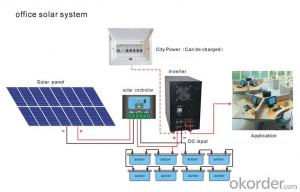
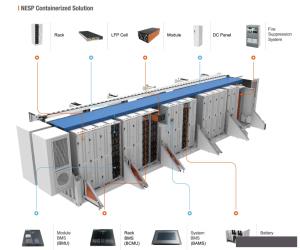
Solar Home Inverter
Solar Home Inverter Related Searches
Best Solar Inverter For Home Solar Panel Inverter For Home Inverter For Home Solar System Home Power Inverter For Solar Hot Water Bags For Pain Relief Solar System For Inverter Ac Mppt Inverter For Solar System Solar Inverter Cost For Home Solar Inverter For Home Led For Growing CannabisHot Searches
Fiberglass Scaffolding For Sale Home Scaffolding For Sale Modern Home Bars For Sale Fiberglass Panels For Sale Small Home Bars For Sale Fiberglass Greenhouses For Sale Home Solar Inverter Price Home Depot Aluminum Coil 1 4 Aluminum Plate Home Depot 1/4 Aluminum Plate Home Depot 1 8 Aluminum Plate Home Depot Aluminum Tread Plate Home Depot Home Depot Aluminum Plate Home Solar Energy Cost Home Depot Solar Inverter Home Depot Solar Cells Ceiling Fan Lowest Price Home Depot Electrical Wire Prices Geogrid Fabric Home Depot Cheap High Tea Sets For SaleSolar Home Inverter Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Okorder.com is a professional Solar Home Inverter supplier & manufacturer, offers integrated one-stop services including real-time quoting and online cargo tracking. We are funded by CNBM Group, a Fortune 500 enterprise and the largest Solar Home Inverter firm in China.Hot Products
FAQ
- Yes, a solar energy system can be used to heat water. Solar water heating systems use the sun's energy to heat water through collectors, which are typically installed on the roof. These collectors absorb sunlight and transfer its heat to a fluid, such as water or antifreeze, which is then circulated through pipes to heat water for domestic or commercial use. This process is efficient and environmentally friendly, making solar water heating a popular choice for reducing energy consumption and costs.
- Solar energy systems have a significant positive impact on job creation. The installation and maintenance of solar panels require skilled workers, leading to the creation of employment opportunities in the renewable energy sector. Additionally, the growth of the solar industry stimulates job creation in related fields such as manufacturing, research, and development. The shift towards solar energy not only contributes to a cleaner environment but also fosters economic growth by generating jobs at various stages of the solar energy supply chain.
- Yes, solar energy systems can certainly be used to power recycling plants and waste management facilities. Solar panels can be installed on the roofs or in open spaces of such facilities to generate electricity from sunlight. This renewable energy source can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower the carbon footprint of these operations. Additionally, solar energy can provide a stable and consistent power supply, contributing to the overall sustainability and efficiency of recycling plants and waste management facilities.
- Solar energy systems require regulations and permits for installation. The specific requirements vary depending on the location and jurisdiction, as regulations are set at local, state, and national levels. These regulations and permits are in place to ensure the safety of solar energy system installations, compliance with building codes, and adherence to local zoning requirements. Typically, a solar energy system installation requires a building permit. This permit guarantees that the installation is done correctly and follows all necessary safety guidelines. The permit process involves submitting detailed plans and documentation, including structural engineering reports and electrical diagrams. The local building department reviews these documents to ensure compliance with applicable codes and regulations. In addition to building permits, there may be other permits or approvals necessary for solar energy systems. These could include electrical permits, zoning permits, or even historic preservation approvals in certain areas. It is crucial to consult with the relevant authorities and obtain all necessary permits before installing a solar energy system to avoid legal or safety issues. Furthermore, some jurisdictions have specific regulations regarding the size, placement, and design of solar energy systems. These regulations aim to preserve the aesthetics of the area and ensure that the systems do not pose any risks or nuisances to neighboring properties. It is important to note that regulations and permit requirements are constantly changing and can differ significantly from one jurisdiction to another. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with local authorities or hire a professional solar energy installer who is familiar with the local regulations to ensure compliance throughout the installation process.
- Shading negatively affects the performance of solar panels as it obstructs the amount of sunlight reaching the panels, reducing their efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. Even a small amount of shading can significantly reduce the overall power output of a solar panel or even render it completely inactive. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that solar panels are installed in areas with minimal shading to maximize their performance.
- Solar energy systems have a minimal impact on water quality. Unlike other forms of renewable energy, such as hydropower, solar energy systems do not require water for their operation. This means that they do not directly contribute to water pollution or degradation. However, it is important to consider the potential indirect impacts during the manufacturing and disposal of solar panels, which may involve the use of chemicals and materials that can affect water quality if not managed properly. Overall, the environmental benefits of solar energy greatly outweigh any potential water quality concerns.
- Excess energy generated by a solar energy system can be stored in batteries for later use, fed back into the power grid for credit, or wasted if no storage or grid connection is available.
- Yes, a solar energy system can definitely be used to power outdoor lighting. In fact, solar-powered outdoor lighting systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their numerous benefits. Solar panels installed on rooftops or in open areas capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which can be stored in batteries for use during the night or on cloudy days. This stored energy can then be used to power outdoor lighting fixtures such as streetlights, garden lights, pathway lights, and even security lights. Solar-powered outdoor lighting systems are cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and do not require any electrical wiring, making them easy to install and maintain. Additionally, they offer the advantage of being independent of the grid, ensuring uninterrupted lighting even during power outages. Overall, solar energy systems are a highly efficient and sustainable solution for powering outdoor lighting.