Ladle Shroud long nozzle Chinese steelmaking
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 set
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description:
Steelmaking long nozzle /refractory materials/refractory nozzles
steelmaking zircon nozzle Zr content 94-95% , and nozzle with metal shell ,
can protect nozzle burst.the casting temperature normally at 1520-1580 ℃.
our zirconia cores temperature resistance up to 2000℃, density is 4.2g/cm3 .
Steelmaking tundish nozzle zircon core contact face made a little big than other,effectively protect the nozzle using life.
tundish zirconia nozzles materials is alumina-zirconia-carbon .composed by Alumina-Carbon Shell, and zirconia core.
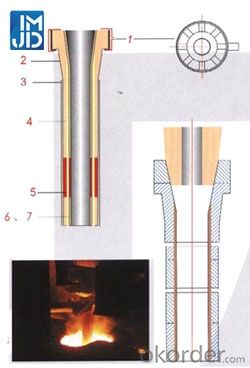
Graphic illustration:
1.Argon injection structure depending on customer specifications.
2.Ceramic glaze layer to prevent the material oxidation effectively.
3.Ceramic fiber blanket to prevent heat lost during casting.
4.High quality Al-C materials having high corrosion and thermal shock resistance.
5.High quality Zr-based composite to provide high corrosion resistance at the slag line.
6.Non-graphite based mased materials to meet the requirements of producing low carbon steel,silicon steel and high purity steel.
Manufacturing and QC
1.Raw materials blending
Independent raw materials blending center to assurestrict control of materials quality.
2.Shaping
Isostatic pressing technoloty,with as 1000 tons of pressure to assure the homogenous bulk density of each product.
3.Machining
To assure the uniform shape,dimension and dimension tolerance of each product.
4.X-ray defect inspection
To assure all products supplied to our customers without any defect and to prevent the un-countable feconomic loss for our customers.
5.Physical and chemistry analysis
To assure all products meet the physical and chemistry characteristics.
6.Packaging
The world-class for packaging to assure the safety transportation.
- Q:Can monolithic refractories be used for lining iron and steel ladles during casting and pouring?
- Yes, monolithic refractories can be used for lining iron and steel ladles during casting and pouring. Monolithic refractories are versatile and can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for such applications. They provide excellent thermal insulation and chemical resistance, ensuring the integrity of the ladle lining and preventing contamination of the molten metal during the casting process.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress?
- Monolithic refractories are designed to withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress due to their unique composition and installation process. These refractories are made from a single, continuous material, eliminating any joints or seams that could weaken the structure. Additionally, they have a high thermal conductivity which allows them to efficiently distribute and dissipate heat, minimizing thermal gradients that can cause cracking. Furthermore, the installation technique involves forming the refractory in situ, ensuring a tight fit and reducing the likelihood of mechanical failure. Overall, the combination of their composition, thermal conductivity, and installation method enables monolithic refractories to withstand thermal shock and mechanical stress effectively.
- Q:What are the typical properties of monolithic refractories used in iron and steel industry?
- Monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry generally possess several key properties that make them suitable for the harsh operating conditions in these industries. Firstly, monolithic refractories have excellent thermal shock resistance. They can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or spalling, which is crucial in the iron and steel industry where the heating and cooling processes can be highly intense. Secondly, these refractories exhibit high refractoriness, meaning they can withstand extremely high temperatures without losing their strength or shape. This is essential in environments where temperatures can reach well above 1000 degrees Celsius. Additionally, monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry are known for their excellent corrosion resistance. They can resist the corrosive effects of molten metals, slags, and gases that are commonly encountered in these industrial processes. Furthermore, these refractories have good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance, allowing them to withstand the physical stresses and wear caused by handling and mechanical operations. Another important property of monolithic refractories is their ability to form strong bonds with the existing refractory lining. This ensures a secure and long-lasting installation, reducing the risk of failure and minimizing downtime for maintenance or repairs. Lastly, these refractories often have low porosity, which prevents the infiltration of molten metal or slag into the lining. This helps to maintain the integrity of the refractory structure and prolong its service life. Overall, the typical properties of monolithic refractories used in the iron and steel industry include thermal shock resistance, high refractoriness, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, strong bonding, and low porosity. These properties collectively contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of iron and steel manufacturing processes.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing emissions in iron and steel processes?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in reducing emissions in iron and steel processes by providing superior insulation, increased energy efficiency, and improved control over the production process. These refractories are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh conditions, effectively minimizing heat loss and reducing the need for excessive fuel consumption. By creating a highly insulated environment, monolithic refractories enable better temperature control, leading to optimized combustion and reduced emissions of greenhouse gases. Additionally, their high resistance to wear and corrosion helps prevent the formation of pollutants, thereby contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable iron and steel industry.
- Q:How are monolithic refractories installed in iron and steel production processes?
- Monolithic refractories are installed in iron and steel production processes using various methods depending on the specific application and requirements. The installation process typically involves the following steps: 1. Surface Preparation: Before installing monolithic refractories, the surface where they will be applied must be properly prepared. This involves cleaning and removing any loose materials, dust, or contaminants from the substrate. 2. Mixing: Monolithic refractories consist of different materials such as aggregates, binders, and additives. These components are mixed in specific proportions to achieve the desired properties and consistency. The mixing process can be done manually or using mechanical mixers. 3. Application: There are different techniques for applying monolithic refractories, including gunning, casting, ramming, and troweling. The chosen method depends on factors such as the shape of the structure, accessibility, and required thickness. - Gunning: This method involves using a gunning machine to spray the refractory material onto the surface. It is commonly used to repair or patch existing linings or for rapid installation in areas that are difficult to access. - Casting: In casting, the refractory material is poured into molds or forms and left to set and harden. This method is suitable for creating complex shapes and large-sized components. - Ramming: Ramming involves manually or mechanically compacting the refractory material into a mold or form using a ramming tool. This technique is commonly used for lining induction furnaces, ladles, and other equipment. - Troweling: Troweling is a manual method where the refractory material is applied and smoothed using a trowel. It is often used for smaller repairs or touch-ups. 4. Curing: After the refractory material is applied, it needs to be cured to achieve its optimum strength and performance. Curing involves allowing the material to dry and harden at a controlled temperature and humidity for a specified period. This step is crucial to ensure the long-term durability and resistance of the monolithic refractory lining. Overall, the installation of monolithic refractories in iron and steel production processes requires careful preparation, proper mixing, and the appropriate application technique. It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and industry best practices to ensure a successful installation that meets the specific needs of the production process.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing?
- Monolithic refractories play a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing processes. These refractories are made of a single material, typically a combination of high-quality aggregates, binders, and additives, which allows for easy installation and repair. One of the main ways monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency is by reducing heat loss. These materials have excellent insulation properties, which help to maintain high temperatures within the furnace or kiln. By minimizing heat loss, the energy required to maintain the desired temperature is significantly reduced, leading to lower energy consumption and cost savings. Moreover, monolithic refractories are designed to have high thermal conductivity. This property ensures efficient heat transfer from the hot gases or flames to the iron and steel being processed. By facilitating efficient heat transfer, monolithic refractories enable faster heating rates and reduce the overall processing time. This time reduction translates into energy savings and increased production capacity. Another significant advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions. These materials have excellent resistance to thermal shock, corrosion, and erosion, which extends their lifespan and reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Consequently, the use of monolithic refractories leads to less downtime, allowing for continuous operation and improved energy efficiency. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer design flexibility, which enables the optimization of furnace and kiln geometries. By tailoring the shape and dimensions of the refractory linings, heat distribution can be improved, ensuring more uniform heating and reducing energy wastage. The ability to customize the refractory linings also facilitates the implementation of advanced combustion technologies, such as regenerative burners or oxy-fuel burners, which further enhance energy efficiency. In summary, monolithic refractories contribute to energy efficiency in iron and steel manufacturing by reducing heat loss, enhancing heat transfer, withstanding extreme conditions, optimizing furnace geometries, and allowing for the implementation of advanced combustion technologies. By utilizing these refractories, the industry can achieve significant energy savings, cost reductions, and environmental benefits.
- Q:What are monolithic refractories?
- Monolithic refractories are a type of heat-resistant materials used to line high-temperature industrial equipment such as furnaces, kilns, and reactors. Unlike traditional refractories, which are made of pre-formed bricks or shapes, monolithic refractories are a single, solid piece that can be easily shaped and installed. They are composed of various aggregates, binders, and additives, providing excellent thermal insulation and resistance to extreme temperatures, chemical attacks, and mechanical stress. Monolithic refractories offer flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and improved installation efficiency compared to traditional brick refractories.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories improve the performance of ladles and tundishes?
- The performance of ladles and tundishes is significantly improved by monolithic refractories in various ways. Firstly, these vessels are thermally insulated by monolithic refractories, which act as a barrier against heat loss and help maintain the desired temperature. This insulation reduces energy consumption and minimizes heat loss. Secondly, monolithic refractories offer excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and erosion. When ladles and tundishes come into contact with molten metal and fluxes, they can be severely corroded and eroded. However, the use of monolithic refractories protects against chemical attacks and extends the lifespan of these vessels. This saves costs associated with frequent repairs or replacements and ensures their integrity and safety. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide superior mechanical strength and structural stability. Ladles and tundishes must withstand the weight of molten metal and the stresses caused during pouring and handling. With high mechanical strength, monolithic refractories can withstand these loads, maintaining their shape and integrity. This reduces downtime and increases productivity in the steelmaking process. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer flexibility in design and installation. They can be shaped and applied in various configurations, allowing customization to meet the specific requirements of ladles and tundishes. This flexibility ensures a better fit and improves the overall efficiency of the refractories, ultimately enhancing the performance of the vessels. In conclusion, monolithic refractories enhance the performance of ladles and tundishes by providing improved thermal insulation, resistance to chemical corrosion and erosion, increased mechanical strength, and flexibility in design and installation. These benefits contribute to the longevity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of ladles and tundishes in steelmaking operations.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories contribute to reducing downtime in iron and steel plants?
- The use of monolithic refractories plays a vital role in minimizing downtime in iron and steel plants. They have several key advantages over traditional brick refractories. To begin with, monolithic refractories are highly adaptable and can be easily shaped and installed. This allows for faster repairs and replacements. In contrast to brick refractories, which require time-consuming and labor-intensive processes like bricklaying and mortar application, monolithic materials can be directly applied in a castable or gunning form. This significantly reduces the time needed for repairs. Furthermore, monolithic refractories offer better thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shocks, which are common in iron and steel plants. This improved thermal performance helps to maintain stable operating temperatures and prevents sudden temperature fluctuations that can lead to refractory failure and subsequent downtime. By minimizing these thermal shocks, monolithic refractories increase the overall lifespan of the refractory lining, reducing the need for frequent repairs. Moreover, monolithic refractories provide superior chemical resistance compared to traditional brick refractories. Iron and steel plants often face aggressive chemical environments due to the presence of molten metal, slag, and other corrosive substances. Monolithic refractories are specifically designed to withstand these harsh conditions, preventing chemical attacks and erosion of the refractory lining. As a result, the occurrence of unscheduled shutdowns due to refractory degradation is significantly reduced. Lastly, monolithic refractories offer better dimensional stability, minimizing the risk of cracks and spalling caused by thermal cycling and mechanical stress. This increased resistance to wear and tear ensures that the refractory lining remains intact for a longer period, reducing the frequency of maintenance and enhancing the overall operational efficiency of the iron and steel plant. In conclusion, monolithic refractories contribute to downtime reduction in iron and steel plants by providing faster installation, improved thermal insulation, superior chemical resistance, and enhanced dimensional stability. Their versatility and performance advantages make them a reliable choice for maintaining an efficient and dependable refractory lining, ultimately reducing the frequency and duration of plant shutdowns.
- Q:How do monolithic refractories perform in reheating furnace roof applications?
- Monolithic refractories prove highly effective when used on the roofs of reheating furnaces. These refractories are renowned for their outstanding ability to withstand extreme temperature conditions, making them an essential component in furnace operations. Their resistance to thermal shock ensures that they do not crack or spall, guaranteeing the long-lasting durability of the furnace roof. Moreover, monolithic refractories offer exceptional insulation properties, thereby helping to maintain the desired temperature inside the furnace. With their low thermal conductivity, they prevent heat loss and reduce energy consumption. This not only enhances the energy efficiency of the furnace but also leads to cost savings for operators. Furthermore, monolithic refractories provide excellent resistance against chemical attacks from gases and molten metals found within the furnace environment. Designed to withstand corrosive atmospheres, they effectively prevent the penetration of harmful substances, thereby extending the lifespan of the roof refractory. Additionally, monolithic refractories offer easy installation and repair options. Their ability to be cast or gunned in place allows for a seamless and precise application to the roof structure. This feature also facilitates quick and efficient repairs or maintenance, minimizing downtime and production losses. In summary, monolithic refractories are a reliable and efficient choice for reheating furnace roof applications. Their outstanding resistance to thermal shock, insulation properties, chemical resistance, and ease of installation make them the ideal solution for maintaining the structural integrity and performance of the furnace roof.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Ladle Shroud long nozzle Chinese steelmaking
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 set
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 set/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























