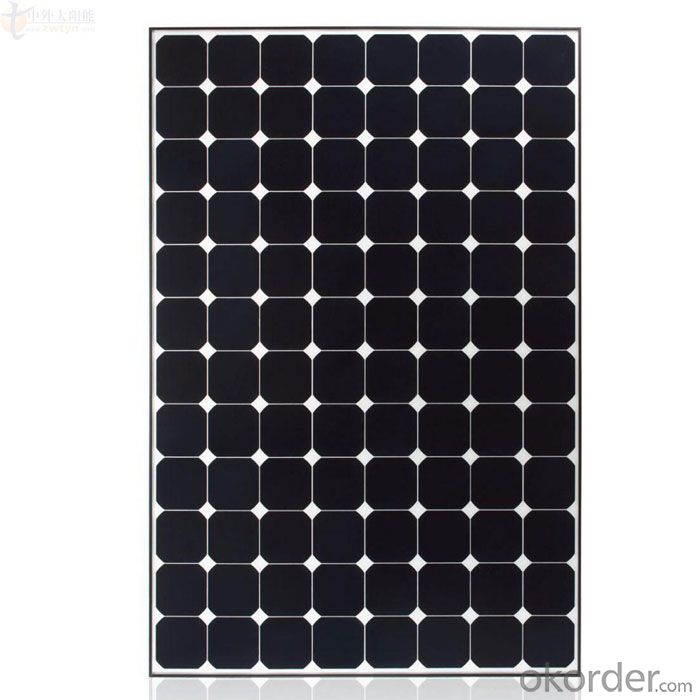
Solar Panels - 285W CNBM Solar Polycrystalline Series III (280W—295W)
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
CNBM Solar Polycrystalline Series III (280W—295W)
Characteristics
Max Power Voltage Vmp(V) | 36.6 | 36.9 | 37.2 | 37.5 | ||
Max Power Current Imp(A) | 7.66 | 7.73 | 7.8 | 7.87 | ||
Open Circuit Voltage Voc(V) | 44.2 | 44.6 | 45.1 | 45.4 | ||
Short Circuit Current Isc(A) | 8.26 | 8.32 | 8.41 | 8 | ||
Max Power Pm(W) | 280 | 285 | 290 | 295 | ||
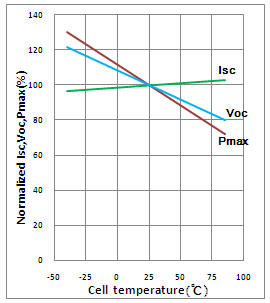
Temperature Coefficient of Cells
NOCT | 45℃±2℃ | |
Temperature Coefficients of Isc (%/℃) | - 0.0492 | |
Temperature Coefficients of Voc (%/℃) | – 0.3374 | |
Temperature Coefficients of Pmp (%/℃) | –0.4677 | |
Mechanical Data
Dimension | 1638 x 982 x 40 mm | |
Weight | 19.5kg | |
No. of Cells and Connections | 60 (6 x 10) | |
Tolerance | 0~+5W | |
Cell Monocrystalline Cell | 156 x 156 mm | |
Packing | 700 Pcs/40ft(H) Container | |
Limits
Operating Temperature | –40 °C to +85°C | |
Storage Temperature | –40 °C to +85°C | |
Max System Voltage | 1000VDC(IEC) / 600VDC(UL) | |
IV Curve
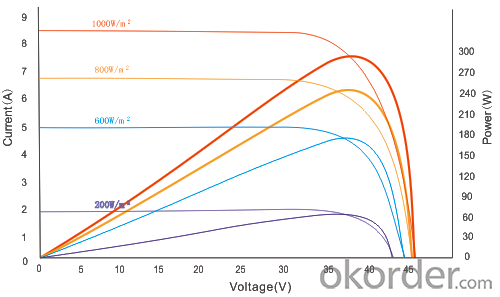
Image


Guarantees
Products Guarantee 12 yrs free from defects in materials and workmanship
Performance Guarantee No less than 90% within 10yrs and no less than 80% within 25yrs
Certificates TUV (IEC61215&IEC61730), VDE(IEC61215&IEC61730), UL, CE
FAQ
1. Q: Do you have your own factory?
A: Yes, we have. Our factory located in Jiangsu province.
2. Q: How can I visit your factory?
A: Before you take off from your country, please let us know. We will show you the way, or arrange time to pick you up if possible.
3. Q: Do you provide free sample?
A: Usually we do not offer free sample
4. Q: Could you print our company LOGO on the nameplate and package?
A: Yes, we can do that.
- Q: i was looking into making solar panels to reduce my electric bill, but i need to know how to actually hook it up.
- Backwoods Home Magazine had a great step by step section in one of their magazines on solar energy, panels, hook-up, etc. You can go to their website, pull that issue up and order the magazine and I believe they offer it on CD. This way you would have a reference guide at the ready when you tackle this project. Godd Luck!
- Q: I need to use solar panels to charge lead acid batteries in an off-grid application. I understand that solar panels have a open circuit maximum voltage and an maximum amperage under no resistance, and that one can optimize the power output by regulating the load (resistance). If so, is just connecting 2 -volt solar panels to a lead-acid battery inefficient? Are there devices that will maximize 2 volt output power (by varying the resistance)? Am I on the right track here? Thanks for any help.
- Hi, okorder / having good batteries like this one make save you the hassel to buy controllers. You can control your own charge buy different tips
- Q: we are planing to move out of the grid. we need to operate constantly 2 laptops online - does any one can tell us how much solar panels we shall need to make sure of that?
- A laptop is about 70 to 00 W, and you have two. You also may need to power a router, and modem. So, about 50W to 250W contineous should cover it. To save power when not in use, you can let the display go blank. This will reduce your solar pannel, and battery size, and cost. You will need batteries, and blocking rectifier to store the energy for use at night, and a 300W to 400W inverter. Checkout the link below for purchasing solar equipment. You can only hope to get about 8 to 9 hours of full output from your solar pannels, and 80% efficiency. The laptops will be on and using about 200W for the 8 hours during the charging period. So your pannels, need to produce that plus 2 times more than this amount, so you can charge the batteries for the evening, at the same time. So for 24 hour operation, you will need 200W x8hrs for the laptops, plus (6 hours*70W)/8=340W avg. Total of ~540W for 8 hours. Assuming you use power saving modes when not in use, you can probably get away with 3x60W -- 520W to 600W pannel. ( Thuja is right, a few cloudy days may knock you offline) Batteries. A common low cost ( $40) automotive battery can hold about 40 Amp/hours at 2V. Under load, you may get 35 Amp hours at 0V, which is about 350Watts for one hour. You need about 80W avg for 6 hours, or ~ 2900Watt Hours. Which means you would need 9 automotive batteries. Deep storage batteries cost more, but are more durable. 6*00W pannels, $460*6 ~ $2800 Inverter $70 Batteries $400 Battery cables, rectifier, lugs, connectors $50 There are probably some other hidden costs. I was rooting for you, but it appears to be pricey. Another thing you can do, is to use the new energy efficient RF florescent bulbs for lighting. The color and brightness are excellent, and a 60W bulb only uses about 3W, and they last a lot longer as well.
- Q: Can solar panels be used to power a data center?
- Yes, solar panels can be used to power a data center. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power various devices and infrastructure, including data centers. By installing a sufficient number of solar panels and using energy storage systems, a data center can be powered entirely or partially by solar energy. This can help reduce reliance on traditional power sources, lower energy costs, and promote environmental sustainability. However, the feasibility and efficiency of using solar panels for powering a data center may depend on factors such as the location, size of the data center, and the availability of sunlight.
- Q: I am moving to Hawaii and the house we are living in has independent electricity. (solar panels and gas powered generators.)
- specific. fairly, here is what you % (i'm holding this ordinary on objective): The panels themselves -- how large a close-by relies upon on effortless potential intake and how plenty potential you will get on effortless. That, in turn , relies upon on climate. you would be wanting extra in Seattle than Tuscon, as an occasion. i could wager something in the neighborhod of 0 sq. ft. relies upon additionally on haow many units (printers, etc.) you have. you would be wanting a potential storage device. Lithium components the perfect poser density (of off-the-shelf stuff) yet an effortless motor vehicle battery works properly and is sturdy. And, of course, a administration device to administration the potential technology/storage/use so each little thing works collectively with out that stressful scent that tells you you in undemanding terms cooked some hundred greenbacks properly worth of equuipment! :)
- Q: I was hearing that we need silver as a medal for the creation of solar panels, is this true? How much silver would be needed to make one solar panel? (if this is true)
- Some research has shown that small amounts of silver can improve the efficiency of solar panels. But this appears to be in the research stage and applies to the the thin film solar cells. Some solar panels makes use silver as the wiring in kind of a screen printing process, but you don't need to use silver, you can use copper or aluminum using different techniques instead. Generally the metal used is in small amounts and not a majority of the cost of the solar panel.
- Q: 3.8 volts is required to fully charge a battery. But at 3.8 volts, the battery can be overcharged without the use of a controller correct? What if I don't care if the battery is fully charged? In the case of our family boat, I just installed a new radio, so I'm a little worried about power consumption. So now for the real question; If I hook a 2 volt panel to the batteries, do I need to worry about overcharging them? Or will the batteries stop the charging process once they reach 2 volt?I built the panel myself, it's 8 volts at 3.5 amps open circuit. I have tabs at every 3 volt increment on the panel so that I can use less voltage than 8 if I want to power something directly, (ex:2 volt radio)So I'm using the 2 volt tab at 3.5 amps(approx) for a total of approx 48 watts
- I have been using solar panels for over ten years never until recently bothered to use a charge controller, it depends really on how much power your batteries can hold how often they will be drained from use of the connected dc-ac inverters. While constant daylight charging at 8v 3.5a/hr is quite heavy it is not excessive, 2v lead acid battery chargers give a voltage output of appx 4.8v but the fluctuating output of a solar panel means you may well charge at 8v for some time but with occasional shade etc it will more likely average at 5v which I think is quite acceptable.
- Q: Has anyone had roof problems caused by rooftop solar panels?
- Rooftop solar panels might cause all sorts of maintenance or poor installation problems but I rather doubt at this point if we can say that there is an issue with solar panels in general that will cause a problem with the roof. Rather solar panels tend to shade a roof on its most exposed side. Without solar panels southern facing roofs will wear out faster than northern facing roofs. Installed solar panels will tend to make the roof last longer.
- Q: Can solar panels be used in areas with high levels of heatwaves?
- Yes, solar panels can be used in areas with high levels of heatwaves. In fact, solar panels are designed to convert sunlight into electricity, and they perform better in areas with higher levels of sunlight and heat. However, it is important to consider the impact of excessive heat on the efficiency and lifespan of solar panels. Proper installation, maintenance, and cooling measures may be required to ensure optimal performance in areas with extreme heat conditions.
- Q: I am heading to Nepal and do not want to lose power on my cameras but they can only be charged via quot;plugging inquot;. A USB connection does not work. Looking for a solar panel to clip to my bag or carry that I can plug in the charger as if plugging in to wall outlet. Thanks.
- Solar panels require a charge converter before it can be used by an AC source. There is no direct solar panel with built in charge converters that I know of because, when purchasing panels, you must purchase the wattage requirements of the job (this can be several panels linked), and a charge converter that will handle the <? panels required. A chain of stores up here in Canada have a portable battery pack that has a solar panel to increase its charge capacity or duration, but its not something you would want to lug around for long periods of time, because is weights in about 3 lbs.
Send your message to us
Solar Panels - 285W CNBM Solar Polycrystalline Series III (280W—295W)
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























