market price for carbon black /Rubber Antioxidant
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 20000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications
Rubber Antioxidant IPPD(4010NA)
1.101-72-4
2.Professional production factory
3.High quality
4.Used in the manufacture of tire
market price for carbon black /Rubber Antioxidant IPPD(4010NA)/ CAS No:101-72-4
(1)Product Name: Rubber Antioxidant IPPD (4010NA)
(2)Chemical Name: N-isopropyl-N'-phenyl-p-phenylene diamine
(3)Structure:
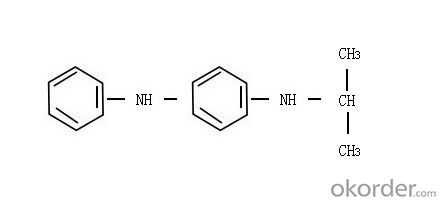
(4)Molecular Formula: C15H18N2
(5)Molecular Weight : 226.4
(6)CAS: 101-72-4
(7)Specification:
Index Name | Qualified Grade |
Appearance(eye measurement) | dark brown to dark violet pastilles |
Initial M.P.,°C ≥ | 70.0 |
Heating loss % ≤ | 0.30 |
Ash content % ≤ | 0.20 |
(GC)/Assay % ≥ | 95.0 |
Properties
Grayish purple to purple brown pastilles. Relative density is 1.14g/cm3. Soluble in benzene, acetone, ethyl acetate,
Carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, etc. Difficultly soluble in gasoline. Insoluble in water.
Application
It is an excellent and universal antioxidant used for natural rubber, synthetic rubber and latex. Better protective
performance of ozone, flex cracking, also the excellent protective agent for the heat, oxygen, light and the general
aging. It is able to inhibit harmful metals. It is mainly used in tires, rubber hose, belt and industrial rubber products.
Storage
The product should be sealed and stored in the dry, cool, well-ventilated area. Avoid exposure to direct
sunlight.
Packaging
25kg plastic woven bag lined with plastic film bag,kraft paper bag.
Following is our main products
Intermediate | Benzothiazole; MBT-NA | |
Rubber Accelerator | Thiazoles | MBT(M); MBTS(DM); ZMBT(MZ) |
Sulfonamides | CBS(CZ); MBS(NOBS); NS(TBBS); DCBS(DZ) | |
Dithiocarbamates | ZDEC(EZ); ZDMC(PZ); ZDBC(BZ) | |
Thiurams | TMTD(TT); TMTM(TS) | |
Guanidines | DPG(D) | |
Rubber Antioxidant | A(PAN); D(PBN); RD(TMQ); 4010(IPPD); 4020(6PPD); BLE | |
Antisorching Agent | PVI(CTP) | |
Rubber Vulcanizing Agent | DTDM; Insoluble Sulfur | |
Our Rubber Accelerator IPPD (4010NA) is produced by new technology---"enclosed clean
production techniques", located the forefront of industry in skill and output. Welcome to inquiry!
- Q: why is palladium/platinum a good catalyst?
- Palladium and platinum can form partial bonds with other molecules. By forming these partial bonds, the bond in the actual molecule gets weaker and weaker and hence, the bond becomes easier to break. Let's say for example a hydrogen molecule. There is a single bond between the 2 hydrogen atoms. Platinum/palladium will form partial bonds with the 2 hydrogen atoms. By doing so, the single bond BETWEEN THE 2 HYDROGEN ATOMS gets weaker and weaker. Hence, a smaller amount of energy is needed to break the bond between the 2 hydrogen atoms (the hydrogen molecule). As the amount of energy needed to overcome the bond between the 2 hydrogen atoms gets smaller, we say the activation energy for the reaction has been reduced. Hence, a greater amount of bonds in hydrogen molecules can be broken in a smaller time, and therefore, we say palladium/platinum has catalysed the reaction.
- Q: Cl + O3 ---> ClO + O2O + ClO ---> Cl + O2= O + O3 ----> 2O2What is the catalyst? The intermediate?How do you know which is which? If the rate law is rate=k [O3] [Cl]determine:a) the overall order.b) unit for k.c) the rate determining step, justify your answer.
- Cl is the catalyst. ClO the intermediate. The catalyst is the component which does not change in overall reaction. He forms some intermediate component(s) with the reactants. In the later reaction steps the intermediate(s) react forming the catalyst in its original state. (a) The overall order is the sum of the orders with respect to the components: n = 1 +1 = 2 (b) the unit of the rate of reaction is r [=] mol/ (Ls) (more general mol per unit time and volume) compare dimensions mol / (Ls) [=] k · mo/L · mol/L =k [=] L/(s mol) (more general unit volume per unit time and mole) (c) First reaction For elementary reaction steps the order of the reaction rate with respect to a reactant is equal to stoichiometric coefficient. Hence the rate of first reaction is: r? = k?·[Cl]·[O?] Overall rate is given by the rate determining step, while other reaction steps are in equilibrium: r = r? = k?·[Cl]·[O?] If second reaction is the rate determine step r? = k?·[O]·[ClO] while reaction 1 is at equilibrium K? = ( [ClO]·[O?] ) / ( [Cl]·[O?] ) =[ClO] = K?·( [Cl]·[O?] ) / [O?] the overall rate would be: r = r? = k?·[O]·[ClO] = K?·k?·[O]·[Cl]·[O?] / [O?] = k·[O]·[Cl]·[O?] / [O?] That doesn't match the observed rate law
- Q: How does the chemical equation calculate the quality of the catalyst?
- Catalyst, the quality of the reaction before and after the same, the same chemical properties.
- Q: To write a 1500 words of small papers, so please help you busy
- Change the course of the reaction
- Q: What is the difference between biological enzymes and chemical catalysts?
- Biological enzyme is a protein, according to the mild reaction conditions, high specificity, the advantages of strong catalytic capacity,
- Q: Why are catalysts so effective in small amounts?
- By definition, catalysts serve to accelerate certain chemical reactions, by lowering the activation energy required for them to proceed. They are not consumed by the reaction, which is why they are effective in small amounts.
- Q: Where are they good catalysts and why?? THanks!
- A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by providing an alternate reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. Catalysts appear not to take part in the reaction. Frequently, catalysts are not very reactive. Acids and bases, on the other hand, are very reactive. Acids (as H+) and bases ( as OH-) sometimes function as catalysts in some organic reactions. They appear to be catalysts because in the course of the mechanism H+ or OH- is regenerated.
- Q: Which chemical reaction is added to the catalyst in order to slow down the reaction
- CaC2 and water reaction to ethylene plus salt water (slow chemical reaction rate)
- Q: Does the nature and quality of the catalyst itself change before and after the chemical reaction?
- A catalyst will induce a chemical reaction to change, leaving the chemical reaction faster or less
- Q: Before and after the chemical reaction, the nature of the catalyst unchanged this statement right? Why?
- Yes, the catalyst only acts as a catalyst and does not participate in chemical reactions
Send your message to us
market price for carbon black /Rubber Antioxidant
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 20000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords