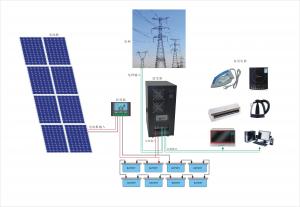
Solar Energy Systems Wholesale - CNBM On Grid System 40000W with Certificate UL, TUV, CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
CNBM On Grid System 40000W with Certificate UL TUV CE
Product description
A photovoltaic (in short PV) module is a packaged, connected assembly of typically 6×10 solar cells. Solar Photovoltaic panels constitute the solar array of a photovoltaic system that generates and supplies solar electricity in commercial and residential applications. Each module is rated by its DC output power under standard test conditions, and typically ranges from 100 to 365 watts. The efficiency of a module determines the area of a module given the same rated output – an 8% efficient 230 watt module will have twice the area of a 16% efficient 230 watt module. There are a few commercially available solar panels available that exceed 22% efficiency[1] and reportedly also exceeding 24%.[2][3] A single solar module can produce only a limited amount of power; most installations contain multiple modules. A photovoltaic system typically includes a panel or an array of solar modules, a solar inverter, and sometimes a battery and/or solar tracker and interconnection wiring.
The price of solar power, together with batteries for storage, has continued to fall so that in many countries it is cheaper than ordinary fossil fuel electricity from the grid (there is "grid parity").[4]
Off-the-grid is a system and lifestyle[1] designed to help people function without the support of remote infrastructure, such as an electrical grid. In electricity, off-grid can be stand-alone power system or mini-grids typically to provide a smaller community with electricity. Off-grid electrification is an approach to access electricity used in countries and areas with little access to electricity, due to scattered or distant population. The term off-the-grid (OTG) can refer to living in a self-sufficient manner without reliance on one or more public utilities. People who adopt this lifestyle are called off-gridders.[2]

Application
Industrial
Commercial
Residential
Feature
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers.[2] They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed.[3] Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Packaging
With carton and box
- Q: Are there any risks of electrical malfunctions or failures during extreme weather events with solar energy systems?
- Solar energy systems may encounter risks of electrical malfunctions or failures during extreme weather events. While solar panels are designed to withstand various weather conditions, such as rain, snow, and wind, they remain susceptible to damage in severe weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, or severe storms. In extreme weather, high winds have the potential to physically harm solar panels by dislodging them from their mounts or causing them to break. Heavy snowfall can also cover the panels, reducing their efficiency and potentially causing them to collapse due to the weight. Additionally, lightning strikes during thunderstorms can jeopardize the electrical components of the solar energy system, leading to potential malfunctions or failures. Nevertheless, it is important to note that solar energy systems are typically equipped with safety measures to minimize these risks. Many solar panels undergo testing and certification to ensure they can withstand specific wind speeds and snow loads. Sturdy and secure mounting systems are utilized, and electrical components often have surge protection to safeguard against lightning strikes. Furthermore, solar energy systems are interconnected with the power grid, enabling a seamless transition to grid power during extreme weather events if needed. This helps mitigate the impact of potential malfunctions or failures. To mitigate the risks associated with extreme weather events, regular maintenance and inspection of solar energy systems are crucial. Periodic check-ups and cleaning can ensure the panels are in good condition, and any signs of damage or wear can be promptly addressed. It is also advisable to seek guidance from a professional installer or technician who can offer advice on specific weather-related risks and potential solutions.
- Q: What is the role of solar energy systems in reducing noise pollution?
- Solar energy systems can play a significant role in reducing noise pollution as they operate silently, unlike conventional power generation methods such as fossil fuel-based power plants or generators. Since solar panels do not have any moving parts, they produce electricity without creating any sound, thereby helping to minimize noise pollution in urban and residential areas.
- Q: How does the angle and orientation of solar panels affect their efficiency?
- The efficiency of solar panels is heavily influenced by their angle and orientation. The angle, which refers to the tilt or inclination of the panels relative to the ground, is crucial. It is adjusted to maximize the amount of sunlight the panels receive throughout the day. The ideal angle varies depending on the geographical location and purpose of the installation. In regions near the equator, where the sun is directly overhead, a steeper tilt angle can help capture more sunlight. On the other hand, in regions further from the equator, the optimal tilt angle may be less steep to ensure consistent sunlight exposure throughout the year, considering the changing angles of the sun during different seasons. The orientation of the panels, or the direction they face, is also important. In the northern hemisphere, panels are typically oriented towards the south, while in the southern hemisphere, they face north. This maximizes their exposure to sunlight since the sun's path across the sky is closer to the equator. The efficiency of solar panels is directly impacted by their angle and orientation. When panels are installed at the perfect tilt and orientation, they receive the maximum amount of sunlight, resulting in higher efficiency. This allows the panels to effectively convert solar energy into electricity or heat. However, if panels are misaligned or improperly oriented, their efficiency can be significantly reduced. For instance, if the tilt angle is too steep or the panels face the wrong direction, they may not receive sufficient sunlight, leading to reduced energy production. Similarly, if the angle is too shallow or the panels are shaded by nearby obstructions like trees or buildings, their efficiency will suffer. In conclusion, the angle and orientation of solar panels are critical factors that determine their efficiency. Proper alignment ensures that panels receive maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day, optimizing their energy production. Installing panels at the ideal angle and orientation is essential for maximizing efficiency and harnessing the full potential of solar energy.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in disaster relief efforts?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in disaster relief efforts. In fact, they have become increasingly popular and valuable in such situations. When disasters strike, they often disrupt the electricity supply, leaving affected areas without power for days or even weeks. This lack of electricity hampers relief efforts, making it difficult to provide basic necessities like lighting, medical care, communication, and clean water. Solar energy systems, on the other hand, can provide a reliable and sustainable source of power in these situations. They consist of solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power various devices and appliances. These systems can be quickly deployed to disaster-stricken areas, providing immediate access to electricity without relying on traditional power grids. There are several advantages to using solar energy systems in disaster relief efforts. Firstly, solar power is renewable and abundant, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity even during prolonged emergencies. Secondly, solar energy systems are generally low maintenance, reducing the need for constant fuel supply or repairs. This makes them more cost-effective and reliable in disaster-prone areas. Solar energy systems can be used in a variety of ways during disaster relief efforts. They can power mobile charging stations, allowing people to charge their phones and stay connected with their loved ones. Solar-powered lighting can be used to illuminate temporary shelters, hospitals, and walkways, improving safety and security for victims and aid workers alike. Solar energy can also be used to power water purification systems, ensuring a supply of clean drinking water in areas where water infrastructure has been damaged or contaminated. Furthermore, solar energy systems can be integrated into existing relief infrastructure. For example, solar panels can be installed on the roofs of hospitals, schools, and community centers, ensuring a reliable source of electricity for critical operations. This reduces the dependence on diesel generators or other fossil fuel-powered alternatives, which are often expensive, noisy, and emit harmful pollutants. In summary, solar energy systems are highly beneficial in disaster relief efforts. They provide a sustainable and reliable source of power, enabling essential services and improving the overall relief operations. As the world faces more frequent and severe natural disasters, the use of solar energy systems in disaster relief will continue to grow in importance.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be used to power electric vehicles?
- Yes, a solar energy system can be used to power electric vehicles. Solar panels can be installed on a roof or any other suitable surface to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This electricity can then be used to charge the batteries of electric vehicles, providing a clean and renewable source of energy. In fact, many people have already started using solar energy to power their electric cars, creating a sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solution. Additionally, advancements in solar technology have made it more efficient and cost-effective, making it an increasingly viable option for powering electric vehicles.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in areas with extreme temperature fluctuations?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in areas with extreme temperature fluctuations. Solar panels are designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, from extremely high to extremely low. Additionally, advancements in technology have made solar panels more efficient in converting sunlight into electricity, even in harsh climatic conditions. However, it's important to note that extreme temperature fluctuations may affect the overall performance and efficiency of solar panels, so proper maintenance and monitoring are necessary to ensure optimal performance.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering off-grid medical clinics?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used to power off-grid medical clinics. Solar panels can provide a reliable and sustainable source of electricity to run essential medical equipment, lighting, and other critical infrastructure in remote areas where grid connections are unavailable or unreliable. This can greatly enhance healthcare services and improve access to medical care in underserved communities.
- Q: Can solar energy systems power an entire home or business?
- Yes, solar energy systems can indeed power an entire home or business. With advancements in technology and improvements in solar panel efficiency, it is now possible to generate enough electricity from solar energy to meet the energy needs of residential and commercial buildings. By installing an appropriately sized solar panel system and incorporating energy storage solutions, it is feasible to rely solely on solar power for all electricity requirements, making it a sustainable and cost-effective choice for powering homes and businesses.
- Q: Can solar panels be used to power streetlights?
- Yes, solar panels can be used to power streetlights. Solar energy can be converted into electricity and stored in batteries, which can then be used to power the streetlights during the night. This renewable energy source is increasingly being employed to reduce reliance on traditional power grids and promote sustainability.
- Q: Are solar energy systems cost-effective?
- Yes, solar energy systems are cost-effective in the long run. While the initial installation cost may be higher compared to traditional energy sources, solar energy systems can save homeowners and businesses significant amounts of money on their electricity bills over time. Additionally, there are various government incentives and tax credits available that further enhance the cost-effectiveness of solar energy systems. Furthermore, solar energy is a renewable and clean source of power, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and benefiting the environment.
Send your message to us
Solar Energy Systems Wholesale - CNBM On Grid System 40000W with Certificate UL, TUV, CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords