Solar Energy Systems 101:High Voltage Lithium LifePO4 Solar Home 240V 12.3 kWh ESS Stacked Battery Energy Storage System
- Loading Port:
- SHANGHAI
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 set
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Specification
Application:
Home
Output Voltage (V):
240 v
Work Time (h):
8 hours
Introduction:
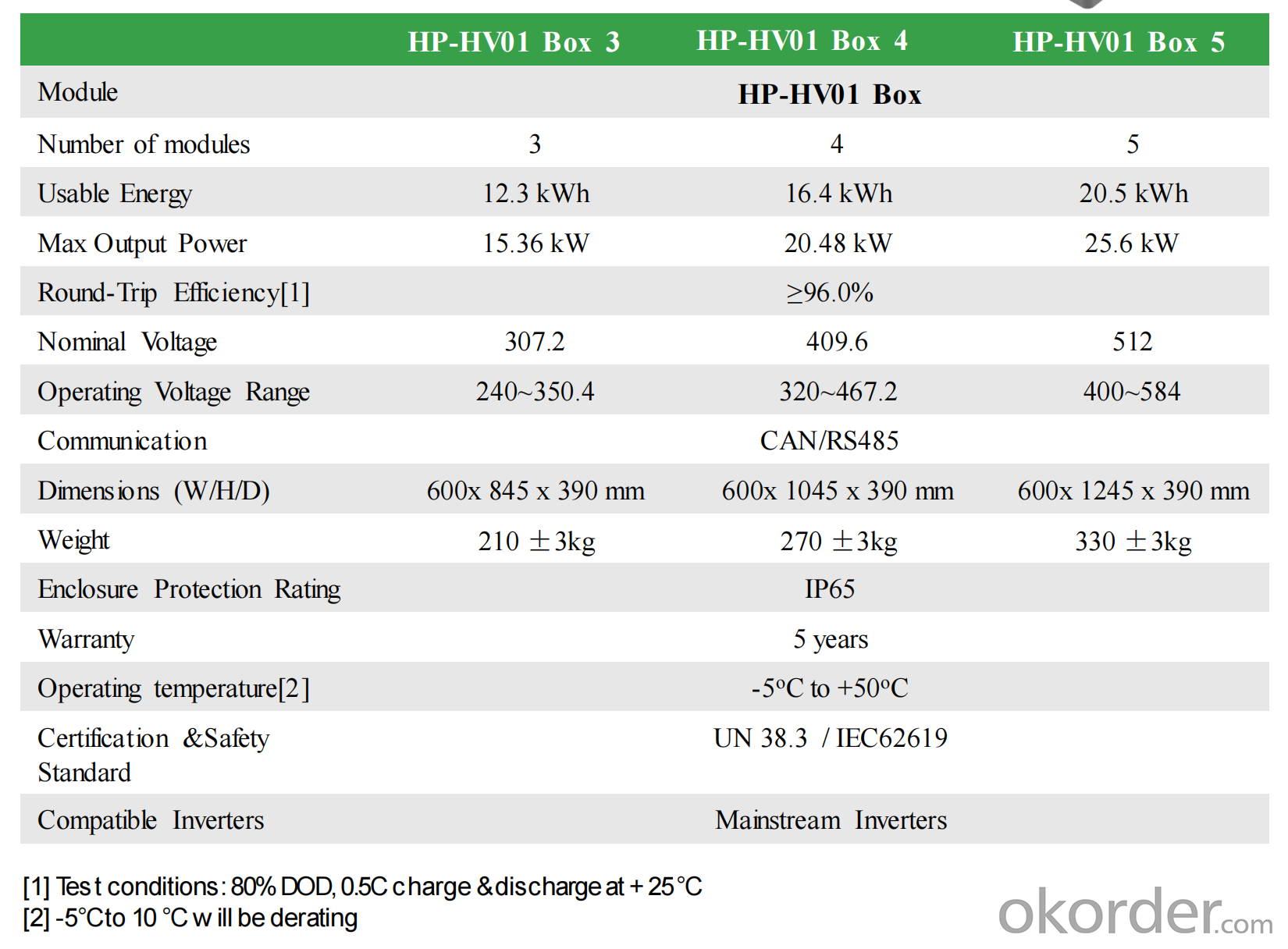
HP-HV01 is a modularly expandable Lithium ion battery storage system.
The system can be built as quickly as a stack of bricks.
The system is composed of brick battery packs and an energy control box.
The brick battery packs are stacked one by one, and the energy control box is placed on the top of the brick battery pack,
it is easy to add up all these to form an energy system for users.



- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering off-grid eco-schools?
- Yes, solar energy systems can indeed be used for powering off-grid eco-schools. Solar panels can be installed on the rooftops or in open spaces surrounding the school to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. This renewable energy source can power various electrical needs within the school, such as lighting, heating, cooling, and running appliances. By utilizing solar energy, off-grid eco-schools can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly educational environment.
- Q: What is the role of solar energy systems in reducing heat island effect?
- Solar energy systems can help reduce the heat island effect by generating electricity from sunlight, which reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and consequently decreases the amount of heat and air pollution emitted into the environment. Additionally, solar panels can provide shade and help to cool urban areas by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, thereby mitigating the intensity of the heat island effect.
- Q: What is the role of batteries in a solar energy system?
- Batteries play a crucial role in a solar energy system by storing excess electricity generated by the solar panels. This stored energy can be used during periods of low or no sunlight, ensuring a continuous and reliable power supply. Additionally, batteries help to balance the supply and demand of electricity, providing stability to the solar energy system and enabling it to operate efficiently.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering remote sensing or surveillance equipment?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used effectively for powering remote sensing or surveillance equipment. Solar panels can convert sunlight into electricity, providing a sustainable and reliable power source for such equipment in remote locations. This eliminates the need for grid connection or reliance on traditional energy sources, making solar energy an ideal choice for powering surveillance or remote sensing systems.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used for powering electric car manufacturing plants?
- Indeed, electric car manufacturing plants can utilize solar energy systems. These systems harness the power of sunlight to generate electricity, which can then be utilized for diverse industrial operations, including the functioning of manufacturing plants. By implementing solar panels on the rooftops or open areas of the manufacturing facility, the plant can effectively tap into renewable energy to satisfy its electricity requirements. This not only diminishes the dependency on fossil fuels but also aids in curbing greenhouse gas emissions linked to conventional electricity generation. Moreover, by integrating energy storage solutions, solar energy systems ensure a consistent power supply, even during periods of limited sunlight or nighttime. Consequently, opting for solar energy systems to power electric car manufacturing plants is a sustainable and environmentally conscious decision.
- Q: Can solar energy systems be used in areas with limited access to healthcare facilities?
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. Solar energy can power medical equipment, refrigeration systems for vaccines and medicines, and lighting in healthcare facilities, allowing them to function even in remote areas without reliable access to electricity. This can greatly improve healthcare services and enable the delivery of essential medical care, diagnostics, and treatments in underserved communities.
- Q: Are there any risks of electrical shock with solar energy systems?
- Solar energy systems carry potential risks of electrical shock. While generally considered safe, these systems can be hazardous due to the presence of high voltages and electrical currents. Failure to handle or manage them properly can result in accidents. Several key risks are associated with solar energy systems: 1. Installation and maintenance: Improper procedures during the installation and maintenance of solar panels can lead to contact with live electrical components. This can happen when safety protocols are not followed or when untrained individuals attempt to handle electrical connections. 2. Equipment or wiring malfunctions: Defective inverters, wiring, or other equipment can increase the risk of electrical shock. Poor installation practices or insufficient maintenance can also result in electrical faults, exposing individuals to dangerous currents. 3. Fire hazards: While not directly related to electrical shock, faulty electrical components or wiring can raise the risk of fires in solar energy systems. Attempting to extinguish such fires without shutting down the electrical system first can further worsen the risk of electrical shock. To minimize these risks, it is essential to adhere to proper installation and maintenance procedures. This often involves seeking assistance from licensed professionals. Furthermore, individuals working with solar energy systems should be trained in safety protocols, including the use of appropriate personal protective equipment and ensuring proper grounding of electrical systems. Regular inspections and maintenance are also crucial to detect and address any potential electrical hazards.
- Q: How do solar energy systems handle power outages?
- Solar energy systems do not provide power during a power outage. However, systems that are connected to the grid can have battery storage or backup generators to provide electricity during such situations. Standalone solar systems with battery storage can also provide limited power during an outage, depending on the capacity of the batteries.
- Q: What is the impact of snow or ice on solar energy system performance?
- Snow or ice can have a significant impact on the performance of a solar energy system. When snow or ice covers the solar panels, it prevents sunlight from reaching the surface and reduces the system's energy production. Additionally, the weight of accumulated snow or ice can cause damage to the panels or mounting structures. However, advancements in technology and the tilt of solar panels can help minimize the impact by allowing the snow or ice to slide off more easily. Regular maintenance and cleaning may also be required to ensure optimal performance during winter conditions.
- Q: What are the maintenance requirements for solar energy systems?
- Maintenance requirements for solar energy systems can vary depending on the type and size of the system. Generally, solar panels are low-maintenance and require minimal upkeep. However, there are a few key maintenance tasks that can ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the system. One important maintenance requirement is regular cleaning of the solar panels. Dust, dirt, leaves, and other debris can accumulate on the surface of the panels, reducing their efficiency. Cleaning the panels with a soft cloth or a gentle spray of water can help remove any build-up and maximize their energy production. Another maintenance task is checking the wiring and connections of the solar system. Over time, the wires can become loose or damaged, compromising the system's performance. Regular inspections and tightening of connections can help prevent any issues and ensure the smooth operation of the system. Monitoring the system's performance is also essential for maintenance. Most solar systems come with monitoring software that allows homeowners to track the energy production and identify any potential issues. Monitoring the system regularly can help detect any drop in performance or malfunctioning components, enabling timely repairs or replacements. In addition to these tasks, it is recommended to have a professional inspection of the solar energy system every few years. A qualified technician can thoroughly evaluate the system's components, including the panels, inverters, and batteries if present. They can identify any signs of wear or damage and address them before they become major problems. Overall, the maintenance requirements for solar energy systems are relatively low, but regular cleaning, checking connections, monitoring performance, and periodic professional inspections are crucial to ensure the optimal functioning and longevity of the system.
Send your message to us
Solar Energy Systems 101:High Voltage Lithium LifePO4 Solar Home 240V 12.3 kWh ESS Stacked Battery Energy Storage System
- Loading Port:
- SHANGHAI
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 set
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords