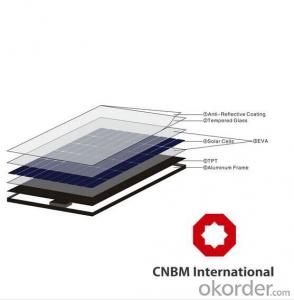
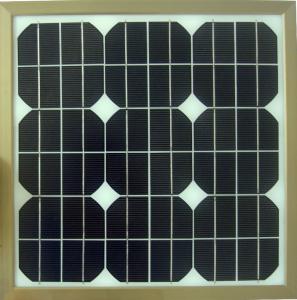
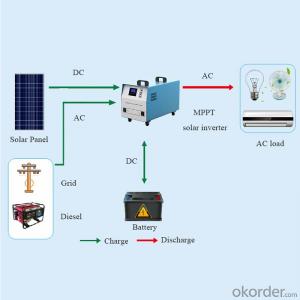
36v Solar Inverter
36v Solar Inverter Related Searches
Best Inverter Solar Panel Solar Panel On Roof Rack Inverter To Solar Panel Ratio Solar Panel Decking Lights Solar Panel Inverter Box 1000 Watt Solar Panel Inverter 12 Volt Solar Panel Inverter Plastic Solar Lanterns Buy Solar Panel Inverter Solar Panel Inverter CostHot Searches
Type Of Inverter For Solar Types Of Inverter For Solar Used Solar Inverter For Sale Inverter Size For Solar System Solar Edge Inverter For Sale 5kw Solar Inverter For Sale Solar Inverter For Sale Solar Inverter For Battery Solar Inverter For Split Ac Solar Inverter For Laptop Solar Inverter For Fridge Solar With Inverter Price Solar Inverter With 2 Battery Solar Inverter Price In China Best Solar Inverter In China Solar Inverter Price In Dubai Solar Inverter Price In Uae Solar Inverter Price In Kenya Solar Inverter Price In Kerala Solar Hot Water Collectors For Sale36v Solar Inverter Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Okorder.com is a professional 36v Solar Inverter supplier & manufacturer, offers integrated one-stop services including real-time quoting and online cargo tracking. We are funded by CNBM Group, a Fortune 500 enterprise and the largest 36v Solar Inverter firm in China.Hot Products
FAQ
- The performance of solar panels can be significantly affected by the color of the roof, although it mainly depends on the type of solar panel technology being used. The color of the roof can have an impact on the overall efficiency and output of solar panels due to its influence on sunlight temperature and reflection. Solar radiation absorption and reflection are influenced by roof color. Dark-colored roofs tend to absorb more sunlight, resulting in increased heat accumulation on the roof's surface. This excess heat negatively affects the performance of solar panels, as they function less efficiently at higher temperatures. The elevated temperature can lead to a decrease in the overall power output of the panels, reducing their energy generation potential. On the contrary, light-colored roofs reflect more sunlight, which helps prevent excessive heat buildup. By reflecting a significant amount of solar radiation, the roof's color assists in keeping the panels cooler and maintaining their optimal operating temperature. This can lead to better performance and higher energy production from the solar panels. However, it is important to note that the impact of roof color can vary depending on the type of solar panel technology used. Certain types of solar panels, such as monocrystalline or polycrystalline, may be more sensitive to temperature changes and therefore more influenced by roof color. In contrast, thin-film solar panels are generally less affected by temperature variations, making the impact of roof color less significant in their case. Furthermore, factors like climate, local weather conditions, and the orientation and tilt of the solar panels can also have a greater impact on their performance than the roof color alone. Proper installation and maintenance of the solar panel system, including adequate ventilation and shading, can further mitigate the impact of roof color on panel performance. In conclusion, while roof color can affect the performance of solar panels, it is just one of many factors that can influence their efficiency and energy production. To maximize the performance of solar panels, regardless of the roof color, it is essential to consider the specific type of solar panel technology, local environmental conditions, and proper installation practices.
- Yes, solar energy systems can indeed be used to power agricultural irrigation systems. Solar panels can generate electricity to power pumps and other equipment needed for irrigation. This allows farmers to harness renewable energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels, making it an environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution for irrigation in remote areas.
- Yes, a solar energy system can be installed on a museum or cultural institution. Solar panels can be mounted on the roof or in an open space surrounding the building to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. This can help the institution reduce its reliance on conventional energy sources, lower its carbon footprint, and potentially save on electricity costs in the long run. Additionally, the installation of solar panels can also serve as an educational display, highlighting the institution's commitment to sustainability and renewable energy.
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in areas with limited access to the grid. In fact, solar energy is particularly well-suited for such areas as it provides a decentralized and independent source of power. By installing solar panels and utilizing batteries, communities and individuals can generate and store their own electricity, reducing their reliance on the grid. This makes solar energy an excellent solution for remote locations, developing countries, and areas prone to grid outages or disruptions.
- Yes, solar energy systems can still be used in areas with limited access to solar surge protection devices. While surge protection devices are recommended for optimal protection against electrical surges, there are alternative measures that can be taken to minimize the risk of damage to solar energy systems. These include using high-quality solar panels and inverters that are built to withstand surges, implementing appropriate grounding techniques, and regularly inspecting and maintaining the system to ensure its proper functioning. Nonetheless, it is always advisable to consult with a professional to assess the specific conditions and requirements of the area in question.
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used in areas with limited access to solar connectors and cables. Off-grid solar systems, also known as standalone solar systems, can be installed in remote locations without relying on a traditional electrical grid or extensive wiring infrastructure. These systems typically include solar panels, batteries for energy storage, and inverters to convert the captured solar energy into usable electricity. By storing excess energy in batteries, these systems can provide power even when sunlight is not available, making them suitable for areas with limited solar connectors or cables.
- To maintain and clean your solar energy system, there are a few key steps you can follow. Firstly, regularly inspect the solar panels for any signs of damage or debris accumulation. If you notice any issues, it's important to address them promptly. Secondly, keep the panels clean by gently washing them with water and a non-abrasive sponge or cloth. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could scratch the surface. Additionally, trimming nearby trees or branches that may cast shadows on the panels can help maximize their efficiency. Lastly, consider scheduling professional maintenance and cleaning services every few years to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your solar energy system.
- Yes, solar energy systems can be used to power warehouses or distribution centers. Solar panels can be installed on the roofs of these buildings to convert sunlight into electricity, which can then be used to meet their energy needs. This can help reduce reliance on traditional energy sources and lower operating costs while also promoting sustainability.