Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose for Professional Supply
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 5000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Building Construction Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC)
Brief introduction:
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) helps building materials apply more easily and perform better. They provide water retention and cohesiveness to mixtures. With special modification, it can be used to control thickening, water demand, workability, sag resistance, strength and other important properties of the final product.
It is widely used as thickener, adhesive, water preserving agent, film-foaming agent in building materials, industrial coatings, synthetic resin, ceramic industry, medicine, food, textile, agricultural, cosmetic and other industries.
Physical and chemical index:
Item | Specification |
CAS NO. | 9004-65-3 |
Appearance | white or light yellow powder |
Moisture Content | ≤5.0% |
PH | 4.0-8.0 |
Particle Size | min. 98% pass through 100 mesh |
Viscosity | 100cps-200000cps, 2% solution |
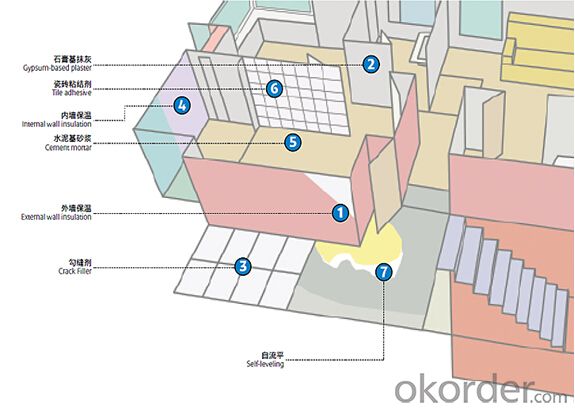
Application in Building:
External wall insulation system (EIFS)
>Bond strength: HPMC can provide the greatest degree of high adhesive bond strength of mortar.
>Performance: The mortar added HPMC has the right consistency, non-sagging. When using, the mortar is easy to work continuously, uninterrupted.
>Water retention: HPMC can wet the wall insulation easily, easy to paste, and also make other additional materials reach the best affects.
>Absorbent: HPMC can minimize the air-entraining volume, lower water absorption of mortar.
>Recommended brand: 75CMAX75000(S), 75CMAX100000(S), 75CMAX200000(S)
Interior and exterior wall interface agent
>Easy to mix, without of agglomeration: HPMC can significantly reduce the friction in the dry powder during the process of mixing with water, which makes it easy to mix and save the blending time.
>Water retention: HPMC can significantly reduce the moisture absorption by the wall. Good water retention can ensure the cement compound with a longer time, also can ensure that workers are able to carry out many times of scraping for the putty on the wall.
>Good working performance stability: even in high temperature environment, HPMC can still maintain good water retention. it is suitable for construction in the summer or hot areas.
>Increased water demand: HPMC can significantly improve the water demand of the putty materials. On the one hand, it improves the operational time after putty put on the wall, on the other hand, it can increase the coating are of the putty, which can make the formula more economical.
>Recommended brand: 75CMAX60000(S), 75CMAX75000(S)
Tile adhesive
>Water retention: HPMC can reduce the moisture absorbed by the substrate and the tile, retain the moisture in the adhesives as much as possible, making mortar still have adhesion after coating for a long time. Significantly extend open time and makes bigger coating area for the worker each time, and improve the efficiency.
>Improve bond strength, improve anti-slip performance: HPMC ensure non sagging of the tiles during working, especially for heavy tile, marble and other stone materials.
>Work performance: The lubricity of HPMC can increase the workability of the mortar significantly, which makes the mortar easy to coating and improve efficiency.
>Improve mortar wetting property: HPMC give mortar consistency, enhance the wetting ability of mortar and substrate, increase the binding strength of wet mortar, especially for the recipe with high water cement ration;
>Recommended brand: 75CMAX40000(S), 75CMAX75000(S), 75CMAX100000(S)
Crack Filler
>Workability: provide the right viscosity, plasticity, and easy to work;
>Water retention: can make the slurry fully hydrated, extending the working time and avoid cracking.
>Anti-hanging: HPMC can make a strong adhesion on the surface for the slurry and not sag;
>Recommended brand: 75CMAX40000(S), 75CMAX75000(S), 75CMAX100000(S)
Self-leveling mortar
>Prevent bleeding: HPMC can play a very good role to prevent the slurry sedimentation, bleeding.
>Maintain liquidity, and improve retention: low viscosity HPMC will not affect the slurry flow effect and easy to work. While possesses certain water retention, makes the good surface effect after self-levelling and avoid cracks.
>Recommended brand: 75CMAX400~600
Gypsum-based plaster
>Water retention: HPMC can retain moisture in the mortar, thus make gypsum completely solid. The higher the viscosity is, the stronger the water-retention capacity, vice versa..
>Sag resistance: allow the worker make the thick coating without causing ripple building.
>Mortar yield: For fixed weight of dry mortar, the exist of HPMC can provide more wet mortar.
>Recommended brand: 75CMAX75000(S), 75CMAX100000(S)

FAQ
Q1.Could we have the sample to test the quality?
Kindly send us your address, we are honored to offer you samples.
Q2. How does your company do regarding quality control?
CNBM a Chinese state-owned enterprise ranked 270th among the global fortune 500 in 2015,
have accreditation in line with standard:ISO 9001:2000,SGS,CIQ certificate.
Q3:What's your Delivery Time?
In generally, the delivery time is 25 days-30 days.We will make the delivery as soon as possible with the guaranted quality.
Q4:What is the convenient way to pay?
L/C , T/T ,Paypal, Western Union and Escrow are accepted,and if you have a better idea , please feel free to share with us .
Q5:Which mode of transport would be better?
In general,we advice to make delivery by sea which is cheap and safe.Also we respect your views of other transportation as well.
- Q: High school chemistry, catalyst activation energy map
- Catalytic reaction is the reaction of the first reaction with the catalyst or attached to the catalyst to form intermediates, and then further reaction to produce products and catalysts, so the amount of catalyst in theory is the same! The activation of these two processes can be reduced! So there will be two peaks! Can be simplified as a peak!
- Q: What is the similarity between enzymes and general chemical catalysts?
- (1) The enzyme is the same in many respects as a biocatalyst and a general catalyst, such as a small amount and a high catalytic efficiency. As with the general catalyst, the enzyme can only change the rate of chemical reaction and does not change the equilibrium of the chemical reaction It is possible to catalyze the activation of a large number of substrates in a short time and to reflect the high efficiency of enzyme catalysis.The enzyme can reduce the activation energy of the reaction (activation) (△ G) during the reaction, but the reaction rate is accelerated and the reaction time is reduced, but the equilibrium constant is not changed. (2) However, the enzyme is a biological macromolecule (1) Enzyme-catalyzed high efficiency: The catalytic effect of the catalyst can increase the reaction rate by 10 ^ 6 ~ 10 ^ 12 times, which is at least several times higher than that of the conventional catalyst. (2) The enzyme catalyst Highly specificity: including specificity of response, substrate specificity, chirality specificity, geometric specificity, etc., that an enzyme can only act on a certain class or a specific substance. Bond, ester bond, peptide bond and so on can be catalyzed by acid-base hydrolysis, but the hydrolysis of these chemical bonds are different, respectively, the corresponding glycosidase, esterase and peptidase, that is, they were specific (3) enzymatic reaction conditions are mild: enzymatic reaction is generally carried out in aqueous solution of pH = 5 ~ 8, the reaction temperature range is 20 ~ 40 ℃
- Q: what is a catalyst ?
- substance accelerate a chemical reaction
- Q: I dont know what it is but when i open up my computer it comes up and it says that its not working? so i really dont know what to do.
- Catalyst is what ATI calls the drivers for their video cards or video devices built into mainboards. Download the newest video driver for your video card from ATI or from your computer manufacturer's site if the video device came with the computer. Install that, and you should be all set. You may want to check your add and remove programs and remove any of the old, malfunctioning ATI or Catalyst drivers before attempting to install the new one. Good luck!
- Q: The role of catalyst in chemical reactions
- The role of the catalyst is to change the reaction required to achieve the activation energy, can reduce the activation energy is called positive catalyst (that is, usually the meaning of the catalyst), to improve the activation energy is negative catalyst
- Q: I was hoping to buy a land rover lr4 or lr2, but with the lr4 having gas mileage in the mid teens, i wanted to know if there is a way to improve it. I dont drive on the highway too much. I'd like to know if there is anything else to improve mileage too. I drive a lot of people around for functions, family, and others and I looked at other suvs but those two looked the best.
- Fuel catalyst is another name for fuel additive, the companies that make these additives make all kinds of claims how it increases power and reduces emiissions.. blah blah blah. Fuel catalyst is nothing more then a octane booster (gas engines) or cetane booster (diesel engines), it like all the other bogus products are worthless, octane booster will only show an improvement in performance IF the octane level in your current fuel supply is too low, higher octane fuel burns slower then lower octane fuel, that's how it quenches pinging and preignition both of which are caused by incorrect engine design and/or settings. Always use the lowest octane fuel that the engine will tolerate, if you have to pull advance out of the total timing then it needs more octane to run full timing and make max power, the only thing you can do to improve the quality of fuel in your tank is add a stabililizing additive such as (Stabil), it treats the fuel and prevents it from going stale or turning to varnish, it's especially useful when the vehicle is parked for long periods with fuel in the tank and carburetor, normally after a month or two of being parked the fuel in the carb turns to varnish and clogs the jets, with Stabil the fuel doesn't change composition.
- Q: Brief introduction of enzyme as biocatalyst and general chemical catalyst and its personality
- can only change the rate of chemical reaction, do not change the equilibrium point of the chemical reaction, the enzyme itself does not change before and after the chemical reaction (3) can reduce the chemical reaction of the activation energy The
- Q: What is the meaning of catalyst in chemistry?
- In the chemical reaction can change the reaction rate of chemical reaction (increase or decrease) without changing the chemical balance, and its own quality and chemical properties in the chemical reaction before and after the material did not change the catalyst.
- Q: Manganese dioxide can be used as a catalyst for various chemical reactions
- MnO2 + 4HCl = heating = MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2HCl
- Q: chemistry subject
- copper nickel zinc common catalysts are solid acids such as the silicas, alumina, and zeolites it depends on the reaction
Send your message to us
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose for Professional Supply
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 5000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 5000000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























