Eapro Solar Inverter SHI 1000W High-Frequency Power Inverter, 220V/230V PV Inverter, Pure Sine Wave Inverter, DC 48V to AC 220V/230V, SHI1000-42
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description
SHI series is a pure sine wave inverter which can convert 12/24/48Vdc to 220/230Vac 50/60Hz based on full digital and intelligent design. It features high reliability, high efficiency, concise outline, small volume, easy installation and operation. The inverter can be applied in many fields, such as household appliances, electric tools and industrial devices etc, especially for solar photovoltaic power system.

Features:
·Adoption of advanced SPWM technology, pure sine wave output
·Wide DC input voltage range
·The output voltage and frequency can be switched
·Low output harmonic distortion(THD≤3%)
·LED indicators for input voltage range, load power range, normal output & failure state
·Optional energy saving mode
·Wide working temperature range (industrial level)
Protections:
·Output short circuit protection
·Input low voltage protection
·Input over voltage protection
·Overheating protection
·Inverter abnormal protection
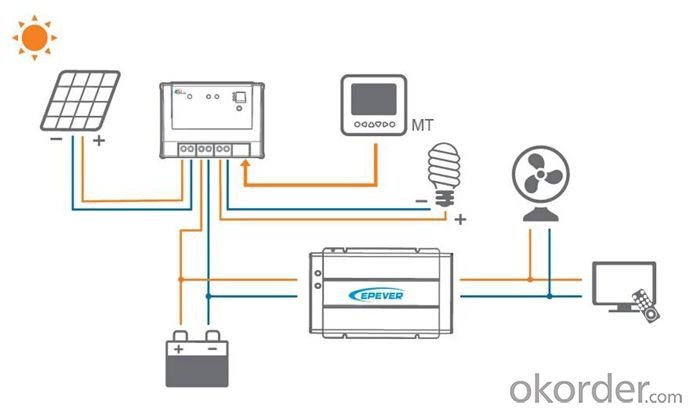
Specification:
Types | SHI1000-22 | SHI1000-42 |
Nominal Battery Voltage | 24V | 48V |
Input Voltage Range | 21.6~32Vdc | 43.2~64Vdc |
No Load Current | ≤0.45A | ≤0.35A |
Output Wave | Pure Sine Wave | |
Output Voltage | 220Vac±3% / 230Vac±10% | |
Continuous Power | 1000W | |
Power 10 sec | 1500W | |
Power 1.5 sec | 2000W | |
Surge Power | 2250W | |
Frequency | 50/60Hz±0.2% | |
Distortion THD | ≤ 3% (resistive load) | |
Efficiency at Rated Power | ≥93% | ≥93.5% |
Max. Efficiency | ≥94% | ≥94% |
Terminal | 25mm2 | |
Dimensions | 295×208×98mm | |
Installation | 150×200mm | |
Hole Size | Φ6mm | |
Net Weight | 3.3kg | |
Working Temperature | -20℃~ +50℃ | |
Storage Temperature | -35℃~ +70℃ | |
Humidity | < 95% (N.C.) | |
Altitude | < 5000m(Derating to operate according to IEC62040 at a height exceeding 1000m) | |
Insulation Resistance | Between DC input terminals and metal case: ≥550MΩ; Between AC output terminals and metal case: ≥550MΩ. | |
Dielectric Strength | Between DC input terminals and metal case: Test voltage AC1500V, 1 minute Between AC output terminals and metal case: Test voltage AC1500V, 1 minute | |
FAQ
Q:Off Grid VS On Grid Panels, what's the difference?
The differences between both panels are related to the system where they are going to be installed.
On-grid installations, as the name said, are thought to feed the produced energy into the grid and for that it is important to have the biggest voltage that it is allowed (1000VDC in Europe, 600 VDC in USA). For a defined power, more voltage means less current (P=V*I) and less losses.
In off-grid installations it is different because you must storage the energy into batteries. Batteries usually work at 12, 24 or 48 VDC and off-grid photovoltaic modules work at the maximum power point (mpp) near this voltage (see the datasheets). So the controller that charges the batteries works also near the batteries voltage.
Your limiting factor here is going to be this controller. You have to see what is the maximum voltage and the maximum current that it can work with, upstream (photovoltaic modules) and downstream (batteries and inverters). Then you have to dimension your PV array (Voltage and Current).
Q: Can a solar powered LED lighting without inverter?
Of course you can run lights without inverters. Both LEDs and incandescent lamps are quite happy on DC. And there are fluorescent ballasts that take a DC input (although they do have a sort of inverter inside). I have one in my shed and it has been working just fine for at least 15 years. It is very simple, easy and efficient. You can do away with the electrical code for wiring, lower you cost. Use less energy and lower the cost to install. In fact is we did this to power may of our day to day items we would also lower the demand for power.
Keep in mind this goes against every manufacturer and government policy and you will be shut down, squashed and run out of town for even talking about this, or at least you used to. I am working on a way to use the current wiring in a home to have direct solar, batter bank lighting. By coming off the grid for your lighting and many other functions, a power outage would hardly make a difference to your home.
- Q: How do you calculate the maximum power point current for a solar inverter?
- To calculate the maximum power point current for a solar inverter, you need to determine the maximum power point voltage (Vmpp) of the solar panel and divide it by the inverter's input impedance. This can be done by using the voltage-current (V-I) curve of the solar panel and locating the point where the product of voltage and current is maximized. By obtaining the Vmpp value, you can then calculate the maximum power point current by dividing it by the inverter's input impedance.
- Q: What is the maximum power rating of a solar inverter?
- The maximum power rating of a solar inverter typically depends on its size and capacity, but it can range from a few hundred watts to several megawatts.
- Q: What is the difference between a transformerless inverter and a transformer-based inverter?
- A transformerless inverter and a transformer-based inverter differ primarily in their design and functionality. A transformerless inverter, as the name suggests, does not include a transformer in its circuitry. Instead, it uses advanced semiconductor components, such as insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), to convert the direct current (DC) power from a source like solar panels into alternating current (AC) power for use in homes or businesses. The absence of a transformer allows for a more compact and lightweight design, making transformerless inverters ideal for space-constrained installations. However, due to the lack of galvanic isolation, transformerless inverters may have slightly less electrical safety compared to transformer-based inverters. On the other hand, a transformer-based inverter incorporates a transformer as an integral part of its circuitry. This transformer serves multiple purposes, including galvanic isolation, voltage step-up or step-down, and impedance matching. Galvanic isolation is particularly important as it provides a barrier between the input and output of the inverter, offering enhanced electrical safety and protection against electrical shocks. The presence of a transformer also helps to stabilize the output voltage, making transformer-based inverters more suitable for applications with sensitive electronics or where grid synchronization is critical. In summary, while transformerless inverters offer compactness and lightweight design, transformer-based inverters provide better electrical safety and stability. The choice between the two depends on the specific application requirements, space availability, and the level of electrical safety desired.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in a solar-powered irrigation system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in a solar-powered irrigation system. A solar inverter is responsible for converting the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various appliances and systems. In the case of a solar-powered irrigation system, the AC power produced by the solar inverter can be used to operate pumps, valves, and other components necessary for irrigation.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in harsh weather conditions?
- Yes, solar inverters are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions such as extreme temperatures, humidity, and even rain. They are typically built with protective enclosures and advanced technology to ensure reliable operation and optimal performance in challenging environmental conditions.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in commercial applications?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in commercial applications. In fact, solar inverters are commonly used in commercial settings to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various electrical devices and appliances. Commercial buildings often have larger solar systems installed, requiring more powerful inverters to efficiently convert the solar energy into usable electricity for the facility's commercial operations.
- Q: How do you size a solar inverter for a solar power system?
- To size a solar inverter for a solar power system, you need to consider the maximum power output of your solar panels. Calculate the total wattage of your solar panels and choose an inverter with a capacity slightly larger than that. It is important to ensure that the inverter's capacity can handle the maximum power output of your solar panels to avoid any performance issues or damage to the system.
- Q: What is the difference between a grid-connected inverter and an off-grid inverter? What are the advantages of a hybrid inverter?
- Off-grid inverter is equivalent to their own to establish an independent small power grid, mainly to control their own voltage, is a voltage source.
- Q: What is the role of a solar inverter in anti-islanding protection?
- The role of a solar inverter in anti-islanding protection is to detect when there is a loss of utility power and to disconnect the solar system from the grid. This is important to prevent the system from continuing to generate power during a power outage, which could pose a safety risk to utility workers who may be working on the grid. The solar inverter ensures that the solar system is synchronized with the grid and only operates when there is a stable utility power supply, thus providing a reliable and safe connection to the grid.
- Q: How does a solar inverter provide ground fault protection?
- A solar inverter provides ground fault protection by continuously monitoring the flow of electricity between the solar panels and the electrical grid. If it detects any abnormal or excessive current leakage to the ground, it quickly shuts off the flow of electricity to prevent electrical hazards, such as electric shocks or electrical fires.
Send your message to us
Eapro Solar Inverter SHI 1000W High-Frequency Power Inverter, 220V/230V PV Inverter, Pure Sine Wave Inverter, DC 48V to AC 220V/230V, SHI1000-42
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























