Solar Energy Systems Oman:5kW Off-Grid System for Long Useful Time
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 set
- Supply Capability:
- 2000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Specification
Application:
Home
Output Voltage (V):
220
Solar System 5KW Made in China Off-Grid System
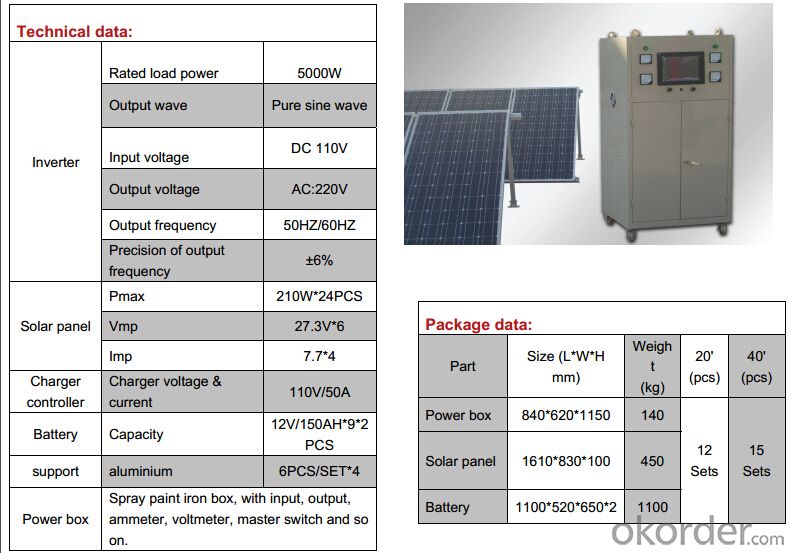
Solar system advantages:
1. CE, ROHS approved.
2. High conversion efficiency, high-transmission rate.
3. Energy saving, environmental-friendly.
4. Advanced technology, strict quality control system.
5. Easy installation, safe operation, free maintenance.
6. Low MOQ, fast delivery time, long service life.
System Device | |
| No | Device name |
| 1 | solar panels |
| 2 | inverter( off grid and on grid) |
| 3 | mounting system |
| 4 | combiner box |
| 5 | cable and other accessories |
| Quick Details | |||||
| Specification: | Mini | Application: | Home | Output Voltage (V): | 72V |
| Load Power (W): | 3.5-4.2KW | Solar Power (W): | 2KW | Work Time (h): | 4-5days |
| Packaging & Delivery | |
| Packaging Detail: | carton pallet |
| Delivery Detail: | within 7 days |
| Specifications | |||||
| 2KW Solar Power System | |||||
| Lifespan >20 years | |||||
| Designed to meet the needs for low power household appliances | |||||
| Base on your situaion ,we design the solar power system as following : | |||||
| 1: PV-system DC voltage level: DC 48V ,ouput AC voltage level: AC220V 50/60HZ | |||||
| 2: load Working time every day: 840W 5hours(3.5-4.2KW*h/day) | |||||
| 3: Primise rainy days: 2 days | |||||
| 4:PV system power Max Input Power: 2KW/DC72V Max AC Output Power: 2000W AC220V 50/60HZ,opration output power:inductive load <=1KW Resistive load:1.6KW | |||||
| 5: PV Array specification: Voc:DC86.4V Vmp:72V Isc:30A Imp:27.8A |
| Name | Type | Number | Remarks |
| MONO-Solar panel | JX200M/36V 1580*808*35mm | 10 | 2KW connection: 2 Series, 5 In parallel |
| Battery | 12V200Ah | 8 | Gel batteries The total capacity:DC48V/400Ah |
| PV-inverter | JX-2KW | 1 | inputDC48V -outputAC220V 50/60HZ,city power automatic switch |
| PV support | JX-S200-10 | 1 | 10 Pcs solar panels use a PV support , Material: Hot -dip galvanized |
| Battery box | JX-C24 | 1 | size:780*800*900mm 4layerdetachable type |
| PV Controller | CM4860 | 1 | DC48V 60A , RS485 communication function |
| PV cable,connect bettwen | PV-1*4.0mm2 | 100 | PV -specific single-core copper 4.0 mm2 cable,Double protection cover 100M |
| Power cable | BVV-1*16mm2 | 50 | single-core copper 16 mm2 cable,Double protection cover |
- Q: Are there any noise concerns associated with solar energy systems?
- While solar energy systems are generally quiet, there are potential noise concerns associated with certain components of the system. The most common source of noise in solar energy systems is the inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used in homes or businesses. Inverters can emit a low humming noise, similar to that of a refrigerator or air conditioning unit, but the noise level is typically very low and not considered disruptive. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of quieter inverters that produce minimal noise. Some inverters are designed with noise reduction features such as soundproof enclosures or fans with low noise levels. Additionally, the location of the inverter can play a role in minimizing noise concerns. Placing the inverter in a well-insulated area, away from living spaces, can further reduce any potential noise disturbances. It's worth noting that other components of a solar energy system, such as the mounting structures or wiring, do not produce any significant noise. Solar panels themselves do not generate noise as they rely on sunlight to generate electricity rather than any moving parts. Overall, while there may be some noise concerns associated with certain components of solar energy systems, advancements in technology and proper installation practices have significantly minimized any potential disruptions.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be installed on schools or educational institutions?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be installed on schools or educational institutions. In fact, many schools and educational institutions around the world have already embraced solar energy systems as a sustainable and cost-effective solution for their energy needs. These systems not only help reduce electricity costs but also provide an opportunity for students to learn about renewable energy and environmental stewardship. Additionally, installing solar panels on educational institutions can serve as a visible commitment to sustainability, inspiring the wider community to adopt clean energy practices.
- Q: I want to put on the roof of the solar system from the building, 100 square meters, daily consumption of 6 to 8 degrees. Some users know how much to install KM? About the cost?
- 2013 PV industry in Europe and the United States antitrust investigation, overcapacity led to the collapse of a large number of photovoltaic industry in Zhejiang, solar prices have fallen. This can be checked at any time online
- Q: Can a solar energy system be installed on a gas station or convenience store?
- A gas station or convenience store can indeed have a solar energy system installed. In fact, many of these establishments have already taken this step to lower their energy expenses and support sustainability. The solar panels can be placed on the roofs of these buildings or in nearby open areas. By doing so, these systems can produce electricity to power the store's lighting, refrigeration systems, and other electrical devices. Furthermore, any excess electricity generated by the solar panels can be redirected into the grid. This allows the gas station or convenience store to earn credits or income through net metering or feed-in tariff initiatives. By installing a solar energy system, these businesses not only reduce their energy bills, but also demonstrate their dedication to renewable energy and minimize their carbon emissions.
- Q: What is the impact of temperature on solar energy system performance?
- The impact of temperature on solar energy system performance is that higher temperatures can decrease the efficiency of solar panels, leading to reduced power output. This is because the materials used in solar panels are sensitive to temperature and can experience a decrease in voltage and current production as temperature increases. Therefore, it is important to consider temperature variations when designing and installing solar energy systems to optimize their performance.
- Q: Are there any risks of electrical short circuits with solar energy systems?
- Solar energy systems, like any other electrical system, have the potential for electrical short circuits. When there is an unintended path of low resistance, a short circuit occurs and allows a large amount of current to flow. This can be caused by faulty wiring, damaged components, or improper installation. Short circuits can lead to overheating, electrical fires, or system damage. The excessive current flow can melt wires, burn insulation, and even harm the solar panels themselves. In extreme cases, short circuits can cause explosions or other dangerous situations. To reduce the risks of short circuits, it is crucial to have qualified professionals install the system according to safety guidelines and local codes. Regular maintenance and inspections are also important for identifying and addressing potential issues. Installing a circuit breaker or fuse within the system can automatically disconnect the circuit in case of a short circuit. Using high-quality components and wiring specifically designed for solar energy systems can also help minimize the risks of short circuits. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for system maintenance and operation. In conclusion, although there are risks of electrical short circuits with solar energy systems, these risks can be effectively managed and minimized through proper installation, regular maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in powering dental clinics or medical clinics?
- Yes, solar energy systems can definitely be used to power dental clinics or medical clinics. Solar energy is a clean, renewable and sustainable source of power that can be harnessed through photovoltaic (PV) panels to generate electricity. These panels convert sunlight into usable energy, which can then be used to power various electrical equipment and appliances in dental or medical clinics. Dental and medical clinics typically require a significant amount of electricity to run their operations, including lighting, air conditioning, medical equipment, computers, and other electrical devices. By installing solar panels, these clinics can reduce their reliance on the traditional power grid and lower their electricity costs. Solar energy systems can be customized to meet the specific energy needs of dental or medical clinics, ensuring that they can operate smoothly and efficiently. The amount of electricity generated by solar panels can be optimized by determining the clinic's energy consumption patterns and installing an adequate number of solar panels to meet the demand. In addition to cost savings, using solar energy systems also has environmental benefits. Solar power is a clean energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants during operation. By switching to solar energy, dental and medical clinics can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier environment. Furthermore, solar panels have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, making them a reliable and durable energy solution for dental and medical clinics. With proper installation and routine inspections, solar energy systems can provide a consistent and uninterrupted power supply for many years. Overall, solar energy systems are a viable and practical option for powering dental or medical clinics. They offer cost savings, environmental benefits, and a reliable source of electricity, enabling clinics to operate efficiently while reducing their impact on the environment.
- Q: How much sunlight do solar panels need to generate electricity?
- Solar panels need direct sunlight for at least 5-6 hours per day to generate a significant amount of electricity.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be used to heat water?
- Yes, a solar energy system can be used to heat water. Solar water heating systems use the sun's energy to heat water through collectors, which are typically installed on the roof. These collectors absorb sunlight and transfer its heat to a fluid, such as water or antifreeze, which is then circulated through pipes to heat water for domestic or commercial use. This process is efficient and environmentally friendly, making solar water heating a popular choice for reducing energy consumption and costs.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering remote monitoring systems?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used for powering remote monitoring systems. Solar panels can generate electricity from sunlight, which can then be stored in batteries or used directly to power remote monitoring equipment. This makes solar energy an ideal and sustainable solution for remote locations where access to electrical grids may be limited or non-existent.
Send your message to us
Solar Energy Systems Oman:5kW Off-Grid System for Long Useful Time
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 set
- Supply Capability:
- 2000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























