Solar Energy Systems Fort Pierce FL CNBM On Grid System 700W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
CNBM On Grid System 700W with Certificate UL TUV CE
Product description
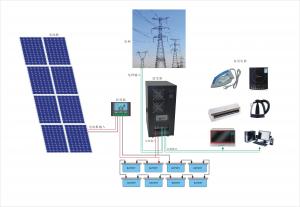
A grid-connected photovoltaic power system, or grid-connected PV system is anelectricity generating solar PV system that is connected to the utility grid. A grid-connected PV system consists of solar panels, one or several inverters, a power conditioning unit and grid connection equipment. They range from small residential and commercial rooftop systems to large utility-scale solar power stations. Unlike stand-alone power systems, a grid-connected system rarely includes an integrated battery solution, as they are still very expensive. When conditions are right, the grid-connected PV system supplies the excess power, beyond consumption by the connected load, to the utility grid.
Connection of the photovoltaic power system can be done only through an interconnection agreement between the consumer and the utility company. The agreement details the various safety standards to be followed during the connection.[4]
Solar energy gathered by photovoltaic solar panels, intended for delivery to a power grid, must be conditioned, or processed for use, by a grid-connected inverter. Fundamentally, an inverter changes the DC input voltage from the PV to AC voltage for the grid. This inverter sits between the solar array and the grid, draws energy from each, and may be a large stand-alone unit or may be a collection of small inverters, each physically attached to individual solar panels. See AC Module. The inverter must monitor grid voltage, waveform, and frequency. One reason for monitoring is if the grid is dead or strays too far out of its nominal specifications, the inverter must not pass along any solar energy. An inverter connected to a malfunctioning power line will automatically disconnect in accordance with safety rules, for example UL1741, which vary by jurisdiction. Another reason for the inverter monitoring the grid is because for normal operation the inverter must synchronize with the grid waveform, and produce a voltage slightly higher than the grid itself, in order for energy to smoothly flow outward from the solar array.

Application
Industrial
Commercial
Residential
Feature
Residential, grid-connected rooftop systems which have a capacity more than 10 kilowatts can meet the load of most consumers.[2] They can feed excess power to the grid where it is consumed by other users. The feedback is done through a meter to monitor power transferred. Photovoltaic wattage may be less than average consumption, in which case the consumer will continue to purchase grid energy, but a lesser amount than previously. If photovoltaic wattage substantially exceeds average consumption, the energy produced by the panels will be much in excess of the demand. In this case, the excess power can yield revenue by selling it to the grid. Depending on their agreement with their local grid energy company, the consumer only needs to pay the cost of electricity consumed less the value of electricity generated. This will be a negative number if more electricity is generated than consumed.[3] Additionally, in some cases, cash incentives are paid from the grid operator to the consumer.
Packaging
With carton and box
- Q: What is the lifespan of solar energy inverters?
- Solar energy inverters can have varying lifespans due to factors such as the inverter's quality, usage, and maintenance. Generally, a solar energy inverter that is of high quality and properly maintained can last approximately 10 to 15 years. However, thanks to technological advancements and enhanced durability, certain inverters can endure for 20 years or even more. It is crucial to bear in mind that regular maintenance, including thorough cleaning and inspection, can assist in prolonging the inverter's lifespan. Furthermore, selecting a reputable brand and ensuring correct installation can also contribute to an extended lifespan for solar energy inverters.
- Q: How do solar energy systems impact energy reliability?
- Solar energy systems can have a positive impact on energy reliability by diversifying the energy mix and reducing dependence on traditional fossil fuel-based power sources. By harnessing the abundant and renewable energy from the sun, solar systems can contribute to a more stable and consistent energy supply, especially when combined with energy storage technologies. This not only reduces the risk of power outages and disruptions but also enhances the overall resilience and reliability of the energy grid.
- Q: Are there any tax credits available for installing a solar energy system?
- Yes, there are tax credits available for installing a solar energy system. The federal government offers a Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) which allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of installing a solar energy system from their federal taxes. As of 2021, the ITC offers a 26% tax credit for systems installed through the end of 2022. However, it is important to note that the tax credit will decrease to 22% in 2023 and will only apply to commercial installations. Additionally, some states also offer their own tax incentives for solar energy systems, such as tax credits, rebates, or exemptions. It is recommended to check with your state or local government to determine if there are any specific tax credits available in your area.
- Q: Can a solar energy system be used to power electric vehicles?
- Yes, a solar energy system can be used to power electric vehicles. Solar panels can be installed on a roof or any other suitable surface to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This electricity can then be used to charge the batteries of electric vehicles, providing a clean and renewable source of energy. In fact, many people have already started using solar energy to power their electric cars, creating a sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solution. Additionally, advancements in solar technology have made it more efficient and cost-effective, making it an increasingly viable option for powering electric vehicles.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in areas with limited space on rooftops due to existing equipment or structures?
- Solar energy systems can still be utilized in areas with limited rooftop space due to existing equipment or structures. In such instances, alternative approaches can be employed to optimize the use of available space. One possibility is to opt for ground-mounted systems rather than rooftop installations. These systems can be positioned in open areas adjacent to buildings or even on unused land nearby. Moreover, solar canopies or awnings can be set up in parking lots or other open spaces to generate solar power. These structures can be designed to offer shade and shelter while simultaneously harnessing solar energy. Consequently, even in areas with limited rooftop space, there are diverse and innovative options to implement solar energy systems.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering electric train systems?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used to power electric train systems. Solar panels can be installed along the train tracks or on the rooftops of train stations to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. This clean and renewable energy source can be utilized to charge the train's batteries or directly power the electric motors, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and reducing carbon emissions.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering mining operations?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used for powering mining operations. Solar panels can be installed on-site to generate electricity, which can then be used to power various mining equipment and operations. This can help reduce reliance on traditional energy sources, lower operating costs, and minimize the environmental impact of mining activities.
- Q: How does the efficiency of solar panels vary across different installation locations?
- The efficiency of solar panels varies across different installation locations due to various factors such as the amount of sunlight received, the angle and orientation of the panels, shading, temperature, and local weather conditions.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering off-grid communities?
- Yes, solar energy systems can definitely be used for powering off-grid communities. They provide a reliable and sustainable source of electricity in remote areas where grid connection is not feasible or economically viable. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which can be stored in batteries for use during nighttime or cloudy days. This makes solar energy an ideal solution for off-grid communities, as it reduces their dependence on fossil fuels and helps in achieving energy independence.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used off-grid?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used off-grid. Off-grid solar systems are designed to generate and store electricity from sunlight, allowing users to power their homes or facilities without relying on the traditional power grid. These systems typically include solar panels, batteries for energy storage, and inverters to convert DC power from the panels into AC power for use. Off-grid solar systems are particularly useful in remote locations or areas with unreliable or no access to electricity, providing a sustainable and independent source of power.
Send your message to us
Solar Energy Systems Fort Pierce FL CNBM On Grid System 700W with Certificate UL TUV CE
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords