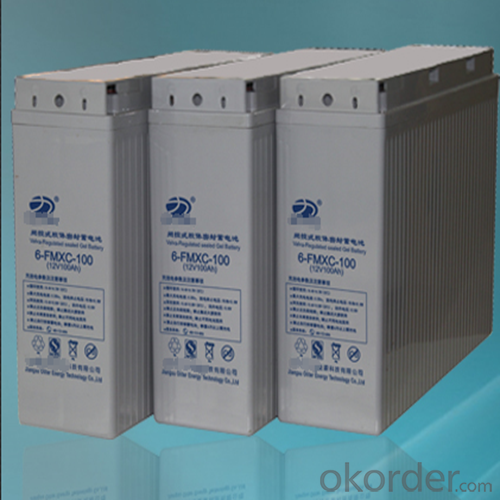
Powerfilm Solar Cells Colloidal Battery 12V Series for Communication
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Product Descrtption:
What is the product?
The FMXA/FMXC (Front Terminal) Series is especially designed for telecommunication use with 12 years design life in float service. By combining the newly developed paste formula with up-to-date AGM structures, this range features 12 years design life and Front Access connection for fast, easy installation and maintenance. This series is highly suited for telecom applications, UPS systems and other back up applications.
What is the purpose of the product?
· Telecommunication
· Control Equipments
· UPS systems
· Communication Equipments
· Medical Equipments
· Emergency Power Systems
What advantages do products have ?
12 years design life at floating condition
Wide operating temperature range from -15°C to 55°C
Advanced paste formula with increased recharge efficiency
Front access terminal with standard width for 19” and 23” ETSI racks
30% decreased float current lead to excellent high temperature resistance
Thick flat plate with high Tin low Calcium alloy
Low self discharge
Excellent deep discharge recovery capability
Main feature of the product
*safety and reliable
*environmental friendly and fast delivery
*low self diacharge

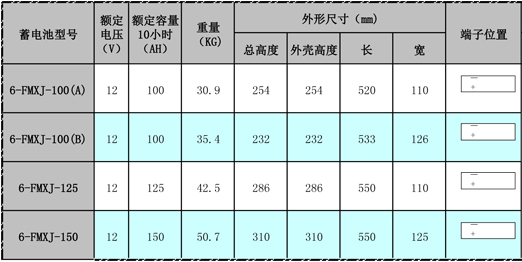
FAQ:
*Question:How do you pack your products?
Answer:We have rich experience on how to pack the panels to make sure the safety on shipment when it arrives at the destination.
*Question:Can you do FOB for us?
Answer:Yes, we can do it for you .
*Question:How long can we receive the goods after purchase?
Answer:In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible. The perfect time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers. Commonly 7 to 10 working days can be served.
Principles of how solar cell works
Solar power is amazing. On average, every square meter of Earth's surface receives 164 watts of solar energy. In other words, you could stand a really powerful (150 watt) table lamp on every square meter of Earth's surface and light up the whole planet with the Sun's energy! So, we want to exploit resources, and solar (or photovoltaic) cells appearance, it converts the sun’s energy into electricity. Whether they’re adorning your calculator or orbiting our planet on satellites, they rely on the the photoelectric effect: the ability of matter to emit electrons when a light is shone on it.
Steps of how solar cell works
Sunlight is composed of miniscule particles called photons, which radiate from the sun. As these hit the silicon atoms of the solar cell, they transfer their energy to loose electrons, knocking them clean off the atoms. The photons could be compared to the white ball in a game of pool, which passes on its energy to the coloured balls it strikes.
A solar cell is a sandwich of two different layers of silicon that have been specially treated or doped so they will let electricity flow through them in a particular way. The lower layer is doped so it has slightly too few electrons. It's called p-type or positive-type silicon (because electrons are negatively charged and this layer has too few of them). The upper layer is doped the opposite way to give it slightly too many electrons. It's called n-type or negative-type silicon.
The electrons use this energy to jump across the barrier into the upper, n-type layer and escape out into the circuit. Flowing around the circuit, the electrons make the lamp light up.
Energy Loss in a Solar Cell when it is working
Visible light is only part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Electromagnetic rad­iation is not monochromatic -- it's made up of a range of different wavelengths, and therefore energy levels.
Light can be separated into different wavelengths, which we can see in the form of a rainbow. Since the light that hits our cell has photons of a wide range of energies, it turns out that some of them won't have enough energy to alter an electron-hole pair. They'll simply pass through the cell as if it were transparent. Still other photons have too much energy. Only a certain amount of energy, measured in electron volts (eV) and defined by our cell material (about 1.1 eV for crystalline silicon), is required to knock an electron loose. We call this the band gap energy of a material. If a photon has more energy than the required amount, then the extra energy is lost. (That is, unless a photon has twice the required energy, and can create more than one electron-hole pair, but this effect is not significant.) These two effects alone can account for the loss of about 70 percent of the radiation energy incident on our cell.
- Q: How long is the long cycle solar cell life?
- Various solar cells according to its working principle, life is different (1) silicon solar cells Silicon solar cells are divided into three kinds of monocrystalline silicon solar cells, polycrystalline silicon thin film solar cells and amorphous silicon thin film solar cells.
- Q: Can solar cells be used in remote monitoring systems?
- Yes, solar cells can be used in remote monitoring systems. Solar cells are an ideal power source for remote monitoring systems as they convert sunlight into electricity, providing a sustainable and reliable source of power even in remote or off-grid locations. This eliminates the need for traditional power sources or frequent battery replacements, making solar cells a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for powering remote monitoring systems.
- Q: What is the role of solar cells in powering remote monitoring systems?
- Solar cells play a crucial role in powering remote monitoring systems by converting sunlight into electricity. These systems are often installed in remote locations where access to traditional power sources is limited or non-existent. Solar cells provide a sustainable and reliable source of energy to continuously power these systems, allowing for continuous monitoring and data collection even in remote areas.
- Q: How do solar cells perform in high pollution areas?
- Solar cells perform less efficiently in high pollution areas due to the reduced amount of sunlight reaching the cells. The presence of pollutants in the air, such as dust, smog, and particulate matter, can block or scatter sunlight, decreasing the overall solar irradiance available for conversion into electricity. This lowers the energy output and effectiveness of solar cells in such areas.
- Q: Can solar cells be used in disaster response vehicles?
- Yes, solar cells can definitely be used in disaster response vehicles. Solar cells can provide a reliable and sustainable source of power, allowing these vehicles to operate even in areas with limited access to electricity. They can be used to charge batteries, power communication and lighting systems, and run necessary equipment, making disaster response vehicles more self-sufficient and efficient during emergency situations.
- Q: Is there any easy way to make a solar cell? I want to make a DIY solar cell with my child at home.
- If you know the principle of solar cells, it can be easy for you to make it yourself.
- Q: Can solar cells be recycled?
- Yes, solar cells can be recycled. The process involves separating and recovering valuable materials like silicon, silver, and aluminum from the cells. This not only reduces waste but also allows for the reuse of these materials in the production of new solar cells.
- Q: Can solar cells be used in powering RVs and campers?
- Yes, solar cells can be used in powering RVs and campers. Solar panels installed on the roof of an RV or camper can convert sunlight into electricity, which can then be used to power various appliances, lights, and charging systems. This allows for a sustainable and self-sufficient power source while on the road or camping in remote locations.
- Q: Can solar cells be used in shopping malls?
- Yes, solar cells can be used in shopping malls. In fact, many shopping malls around the world have already adopted solar panel systems to generate clean and renewable energy. These solar cells can be installed on rooftops, parking lots, or even as shading structures in outdoor areas, helping to reduce electricity costs and environmental impact.
- Q: Can solar cells be used for water heating?
- Yes, solar cells can be used for water heating. Solar water heating systems use solar panels, which contain solar cells, to capture energy from the sun and convert it into heat. This heat is then used to warm water for various applications, such as domestic hot water or space heating.
Send your message to us
Powerfilm Solar Cells Colloidal Battery 12V Series for Communication
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
























