Oil Drill Pipe with API Spec 5DP Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Structure of Oil Drill Pipe Description
We can supply all kinds of drill pipes that are consistent with API SPEC 5DP. Advanced drill pipe production lines can transfer the welding parameters to the best position to ensure the quality of welding zone; the heat treatment process with the feature of internal and external cooling at the same time can make a more reliable and stable mechanical character. Application of automatic weight, length measurement and automatic spray records can ensure products' traceability. Application of thickening and heating lines and 1250 tons of upsetting machine can ensure the thickening size meet the standard of API SPEC 5DR Using of CN furnace for whole pipe body heating and quenching, tempering machine's advanced heat treatment process can ensure the pipe's mechanical character. Tube hydraulic straightening machine ensures the straightness and coaxiality of pipe body.
2. Main Features of Oil Drill Pipe
1) Advanced test for quality
2) MTC provided
3) API Standard
3. Oil Drill Pipe Images



4. Oil Drill Pipe Specification
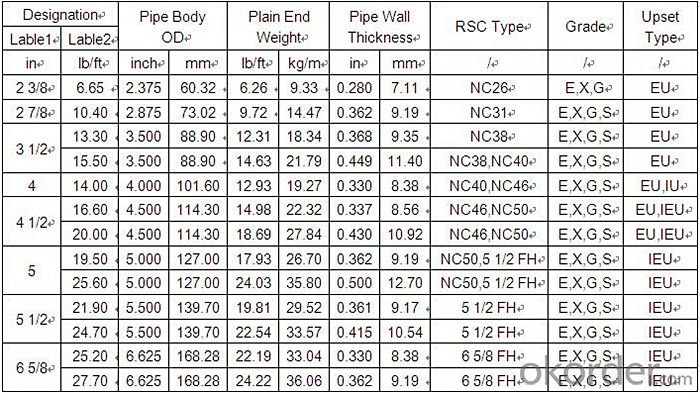
5. FAQ of Oil Drill Pipe
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
①How about your company?
One of the leading manufacturers and suppliers specializing in drill pipe products in China, mainly offering drill pipes including oil drill pipe, water well drill pipe, flat drill pipe, geological drill pipe and non-dig drill pipe.
Other than drill pipes we are also capable of supplying a wide variety of pipeline accessories, drill joints, steel pipe fittings, valves etc. consists of our one-stop sales. The integrated sales & service ensures customers with various demands an easier access for purchasing management.
②How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
③How long can we receive the product after purchase?
In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible.
- Q: What are the different types of steel pipe coatings for nuclear power plants?
- There are several types of steel pipe coatings used in nuclear power plants, including epoxy coatings, polyethylene coatings, fusion bonded epoxy coatings, and coal tar enamel coatings. These coatings are applied to steel pipes to provide protection against corrosion, enhance durability, and maintain the integrity of the pipes in the demanding environment of nuclear power plants.
- Q: Is steel pipe made of profiles?
- In accordance with the different smelting quality of steel, steel is divided into ordinary steel and high quality steel. According to the current catalogue of metal products, ordinary steel can be divided into large section steel, medium section steel and small section steel. The section steel can be divided into I-beam, channel steel, angle steel, round steel and so on according to its sectional shape.
- Q: What are the different coatings used on steel pipes?
- There are several different coatings used on steel pipes, including but not limited to epoxy coatings, polyethylene coatings, zinc coatings, and galvanized coatings.
- Q: How are steel pipes measured and specified?
- Several key parameters are used to measure and specify steel pipes. These parameters include the outer diameter (OD), wall thickness, and length of the pipe. The outer diameter is the measurement of the pipe's outside surface from one end to the other. It is typically expressed in millimeters or inches and plays a critical role in determining the pipe's strength and carrying capacity. Different applications require different OD sizes, which can range from a few millimeters to several feet. The wall thickness refers to the distance between the pipe's outer and inner surfaces. It is measured in millimeters or inches and is crucial for determining the pipe's durability and resistance to pressure. Thicker walls can handle higher pressure, making them suitable for applications that require transporting liquids or gases under high pressure. Steel pipes are generally specified in meters or feet for their length. Standard pipe lengths are often 6 or 12 meters (20 or 40 feet), but custom lengths can be requested based on project requirements. It is important to note that longer pipes may require additional support to prevent sagging or structural issues. In addition to these primary measurements, steel pipes may also be specified based on other factors such as material grade, manufacturing standard, and surface finish. Material grade refers to the quality and composition of the steel used in the pipe, determining its strength and corrosion resistance. Manufacturing standards, such as ASTM or API, ensure that the pipes meet specific quality and performance criteria. Surface finish specifications may include factors like galvanized coating, providing protection against corrosion or other specific requirements based on the intended application. Overall, the measurement and specification of steel pipes involve considering the outer diameter, wall thickness, length, material grade, manufacturing standard, and surface finish. These parameters are crucial in determining the suitability of the pipe for various applications and ensuring its performance and durability in different environments.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for sewage treatment plants?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for sewage treatment plants. Steel pipes are durable and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for handling sewage and wastewater in such facilities. They are commonly used for conveying and distributing sewage, as well as for constructing various components like pipelines, pump stations, and treatment tanks. Additionally, steel pipes can withstand high pressure and are available in various sizes, making them suitable for the diverse needs of sewage treatment plants.
- Q: Seamless steel tube DN15 specification phi 18*3 what do you mean?
- Seamless steel pipe having a hollow cross section, used as a conduit for conveying fluids, such as pipelines for transporting petroleum, natural gas, gas, water, and certain solid materials. Compared with solid steel such as round steel, steel tube is lighter in strength and equal in resistance to bending and torsion. It is an economical cross section steel and is widely used in the manufacture of structural and mechanical parts.
- Q: How do you determine the maximum allowable stress for steel pipes?
- In order to establish the maximum allowable stress for steel pipes, several factors must be taken into account. These factors encompass the type of steel, the dimensions of the pipe, and the operating conditions it will be exposed to. To begin with, the type of steel chosen is a pivotal aspect in determining the maximum allowable stress. Different steel grades possess distinct mechanical properties, including yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation. These properties define the steel's capacity to withstand stress before deforming or failing. Hence, it is crucial to comprehend the specific grade of steel employed in the pipes to ascertain the maximum allowable stress. Additionally, the dimensions of the pipe are of utmost importance. The external diameter, wall thickness, and length all impact the pipe's strength and ability to handle stress. By calculating the cross-sectional area and moment of inertia, engineers can evaluate the pipe's resistance to bending and axial stresses. These calculations, combined with the material properties, facilitate the determination of the maximum allowable stress. Finally, the operating conditions under which the pipe will be utilized play a critical role. Variables such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of corrosive substances can significantly influence the maximum allowable stress of a steel pipe. Elevated temperatures can alter the mechanical properties of the steel, while high pressures can induce additional stress. Furthermore, the presence of corrosive substances can lead to material degradation and diminish the pipe's strength. Thus, considering these operational factors is essential when determining the maximum allowable stress. To summarize, the process of establishing the maximum allowable stress for steel pipes entails assessing the specific steel grade, the pipe's dimensions, and the operating conditions. By analyzing these factors, engineers can ensure that the steel pipe is designed and utilized within its safe stress limits.
- Q: What is the difference between steel pipe and ductile iron pipe?
- Steel pipe and ductile iron pipe are both commonly used in various industries for transporting fluids and gases. However, there are some key differences between the two materials. One of the main differences is their composition. Steel pipe is made primarily of iron and carbon, with other alloying elements added to enhance its strength and corrosion resistance. On the other hand, ductile iron pipe is a form of cast iron that has been treated to improve its ductility and toughness. It contains higher amounts of carbon and silicon, along with small amounts of other elements such as magnesium and copper. Another difference is their strength and durability. Steel pipe is known for its high strength and can withstand higher pressures and stresses compared to ductile iron pipe. It is also more resistant to impact and bending, making it suitable for applications where high strength is required. Ductile iron pipe, although not as strong as steel, still offers good strength and durability, especially in applications where there is a risk of external damage or heavy loads. Corrosion resistance is another factor to consider. Steel pipe is typically more resistant to corrosion due to the addition of alloying elements such as chromium and nickel. This makes it suitable for applications where there is a high risk of corrosion, such as pipelines carrying corrosive fluids. Ductile iron pipe, while also having some corrosion resistance, may require additional protective coatings to enhance its durability in corrosive environments. Installation and maintenance are also different for these two types of pipes. Steel pipe is generally lighter and easier to handle, making it easier to install. It can also be welded, which allows for more flexibility in the construction process. Ductile iron pipe, being a cast iron material, requires more specialized installation techniques, such as using mechanical joints or flanges. It is also more prone to cracking during installation if not handled properly. In terms of cost, steel pipe is generally more expensive than ductile iron pipe. This is due to the higher cost of raw materials and the additional processing required to produce steel pipe. However, it is important to consider the overall lifecycle cost, as steel pipe's higher strength and corrosion resistance may result in lower maintenance and replacement costs in the long run. In summary, while both steel pipe and ductile iron pipe have their own advantages and applications, the choice between the two depends on factors such as strength requirements, corrosion resistance, installation methods, and budget considerations. Careful consideration of these factors will help determine which pipe material is most suitable for a specific application.
- Q: What are the different manufacturing standards for steel pipes?
- Various manufacturing standards for steel pipes are widely recognized and implemented in the industry, ensuring that specific requirements and quality standards are met. Some of the most common standards for steel pipes are as follows: 1. ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials): Widely used in the United States, ASTM standards encompass a wide range of steel pipe specifications. These standards include specifications for seamless and welded pipes, as well as different grades and dimensions. 2. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Globally recognized, ISO standards provide guidelines for steel pipe production. They cover areas such as dimensions, materials, testing, and quality control. 3. EN (European Norm): Applicable in Europe, EN standards specify various types of steel pipes. They cover dimensions, materials, manufacturing processes, and testing. 4. JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards): Widely used in Japan and internationally recognized, JIS standards cover dimensions, materials, and testing methods for steel pipes. 5. BS (British Standards): Commonly used in the United Kingdom, BS standards encompass a range of steel pipe specifications. They include requirements for dimensions, materials, and testing procedures. 6. API (American Petroleum Institute): Specifically developed for the oil and gas industry, API standards cover different aspects of steel pipe manufacturing. They include specifications for seamless and welded pipes used in oil and gas exploration, production, and transportation. Manufacturers, buyers, and users of steel pipes should be aware of these standards to ensure the quality, compatibility, and reliability of the pipes. Compliance with these standards helps to ensure that the steel pipes meet necessary requirements and are suitable for their intended applications.
- Q: 25 of the steel pipe with 6 in charge of what is the difference?
- 25 of the steel pipe with 6 in charge of the difference:25 of the steel pipe refers to the DN25 tube, the outer diameter of 25mm; 6, in charge of refers to DN20 steel pipe, the outer diameter is 20mm.
Send your message to us
Oil Drill Pipe with API Spec 5DP Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























