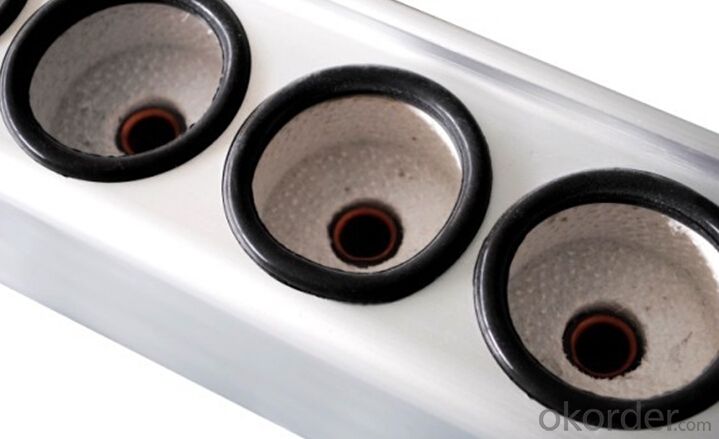
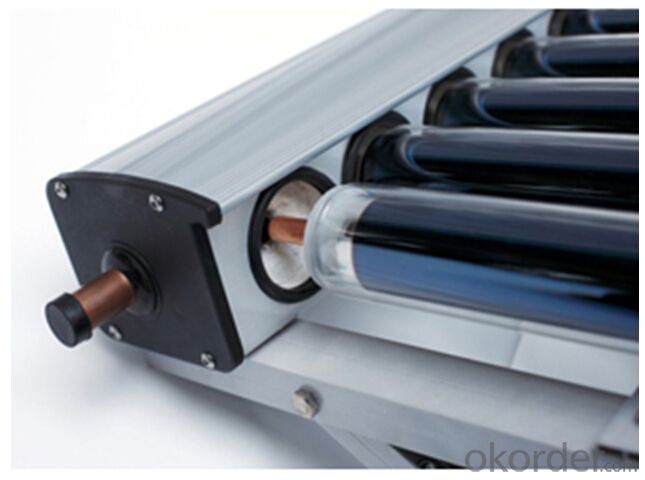
Apricus Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors - Polyurethane Foaming Insulation Model SC-HP
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 set
- Supply Capability:
- 200 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Structure of Polyurethane Foaming Insulation Solar Collector Model SC-HP:
This product is composed of aluminium alloy for frame, polyurethane and aluminium silicate for the insulation,tri-element vacuum glass tube and antifreeze heat pipe. It can work under the environmental temperature from -40℃ to 95℃.The solar collector has the structure as follows:
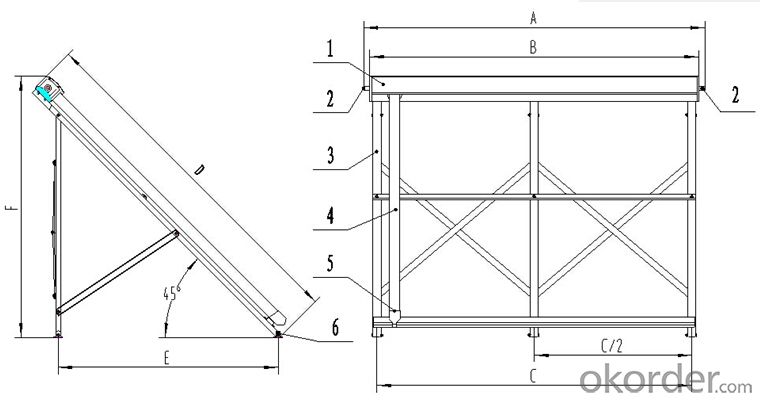
1,Solar collector manifold :
2,Solar collector connector
3,Solar collector bracket
4,All glass vacuum tube:
5,Tube holder
6,Wind feet
2. Main Features of Polyurethane Foaming Insulation Solar Collector Model SC-HP:
The heat insulation properties is higher than for other types of the same collector design
Three layers of insulation incorporated in the mainfold casing :
(1)first and third layer is Aluminium Silicate and resist temperatures of up to 800℃;
(2)second layer is Polyurethane formed by Italian machine that insulates the tanks with a density of 38.5-42;
3. Polyurethane Foaming Insulation Solar Collector Model SC-HP Images:
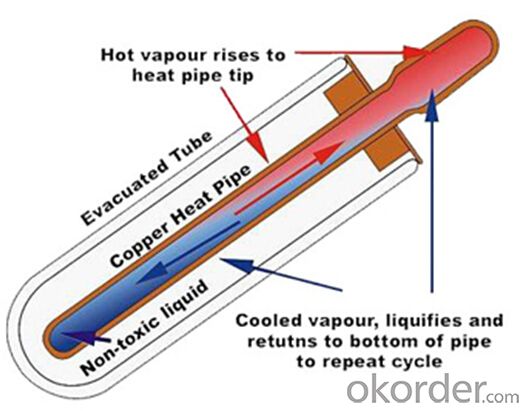
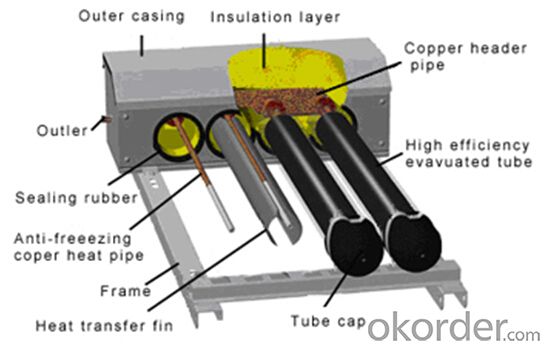
4. Polyurethane Foaming Insulation Solar Collector Model SC-HP Specifications
Model | SC-HP-10 | SC-HP-15 | SC-HP-18 | SC-HP-20 | SC-HP-24 | SC-HP-25 | SC-HP-30 |
SC-H1-10 | SC-H1-15 | SC-H1-18 | SC-H1-20 | SC-H1-24 | SC-H1-25 | SC-H1-30 | |
Vacuum tube quantity(pcs) | 10 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 24 | 25 | 30 |
Tube spacing (㎜) | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 | 75 |
Vacuum tube diameter/length (㎜) | φ58/1700 | φ58/1700 | φ58/1700 | φ58/1700 | φ58/1700 | φ58/1700 | φ58/1700 |
Vacuum tube material | high borosilicate glass 3.3 | high borosilicate glass 3.3 | high borosilicate glass 3.3 | high borosilicate glass 3.3 | high borosilicate glass 3.3 | high borosilicate glass 3.3 | high borosilicate glass 3.3 |
Vacuum tube inner/outer pipe wall thickness (㎜) | 1.6/1.8 | 1.6/1.8 | 1.6/1.8 | 1.6/1.8 | 1.6/1.8 | 1.6/1.8 | 1.6/1.8 |
Heat pipe condensing end diameter/length (㎜) | φ14/1750 | φ14/1750 | φ14/1750 | φ14/1750 | φ14/1750 | φ14/1750 | φ14/1750 |
heat pipe material/wall thickness (㎜) | Copper tp2/0.6 | Copper tp2/0.6 | Copper tp2/0.6 | Copper tp2/0.6 | Copper tp2/0.6 | Copper tp2/0.6 | Copper tp2/0.6 |
inner tank diameter/wall thickness (㎜) | φ35/1.0 | φ35/1.0 | φ35/1.0 | φ35/1.0 | φ35/1.0 | φ35/1.0 | φ35/1.0 |
connector size | φ22 or 3/4″ | φ22or 3/4″ | φ22or 3/4″ | φ22or 3/4″ | φ22or 3/4″ | φ22or 3/4″ | φ22or 3/4″ |
collector insulation material/thickness (㎜) | Polyurethane/40 | Polyurethane/40 | Polyurethane/40 | Polyurethane40 | Polyurethane40 | Polyurethane/40 | Polyurethane/40 |
solar collector rated pressure (MPa) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
collector operating temperature ℃ | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 |
collector volume (L) | 0.69 | 0.98 | 1.15 | 1.27 | 1.50 | 1.56 | 1.85 |
collector aperture area (㎡) | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 3.0 |
collector total area (㎡) | 1.56 | 2.30 | 2.74 | 3.04 | 3.63 | 3.77 | 4.51 |
referral traffic (L/min) | 0.75 | 1.13 | 1.35 | 1.50 | 1.81 | 1.88 | 2.26 |
intensity pressure (Pa) | 23.2 | 59.2 | 90.6 | 116.7 | 181.7 | 200.2 | 314.0 |
intercept efficient η0 | 0.744 | 0.744 | 0.744 | 0.744 | 0.744 | 0.744 | 0.744 |
heat loss coefficient a | 2.09 | 2.09 | 2.09 | 2.09 | 2.09 | 2.09 | 2.09 |
collector power (W)1000W/㎡ irradiation | 620 | 870 | 1047 | 1165 | 1401 | 1457 | 1748 |
collector net weight (kg) | 38.25 | 50.75 | 59.75 | 64.75 | 79.00 | 83.35 | 98.70 |
a (㎜) | 895 | 1270 | 1495 | 1645 | 1945 | 2020 | 1395 |
b (㎜) | 800 | 1175 | 1400 | 1550 | 1850 | 1925 | 2300 |
c (㎜) | 725 | 1100 | 1325 | 1475 | 1775 | 1850 | 2225 |
c/2 (㎜) | —— | —— | —— | —— | 887.5 | 925 | 1112.5 |
d (㎜) | 1980 | 1980 | 1980 | 1980 | 1980 | 1980 | 1980 |
e (㎜) | 1240 | 1240 | 1240 | 1240 | 1240 | 1240 | 1240 |
f (㎜) | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 | 1470 |
5. FAQ
(1) Which collector is the best value for money?
Rather than looking at just peak efficiency levels when comparing solar collectors, cost per unit of energy produced is much more logical. For example: Although collector A may be 20% more efficient than collector B, if collector A is 30% more expensive, then in fact collector B may be a better choice, as per kWh of energy produced per day it is cheaper. When payback time is of concern, not only price per kWh of the product is important, but also of the end system.
(2) Can this solar collectors be used for a large scale hot water production?
Yes. This solar collectors can be connected in series or parallel to provide large scale hot water production for a commercial settings such as a school, hotel or office building. There is really no limit to the size of the system, however collectors must be installed in banks of no more than 150 tubes (in series), otherwise the water may boil.
(3) What maintenance of the solar collector is required?
Under normal circumstances no maintenance of the system is required. Due to the shape of the tubes regular rainfall and wind should keep the tubes clean. Should a tube even be broken it should be replaced. This, however, is an inexpensive and easy job. Any "handy" person can install a new tube (while adhering to local health and safety regulations). Sidite solar collectors can operate with several broken tubes, however the efficiency will be reduced slightly.
- Q: Can solar collectors be used in wind farms?
- No, solar collectors cannot be used in wind farms as they are designed specifically to harness the energy from sunlight and not wind. Wind farms utilize wind turbines to generate electricity from the kinetic energy of wind.
- Q: Can solar collectors be used to generate electricity during nighttime hours?
- No, solar collectors cannot be used to generate electricity during nighttime hours. Solar collectors rely on sunlight to generate electricity, as they convert sunlight into usable energy. At night, when the sun is not shining, there is no source of sunlight available for the solar collectors to generate electricity. However, there are alternative methods to generate electricity during nighttime hours, such as using batteries to store excess solar energy generated during the day for later use.
- Q: Can solar collectors be used in areas with limited skilled labor?
- Yes, solar collectors can be used in areas with limited skilled labor. Solar collectors are relatively simple to install and maintain, requiring basic technical knowledge. Additionally, many manufacturers provide training and resources to support the installation and maintenance process. Furthermore, there are organizations and initiatives aimed at promoting solar energy in developing regions, which often include capacity-building programs to train local individuals in the necessary skills.
- Q: Are there any fire risks associated with solar collectors?
- Yes, there are some fire risks associated with solar collectors. While solar collectors themselves do not produce heat or flames, the electrical components used in solar panel systems can pose a fire hazard if not installed or maintained properly. Additionally, if debris such as leaves or branches accumulate around the panels, it can increase the risk of fire. However, with proper installation, regular maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines, these risks can be minimized.
- Q: Can solar collectors be used in areas with limited space?
- Yes, solar collectors can be used in areas with limited space. There are various types of solar collectors, including rooftop solar panels, solar water heaters, and solar concentrators, which can all be installed in small spaces like rooftops, balconies, or even walls. Additionally, advancements in solar technology have led to the development of more compact and efficient solar collectors, making them suitable for areas with limited space.
- Q: Are solar collectors suitable for schools and universities?
- Schools and universities can benefit greatly from the use of solar collectors. These devices, like solar panels, are an eco-friendly and sustainable way to generate energy. When installed in educational institutions, such as schools and universities, solar collectors offer numerous advantages. To start, solar collectors can help these institutions reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more environmentally-conscious future. By harnessing the power of the sun, schools and universities can generate clean energy, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns perfectly with the educational mission of these institutions, as it allows them to educate students on renewable energy and sustainable practices. In addition, solar collectors can lead to significant cost savings for schools and universities. Educational institutions typically have high energy demands, with many buildings and facilities requiring electricity. By installing solar collectors, these institutions can produce their own electricity, reducing their dependence on the grid and lowering their energy bills. As time goes on, the savings from using solar energy can be substantial, allowing schools and universities to allocate more resources to educational programs and initiatives. Furthermore, solar collectors can serve as educational tools themselves. By integrating solar energy systems into the curriculum, students can learn about renewable energy technology, energy efficiency, and the science behind solar power. This hands-on learning experience can enhance students' understanding of sustainable practices and inspire them to pursue careers in renewable energy or related fields. Moreover, solar collectors can act as a visual representation of an educational institution's commitment to sustainability. By showcasing their use of clean energy, schools and universities can inspire their students, staff, and the surrounding community to adopt more eco-friendly practices. This can foster a culture of sustainability within the institution and contribute to a positive image in the community. In conclusion, solar collectors are highly suitable for schools and universities. They provide a sustainable energy source, reduce carbon emissions, and offer significant cost savings. Additionally, they serve as educational tools and promote a culture of sustainability. By embracing solar energy, educational institutions can demonstrate their dedication to a greener future while providing valuable learning opportunities for their students.
- Q: Are solar collectors easy to install?
- Yes, solar collectors are relatively easy to install. They require basic tools and can be installed on rooftops or in open spaces. However, professional installation is recommended to ensure optimal positioning and performance.
- Q: Can solar collectors be used to generate electricity for remote communication systems?
- Yes, solar collectors can definitely be used to generate electricity for remote communication systems. Solar collectors, also known as solar panels or photovoltaic systems, convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This makes them a highly suitable and efficient source of power for remote communication systems that are typically located in areas with limited access to the main power grid. The use of solar collectors for remote communication systems offers several advantages. Firstly, solar power is a renewable and sustainable energy source, meaning it relies on the abundance of sunlight rather than depletable resources like fossil fuels. This makes it an environmentally friendly choice for powering communication systems in remote locations. Furthermore, solar collectors require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a reliable and cost-effective solution for remote areas. They can be installed on rooftops, poles, or even compactly integrated into the design of the communication system itself. This flexibility allows for easy deployment in various remote locations, including rural areas, mountaintops, deserts, and offshore installations. Solar collectors can generate electricity even in low light conditions, thanks to advancements in solar technology. This ensures a continuous power supply for remote communication systems, even during cloudy or overcast days. Additionally, excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours can be stored in batteries for use during periods of low sunlight or at night, providing uninterrupted power to the communication system. Overall, the use of solar collectors for remote communication systems is a practical and sustainable solution. It enables reliable and independent power generation, reduces reliance on traditional energy sources, and contributes to the overall goal of achieving energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
- Q: Can solar collectors be used in grid-tied systems?
- Solar collectors are indeed capable of being utilized in grid-tied systems. By employing solar collectors in a grid-tied system, one can effectively capture solar energy and convert it into electrical power. This electrical power can subsequently be utilized to operate various household appliances, lighting fixtures, and other electrical devices. Additionally, any surplus electricity produced by the solar collectors can be returned to the grid, enabling the homeowner to receive credits or payments from the utility company. Grid-tied systems integrated with solar collectors are a highly favored option among homeowners seeking to diminish their reliance on fossil fuels, decrease electricity expenses, and contribute to the development of a more sustainable energy landscape.
- Q: Can solar collectors be used for agricultural purposes?
- Yes, solar collectors can be used for agricultural purposes. Solar collectors can provide renewable energy to power various agricultural operations such as irrigation systems, livestock watering, greenhouse heating, and crop drying. They can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels, lower energy costs, and contribute to a sustainable and eco-friendly farming approach.
Send your message to us
Apricus Evacuated Tube Solar Collectors - Polyurethane Foaming Insulation Model SC-HP
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 set
- Supply Capability:
- 200 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords