Solar Energy Systems Quotes:CNBM On Grid System 800W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
CNBM On Grid System 800W with Certificate UL TUV CE
Product description
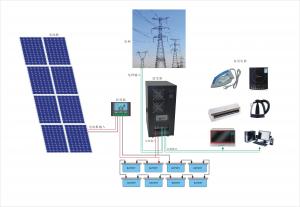
They range from small residential and commercial rooftop systems to large utility-scale solar power stations. Unlike stand-alone power systems, a grid-connected system rarely includes an integrated battery solution, as they are still very expensive. When conditions are right, the grid-connected PV system supplies the excess power, beyond consumption by the connected load, to the utility grid.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.[4]
Solar energy gathered by photovoltaic solar panels, intended for delivery to a power grid, must be conditioned, or processed for use, by a grid-connected inverter. Fundamentally, an inverter changes the DC input voltage from the PV to AC voltage for the grid. This inverter sits between the solar array and the grid, draws energy from each, and may be a large stand-alone unit or may be a collection of small inverters, each physically attached to individual solar panels. See AC Module. The inverter must monitor grid voltage, waveform, and frequency. One reason for monitoring is if the grid is dead or strays too far out of its nominal specifications, the inverter must not pass along any solar energy. An inverter connected to a malfunctioning power line will automatically disconnect in accordance with safety rules, for example UL1741, which vary by jurisdiction. Another reason for the inverter monitoring the grid is because for normal operation the inverter must synchronize with the grid waveform, and produce a voltage slightly higher than the grid itself, in order for energy to smoothly flow outward from the solar array.

Application
Industrial
Commercial
Residential
Feature
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers.[2] They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed.[3] Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Packaging
With carton and box
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering wastewater treatment plants?
- Absolutely, wastewater treatment plants can definitely utilize solar energy systems for power. To generate electricity, solar panels and other solar energy systems can be installed on the rooftops or in open areas surrounding the treatment plants. This generated electricity can then be utilized to power the various components and processes involved in wastewater treatment, including pumps, motors, blowers, and filtration systems. Using solar energy for wastewater treatment plants brings several advantages. Firstly, it is an environmentally friendly and sustainable energy source, helping to reduce the carbon footprint and environmental impact of these facilities. Solar energy systems produce electricity without releasing any greenhouse gases or pollutants into the air, making them an excellent choice for preserving the environment. Secondly, solar energy systems can provide a consistent and dependable power supply to the treatment plants. The availability of sunlight is generally predictable, and advancements in solar technology have enabled the storage of excess energy in batteries for use during cloudy days or at night. This ensures uninterrupted operation of the wastewater treatment plants, even in areas with unreliable grid connections or frequent power outages. Moreover, solar energy systems can also contribute to cost reduction for wastewater treatment plants. By generating their own electricity, these facilities can potentially decrease their reliance on the grid, resulting in substantial savings on energy bills. Additionally, solar energy systems require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan, leading to further cost savings over time. In conclusion, solar energy systems can be effectively utilized for powering wastewater treatment plants. They provide a clean, dependable, and cost-effective solution that not only reduces the environmental impact but also offers energy independence to these crucial facilities.
- Q: What maintenance is required for a solar energy system?
- To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of a solar energy system, regular maintenance is required. This maintenance primarily involves inspecting, cleaning, and monitoring various components of the system. Here are some key maintenance tasks for a solar energy system: 1. Regular visual inspections: It is essential to visually inspect the solar panels, mounts, and other components regularly. Look for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or loose connections, and address them promptly. 2. Cleaning the solar panels: Dust, dirt, leaves, and other debris can accumulate on the solar panels over time. Cleaning the panels periodically, especially in areas with low rainfall or high pollution, is crucial to maintain their efficiency. Use a soft brush, non-abrasive cloth, or a hose to remove any debris. 3. Checking for shading: Ensure that there are no obstructions or objects casting shadows on the solar panels. Even partial shading can significantly affect the system's performance, so trim overhanging branches or remove any other sources of shading. 4. Monitoring system performance: Regularly check the system's performance using the monitoring tools provided by the manufacturer or installer. These tools help identify any deviations from the expected energy production and can indicate potential issues. 5. Inspecting electrical connections: Check all electrical connections, including wiring, junction boxes, inverters, and batteries (if applicable). Look for loose connections, corrosion, or any signs of damage that might affect the system's performance or safety. 6. Inverter maintenance: Inverters convert the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into usable AC electricity. Depending on the type of inverter, some may require periodic inspections, firmware updates, or replacement after a certain period. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for proper inverter maintenance. 7. Battery maintenance (if applicable): If your solar energy system includes battery storage, you might need to perform additional maintenance tasks. This may involve checking the battery charge levels, electrolyte levels (for lead-acid batteries), and overall battery health. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for battery maintenance. 8. Professional inspections: It is advisable to have a professional solar installer or technician inspect the system at least once a year. They can conduct a more thorough examination, perform any necessary repairs or replacements, and ensure that the system is operating optimally. By following these maintenance practices, you can maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your solar energy system, ensuring that it continues to generate clean and sustainable energy for years to come.
- Q: How do solar energy systems handle excess energy production?
- Solar energy systems handle excess energy production through a process called net metering. When the solar panels produce more electricity than needed, the excess energy is fed back into the grid, and the solar system owner receives credits for the surplus electricity. These credits can then be used to offset the electricity consumed from the grid during periods of low solar energy production, such as at night or during cloudy days.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be installed on a concrete roof?
- Yes, a solar energy system can be installed on a concrete roof. In fact, concrete roofs are one of the most ideal surfaces for solar panel installation. Concrete roofs are typically flat, stable, and durable, providing a solid foundation for the panels. Additionally, concrete roofs often have ample space and are not obstructed by nearby trees or buildings, allowing for maximum sunlight exposure. The installation process involves securing the panels to the concrete roof using special mounting systems designed to withstand the weight and ensure a secure attachment. Overall, concrete roofs are a great choice for solar energy system installation.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in areas prone to hurricanes?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in areas prone to hurricanes. However, it is important to ensure that the systems are designed and installed with the specific hurricane risks in mind. This includes using hurricane-resistant materials, securing panels and other components properly, and implementing backup power storage solutions to ensure continuous energy supply during and after a hurricane. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to ensure the system's durability and functionality in such areas.
- Q: What is the role of tracking systems in solar energy systems?
- The role of tracking systems in solar energy systems is to optimize the collection of sunlight by continuously adjusting the position of solar panels to maximize their exposure to the sun. Tracking systems help solar panels follow the sun's movement throughout the day, enabling them to capture the maximum amount of solar energy and generate more electricity. This enhances the overall efficiency and output of the solar energy system.
- Q: What is solar battery storage?
- Solar battery storage refers to the technology that allows energy generated from solar panels to be stored in batteries for later use. It is a system that captures excess electricity produced by solar panels during the day and stores it in batteries, instead of sending it back to the grid. This stored energy can then be utilized during times when the solar panels are not producing enough electricity, such as at night or during cloudy days. Solar battery storage has several benefits. Firstly, it enables homeowners and businesses to become more self-sufficient and reduce their reliance on the traditional electrical grid. By storing excess energy, they can use it during peak demand periods or when there is a power outage, ensuring a constant and uninterrupted power supply. Additionally, solar battery storage helps optimize the use of solar energy. As solar panels often produce more electricity than what is immediately needed, the excess energy would typically be wasted or sent back to the grid. With battery storage, this excess energy can be stored and used later, maximizing the utilization of solar power and reducing the need for fossil fuel-based electricity. Furthermore, solar battery storage can also help in reducing electricity bills. By using stored energy during peak demand periods when electricity rates are higher, users can avoid paying higher prices for electricity from the grid. This can result in significant cost savings over time. Overall, solar battery storage is an innovative technology that enhances the efficiency and reliability of solar energy systems. It enables users to store excess energy for later use, reducing reliance on the grid, optimizing solar power utilization, and potentially saving money on electricity bills.
- Q: How does the size of solar panels impact energy production?
- Energy production is directly affected by the size of solar panels, as it dictates the quantity of sunlight that can be captured and transformed into electricity. Solar panels of larger dimensions possess a greater surface area, enabling them to absorb a larger amount of sunlight and generate a higher electricity output. Consequently, larger panels have the capability to produce more energy in comparison to smaller ones. Moreover, larger panels can accommodate a greater number of solar cells, thereby further augmenting their energy production capacity. Nevertheless, it is crucial to consider the available space, cost, and specific energy requirements when determining the appropriate size of solar panels.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be used to charge electric vehicles?
- It is indeed possible to utilize a solar energy system for the purpose of charging electric vehicles. The sun's rays are harnessed by solar panels, also referred to as photovoltaic (PV) panels, to generate electricity. This electricity can then be employed to charge the batteries of electric vehicles. The PV panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. Subsequently, an inverter is used to transform this DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which aligns with the charging requirements of electric vehicles. By establishing a link between the solar energy system and an electric vehicle charging station, the solar-generated electricity can directly charge the vehicle's battery. This renewable energy source not only diminishes the dependence on fossil fuels but also aids in reducing the emission of greenhouse gases associated with transportation. Moreover, any surplus electricity generated by the solar panel system during daylight hours can be stored in batteries or returned to the grid for future use, guaranteeing a continuous and sustainable power supply for charging electric vehicles.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be installed in areas with high humidity?
- Yes, a solar energy system can be installed in areas with high humidity. While high humidity can affect the efficiency of solar panels to some extent, it does not completely prevent the installation or functioning of solar energy systems. The performance of solar panels is primarily influenced by the amount of sunlight they receive rather than humidity levels. However, it is important to note that excessive humidity or moisture can potentially lead to corrosion or damage to the electrical components of the system. Therefore, proper precautions and maintenance should be undertaken to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the solar energy system in high humidity areas.
Send your message to us
Solar Energy Systems Quotes:CNBM On Grid System 800W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords