5p/Ps Steel Billets Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
5p/Ps Steel Billets Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Specification
Steel billet(ingot) by cogging or breakdown of semi-finished products, is the raw material of all kinds of steel mill. Billet section of square, round, flat, rectangular and abnormity of several kinds of, mainly related to the shape of rolled products.
CNBM Q235,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi Billets Steel
Hot Rolled Steel Billets/ Mild Steel Bar/ Billet Steel
Specification (see below)
Standard: GB/JIS/ASTM
Size: 50*50mm-180*180mm
Length: 3-12mtrs or Customised
Steel material: Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
Technique: Hot rolled
FOB Unit Ton Price $250-350 and Usually I will quote you CFR price.
MOQ: Usually 1000-10000MT/size
Shipment:By Container,Bulk Vessel
Packaging Details: bundles with steel strips or as customers's requirements
Delivery time: Usually within 30 days after the deposit/LC
Inspection:Third party inspection before loading.
Technical data
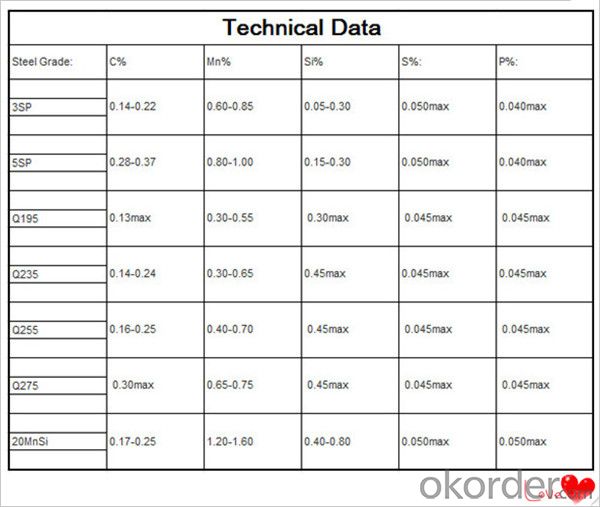
Feature Steel Billet
Rectangular billet continuous casting billet and mainly general carbon steel, low carbon low silicon cold-rolled material, high quality carbon structural steel, high strength low alloy steel, special steel, etc.
The billet is mainly divided into two kinds from the shape:
Slab: cross section width and height of the ratio of the larger, mainly used for rolling plate.
Billet: equal cross section width and height, or a huge difference, mainly used for rolling steel, wire rod. ,
Steel billets have distinct characteristics as compared with already furnished steel bars and products. Billets have a specific grain structure, which enables the metal to be processed more intricately. Steel billets are also known for their malleability and ductility, especially when exposed to varying temperatures during shaping and molding.
Packaging & Shipping
1. Packaging:
1) Small size: in bundles
2)Big size: in bulk
3)in plastic packing or as per customer requirement
2. Delivery time:
1) Normal size: within 7days send from warehouse directly
2) Special size: with 25-30days customer made for you
3. Trade terms:FOB/CFR/CIF
4. Shippment:
1) length:≤5.8m loaded in 20FT Container with 25-27tons
2) length:≤11.8m loaded in 40FT Container with 25-27tons
3) lengnth:≥12m shipped by bulk vessel, FILO terms
Steel Billet Images
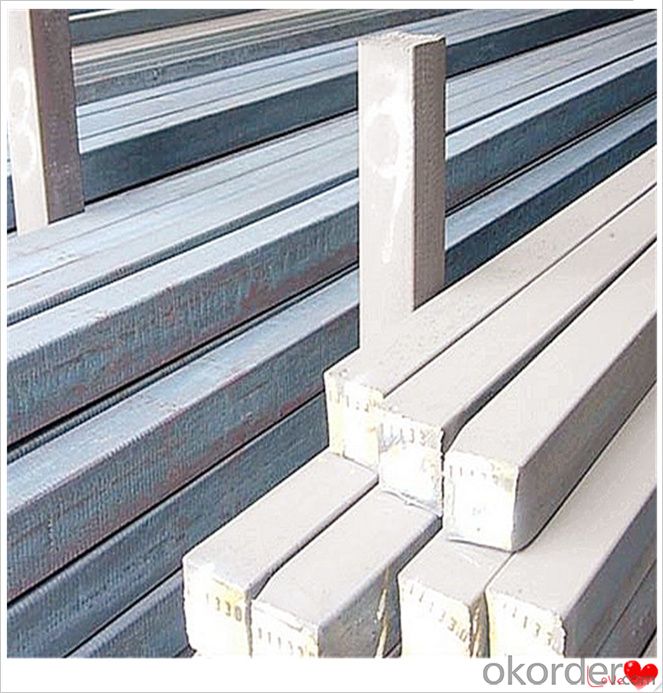
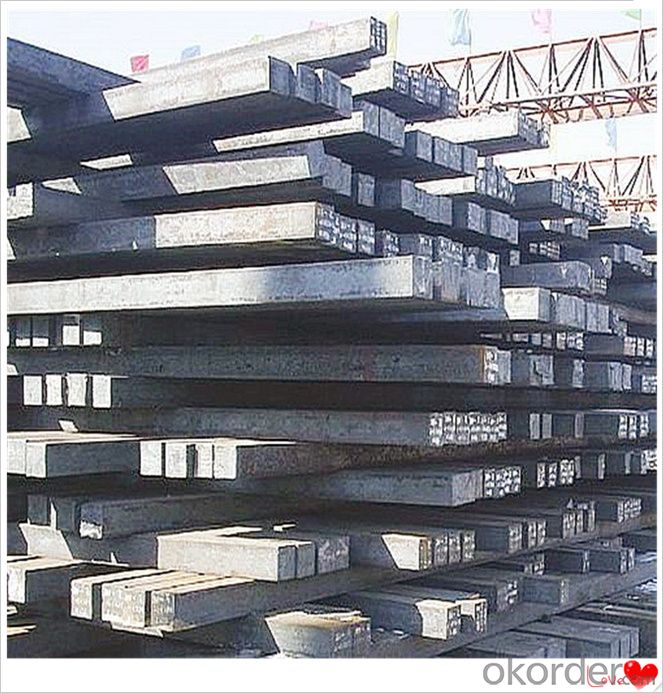
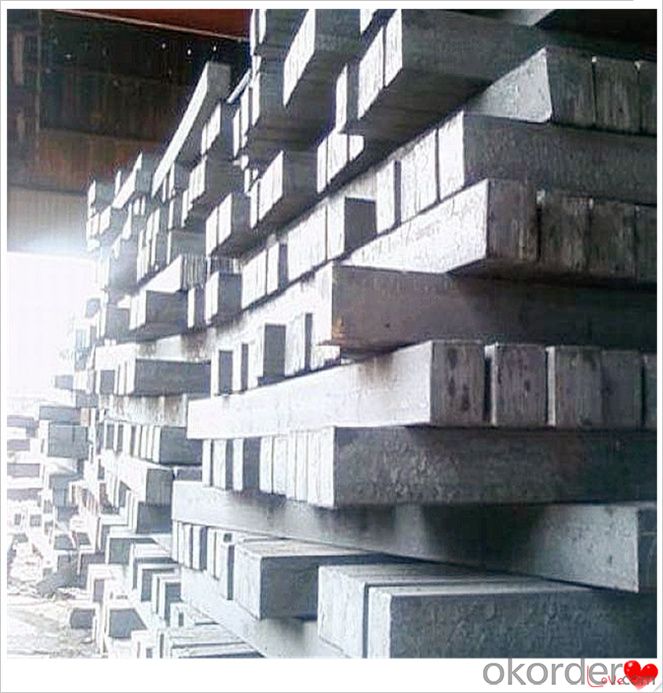
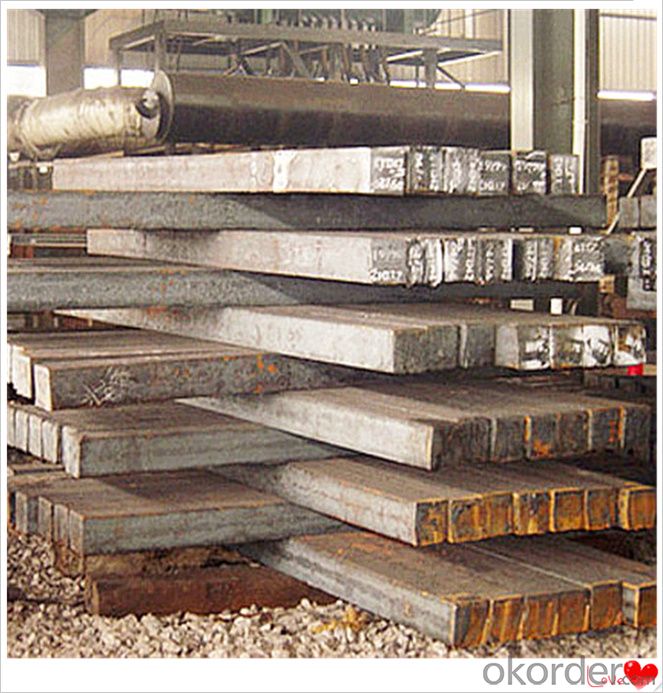
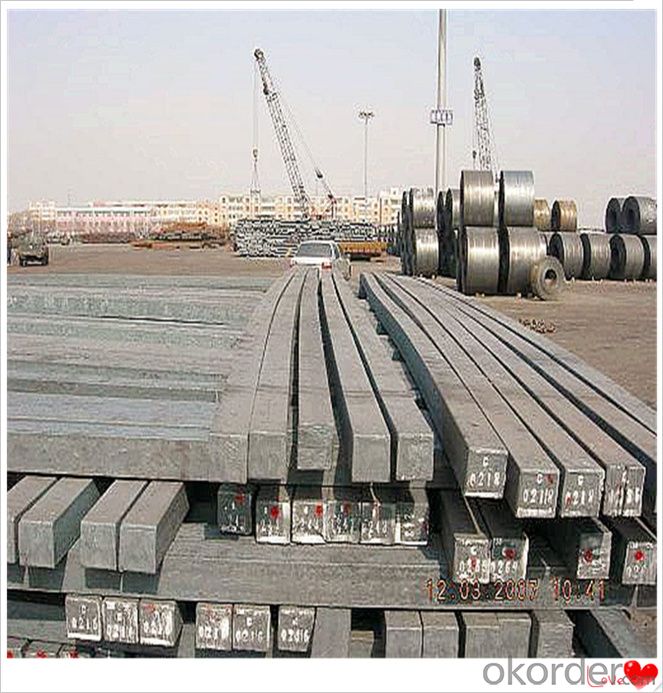






Processing
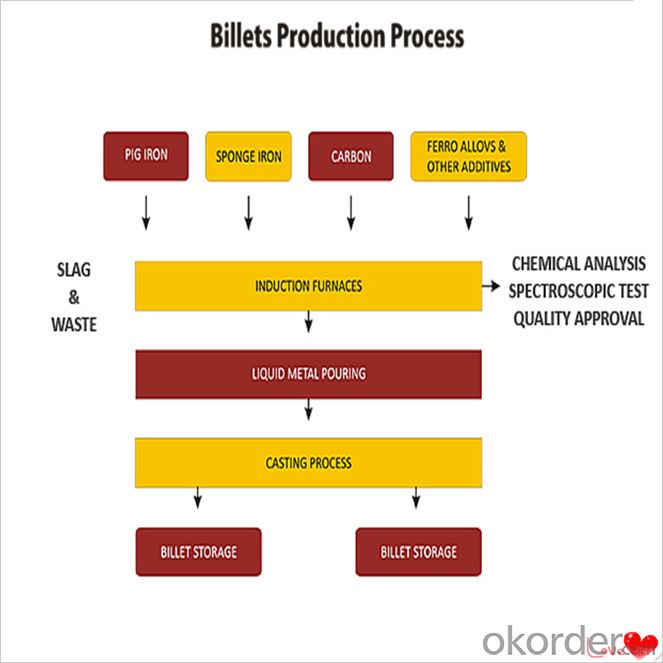
Usage-Billet Steel
Used for the plant, the bridge,shipment building high-rise building construction,lifting and transportation machinery, equipment manufracturing base building the support foundation pile manufacturing.
Billets, or ingots (as they sometimes referred to), are not of practical use until they have been formed into more functional shapes and sizes. While they have already been put in the furnace, they still require a series of shaping and molding procedures such as hot and cold working, milling and cutting before they are sold in hardware stores, or used for different applications. The unformed billets, however, can be used in striking currency such as coins and as reserves, similar to gold bars.
FAQ-Billet Steel
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1) How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2) How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3) How long can we receive the product after purchase?
In the purchase of product within three working days, We will arrange the factory delivery as soon as possible. The pecific time of receiving is related to the state and position of customers.Commonly 7 to 10 working days can be served.
4)Do you have your own QC department?
Yes, we have, our QC department will inspect the goods during the process of mass production and after completion of production.
hot sale!!! Cast Steel Grades/ mild steel bar/ billet steel
(1): High quality steel with reasonable price.
(2): Wide excellent experiences with after-sale service.
(3): Every process will be checked by responsible QC which insures every product's quality.
(4): Professional packing teams which keep every packing safely.
(5): Trial order can be done in one week.
(6): Samples can be provided as your requirements.
- Q:What are the main differences between carbon steel and alloy steel billets?
- Carbon steel and alloy steel billets are both types of steel used in various industries, but they have some key differences. The main difference between carbon steel and alloy steel billets lies in their composition. Carbon steel billets are primarily made up of iron and carbon, with carbon content usually ranging from 0.05% to 2.1%. This makes carbon steel relatively more affordable and easier to produce compared to alloy steel. On the other hand, alloy steel billets contain additional elements like manganese, nickel, chromium, and molybdenum, which are added to enhance specific properties of the steel. These alloying elements give alloy steel superior strength, hardness, and resistance to corrosion compared to carbon steel. Another major difference between carbon steel and alloy steel billets is their mechanical properties. Carbon steel billets are generally known for their high ductility and ability to be easily shaped or formed, making them suitable for applications that require flexibility and easy machinability. Alloy steel billets, on the other hand, have higher tensile strength, toughness, and wear resistance due to the presence of alloying elements. This makes alloy steel billets ideal for applications that require high strength and resistance to wear, such as in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries. Furthermore, the heat treatment process for carbon steel and alloy steel billets also differs. Carbon steel billets are often heat-treated to improve their hardness and strength, with common treatments including quenching and tempering. Alloy steel billets, on the other hand, can undergo a wider range of heat treatment processes, including annealing, normalizing, and precipitation hardening. These heat treatments help to optimize the properties of alloy steel billets for specific applications, such as increasing strength or improving machinability. In summary, the main differences between carbon steel and alloy steel billets lie in their composition, mechanical properties, and heat treatment processes. Carbon steel is primarily made up of iron and carbon, while alloy steel contains additional alloying elements. Carbon steel has high ductility and is easily shaped, while alloy steel has superior strength, hardness, and resistance to corrosion. The heat treatment processes for these two types of steel also differ, with alloy steel having a wider range of treatment options.
- Q:Charcoal classification
- Hard charcoal. By hardwood such as Fagaceae Quercus, Castanopsis trees, secondary birch and etc..Broad-leaved charcoal. Charcoal made from a mixture of hard and soft hardwood.Pine charcoal. Carbon fired from pine or other needle wood. In addition to bamboo and bamboo charcoal burning with shells, stones (coconut shell, peach stone charcoal etc.) wood raw material firing. Charcoal collected from household stoves in the cell known as carbon. If the charcoal is crushed and mixed with proper adhesive, and then pressed, formed and roasted, the deposit is made. According to the burning process of silica and carbon black.
- Q:What are the different types of steel billet casting defects?
- There are several types of steel billet casting defects, including surface defects like cracks, laps, and scabs, as well as internal defects such as shrinkage cavities, porosity, and inclusions.
- Q:How are steel billets used in the production of automotive suspension components?
- Steel billets are used in the production of automotive suspension components due to their strength, durability, and malleability. Billets are essentially semi-finished steel products that are formed into specific shapes, such as bars or rods, through a process called hot rolling. In the case of automotive suspension components, steel billets are first heated to a high temperature and then passed through a series of rollers to shape them into the desired form, such as coil springs, shock absorber rods, or stabilizer bars. The hot rolling process helps to refine the grain structure of the steel, resulting in improved mechanical properties. The use of steel billets in suspension components is crucial as they provide the necessary strength and stiffness to withstand the various forces and loads encountered during vehicle operation. Suspension components, such as coil springs, are responsible for supporting the weight of the vehicle and providing a comfortable ride by absorbing impacts and vibrations. Steel billets are preferred for automotive suspension components due to their high tensile strength, which allows them to withstand heavy loads and maintain their shape over long periods. Additionally, the malleability of steel allows for easy forming and shaping into various complex geometries, ensuring a precise fit and functionality within the suspension system. Moreover, steel billets offer excellent fatigue resistance, which is crucial for suspension components as they undergo repetitive loading and unloading throughout the vehicle's lifespan. This fatigue resistance helps to prevent failure and ensures a long-lasting and reliable suspension system. Overall, the use of steel billets in the production of automotive suspension components is essential for achieving the necessary strength, durability, and performance required for safe and comfortable vehicle operation.
- Q:How are steel billets used in the manufacturing of construction equipment?
- Steel billets are used as raw material in the manufacturing of construction equipment, particularly in the fabrication of heavy-duty components such as frames, chassis, and structural supports. These billets are heated, shaped, and machined to create the desired parts, ensuring strength, durability, and stability in construction equipment.
- Q:What are the different methods of steel billet surface painting?
- There are several methods of steel billet surface painting, including spray painting, powder coating, electrostatic coating, and dip coating. Spray painting involves using compressed air or a sprayer to apply a liquid paint to the surface of the billet. Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the surface, which is then heated to create a durable and protective coating. Electrostatic coating uses an electric charge to attract the paint particles to the billet surface, creating an even and uniform coating. Dip coating involves immersing the billet in a tank of paint, allowing the paint to adhere to the surface. Each method has its own advantages and is chosen based on factors such as the desired finish, cost, and environmental considerations.
- Q:What are the different surface treatments for improved machinability in steel billets?
- There are several surface treatments that can be applied to steel billets to improve machinability. Some of the commonly used treatments include machining with a controlled feed rate and cutting tool selection, which helps in reducing tool wear and improving surface finish. Additionally, coatings such as ceramic or diamond-like carbon coatings can be applied to the billet surface to reduce friction and increase tool life. Heat treatments like carburizing or nitriding can also be employed to create a hardened surface layer, improving wear resistance during machining operations. Overall, these surface treatments aim to enhance the machinability of steel billets by minimizing tool wear, improving surface finish, and increasing productivity.
- Q:How are steel billets recycled or reused?
- Steel billets, which are semi-finished metal products, are commonly recycled or reused in various ways. One common method of recycling steel billets is through the process of electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking. In this method, the billets are melted down in an electric arc furnace and then used to produce new steel products. This process not only allows for the efficient use of resources but also helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption compared to primary steel production. Steel billets can also be reused in various industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. They can be reshaped and reformed to create new steel products or used as raw material for forging, rolling, or extrusion processes. By reusing steel billets, the industry can reduce the demand for newly manufactured steel and conserve natural resources. Additionally, steel billets can be recycled through a process called continuous casting. In this process, the molten steel is poured into a continuous casting machine, which produces a solid billet. These billets can be further processed into various steel products such as bars, rods, or wire through hot rolling or cold rolling processes. Furthermore, steel billets can be melted and recast into other forms through the process of remelting. This can be done using technologies like induction melting or vacuum arc remelting, which help in purifying the steel and obtaining desired chemical and mechanical properties. Remelting allows for the production of high-quality steel billets that can be used in specialized applications such as aerospace, defense, or medical industries. In conclusion, steel billets are recycled or reused through various processes such as electric arc furnace steelmaking, continuous casting, remelting, and reshaping. These methods not only contribute to the sustainability of the steel industry but also help in conserving resources, reducing emissions, and meeting the growing demand for steel products.
- Q:What are the main factors that influence the strength of steel billets?
- The main factors that influence the strength of steel billets are the chemical composition, heat treatment, and microstructure of the steel. The chemical composition of steel billets plays a significant role in determining their strength. The presence of alloying elements such as carbon, manganese, silicon, and chromium can enhance the strength of steel by forming solid solutions or precipitates that increase the hardness and tensile strength of the material. Additionally, controlling the impurity levels and ensuring the desired balance of alloying elements is crucial in achieving the desired strength properties. Heat treatment is another crucial factor that influences the strength of steel billets. The heat treatment process involves heating the steel to a specific temperature, followed by cooling at a controlled rate. This process can significantly affect the microstructure of the steel, which in turn impacts its strength. For instance, quenching and tempering can result in the formation of a desired microstructure, such as martensite or bainite, which enhances the strength and toughness of the steel. The microstructure of steel billets is a key factor in determining their strength. The arrangement of the crystal grains and the presence of various phases within the steel can greatly influence its mechanical properties. Fine-grained structures generally exhibit higher strength due to a greater number of grain boundaries, which inhibit dislocation movement and enhance strength. Additionally, the presence of specific microstructural features, such as precipitates or second-phase particles, can also contribute to the strength of steel billets. Furthermore, factors such as the manufacturing process, cooling rate during solidification, and mechanical working (such as rolling or extrusion) can affect the strength of steel billets. These factors influence the grain size, grain boundary density, and defect concentration, all of which impact the mechanical properties of the steel. In summary, the strength of steel billets is influenced by the chemical composition, heat treatment, and microstructure of the steel. These factors can be carefully controlled and optimized to achieve the desired strength properties for various applications.
- Q:What are the main differences between hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel billets?
- The main differences between hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel billets lie in the manufacturing process and the resulting characteristics of the steel. Hot-rolled steel billets are produced by heating the steel above its recrystallization temperature, typically around 1200°C (2200°F), and then rolling it into the desired shape or size. This process involves the use of large-scale machinery, such as rolling mills, which apply significant pressure to shape the steel. As a result, hot-rolled steel billets have a characteristic rough and scaled surface. On the other hand, cold-rolled steel billets are produced by further processing the hot-rolled steel. The hot-rolled steel is first cooled down to room temperature and then passed through a series of rollers at lower temperatures, typically below 1000°C (1832°F). This process provides more precise control over the dimensions and surface finish of the steel. Cold-rolled steel billets have a smoother and more polished appearance compared to their hot-rolled counterparts. In terms of physical and mechanical properties, hot-rolled steel billets tend to have a higher yield strength and lower ductility compared to cold-rolled steel. This is because the hot-rolling process causes the steel to undergo strain hardening, resulting in increased strength but reduced ability to deform without breaking. Cold-rolled steel, on the other hand, retains more of its ductility due to the controlled process of rolling at lower temperatures. Another significant difference is in the dimensional accuracy of the two types of steel billets. Hot-rolled steel billets are known to have larger dimensional tolerances, which means that there can be variations in the thickness, width, and length of the billets. In contrast, cold-rolled steel billets have tighter dimensional tolerances, resulting in more precise and consistent dimensions. In summary, the main differences between hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel billets lie in the manufacturing process, surface finish, physical and mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate type of steel billets for specific applications, as each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
5p/Ps Steel Billets Q235,Q255,Q275,Q345,3SP,5SP,20MnSi
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 20 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


































