranes offer a versatile and exciting platform for a wide range of applications. Ongoing research and development in this field aim to further explore and harness the unique properties of CNMs for the advancement of various industries.
- Q: How does carbon affect the formation of blizzards?
- Carbon does not directly affect the formation of blizzards. Blizzards are intense winter storms characterized by strong winds, low temperatures, and heavy snowfall. They typically occur when a low-pressure system moves into an area with sufficient moisture and cold air. The primary factors that influence the formation of blizzards are temperature, moisture, and wind patterns. However, carbon emissions and their impact on the climate can indirectly influence the frequency and intensity of blizzards. Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming. This warming effect can alter weather patterns, including the conditions necessary for blizzard formation. Warmer temperatures caused by carbon emissions can lead to changes in precipitation patterns, including increased moisture content in the atmosphere. This additional moisture, combined with the cold air necessary for blizzards, can contribute to heavier snowfall during these storms. Furthermore, climate change can affect wind patterns, which can impact the intensity and duration of blizzards. Changes in atmospheric circulation patterns can alter the tracks and strength of storms, potentially leading to more or less frequent blizzard events in certain regions. It is important to note that the specific impact of carbon emissions on blizzard formation varies depending on regional and local factors. The complex nature of weather systems and the interaction between different variables make it challenging to attribute any single weather event solely to carbon emissions. However, the overall influence of carbon emissions on the climate system increases the potential for more extreme weather events, including blizzards.
- Q: How is carbon used in the production of fuels?
- Carbon is used in the production of fuels through a process called carbonization, where organic materials such as coal, oil, and natural gas are heated in the absence of air to produce carbon-rich substances like coke and charcoal. These carbon-rich substances can then be further processed to create various types of fuels, including gasoline, diesel, and natural gas, which are essential for powering vehicles, generating electricity, and heating homes and industries.
Send your message to us
Low Ash and Low Sulphur Calcined Petroleum Coke
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords