SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass,Clay Graphite Crucible
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Graphite Crucibles
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Graphite Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
5.Resistance to oxidation: advanced process dramatically improves its oxidation resistance, which ensures persistent heat conductivity and long working lifetime.
6.High-strength: high-density body and logical structure make the product better compression property.
7.Eco-friendly: energy-efficient and pollution-free, not only ensure metal product purity, but also ensure sustainable development on environment.
8.Multi-function: Can be used in induction graphite crucible furnace
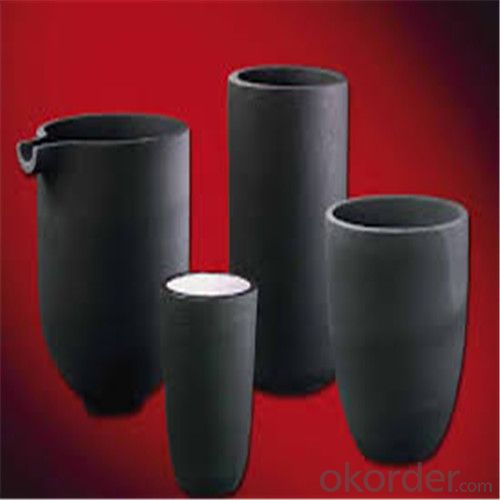
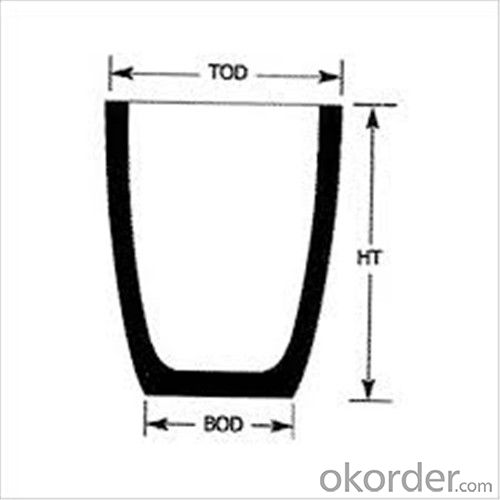

Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
- Q:Graphite can react with alkali in high temperature
- Graphite can react with alkali in high temperatureThe chemical properties of graphite are very stable at room temperature and do not react with acids, bases and other substances.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for melting composite materials?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for melting composite materials. Graphite crucibles are known for their high melting point and good thermal conductivity, which makes them suitable for melting a wide range of materials, including composite materials. Additionally, graphite crucibles are resistant to chemical reactions, making them ideal for handling and containing composite materials during the melting process. However, it is important to consider the specific composition and melting point of the composite material to ensure that it is compatible with the graphite crucible.
- Q:Intermediate frequency induction furnace melting copper with what dry pot?
- The filler to the insulation cloth and the crucible, use a sharp object to play, a dozen layers, to tell the truth, very complicated things, if not, there will be consequences --- as filler, can with mullite sand, quartz sand and so on.
- Q:What is the purpose of using a graphite crucible?
- The primary function of a graphite crucible is to contain and endure high temperatures in diverse industrial procedures. Graphite possesses exceptional refractory properties, which means it can withstand intense heat without easily melting or reacting with surrounding materials. This makes graphite crucibles highly suitable for tasks involving metal melting, casting, and purification. Graphite crucibles find widespread usage in foundries, laboratories, and manufacturing facilities that require temperatures surpassing the melting point of most metals. The crucible serves as a vessel for the molten metal, preventing its escape and ensuring precise control over the melting process. Moreover, graphite crucibles exhibit outstanding thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer to the substance being melted. This facilitates uniform heating and consistent melting, resulting in the production of high-quality end products. Additionally, graphite's high thermal shock resistance allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles without causing any harm to the crucible. Graphite crucibles are also chemically inert, meaning they do not react with the majority of substances. This renders them suitable for handling various corrosive materials or compounds that have the potential to react with other materials. The inert nature of graphite guarantees the preservation of the purity and integrity of the materials being processed. In conclusion, the purpose of employing a graphite crucible is to provide a long-lasting, heat-resistant, and chemically inert container for high-temperature operations such as melting, casting, and purification. The ability of graphite crucibles to endure extreme heat, exhibit excellent thermal conductivity, and remain chemically inert makes them indispensable tools in a wide array of industrial applications.
- Q:How do you prevent graphite crucibles from thermal shock during use?
- To prevent thermal shock when using graphite crucibles, there are several precautions that can be taken: 1. Gradual preheating is essential. The crucible should be placed in a kiln or furnace and the temperature should be increased slowly. This allows for uniform expansion of the crucible and minimizes the risk of thermal shock. 2. Avoid sudden temperature changes. It is important to heat and cool graphite crucibles slowly to prevent thermal stress and potential cracking or breakage. It is recommended to use a programmable kiln or furnace that allows for controlled temperature ramping and cooling rates. 3. Insulating materials can be utilized. Surrounding the crucible with ceramic fiber blankets or boards during the heating and cooling processes provides thermal insulation. This reduces the rate of temperature change and minimizes the risk of thermal shock. 4. Handle with care. Graphite crucibles should be handled cautiously to prevent accidental impacts or drops that could lead to cracks or fractures. Always use appropriate tools or tongs when moving or manipulating the crucible to avoid physical damage. 5. Avoid contact with water or coolants. Direct contact between graphite crucibles and water or coolants while at high temperatures can cause rapid cooling and thermal shock. If cooling is necessary, it is recommended to allow the crucible to cool naturally in the ambient environment or use a controlled cooling process. By implementing these preventive measures, the likelihood of thermal shock in graphite crucibles can be significantly reduced, ensuring their durability and optimal performance in high-temperature applications.
- Q:How is a graphite crucible disposed of at the end of its life?
- A graphite crucible is typically disposed of by being recycled or sent to a specialized facility for proper disposal.
- Q:Where is the difference between the silicon carbide crucible and the graphite crucible?
- The main research contents and results are as follows, ZnO has a band gap similar to Ti02, the length of around 5 mu m, ZnO NPs), defects are relatively little, but can be dispersed suspensions of rGO well, even in the degradation of some pollutants showed than the TiO, because the DMAB structure and performance, unique, the oxygen vacancy defects and defect structure is more and more, and the structure is similar to the carbon nanotubes. Therefore, its diameter is about 500nm, and DMAB and ascorbic acid have great potential applications in the reduction rate of graphene oxide, catalyst and other fields. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties of compound 20 has the best light absorption ability and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanorods is more capable of absorbing light than ZnO nanoparticles, consistent absorption spectra of ZnO nanorods and nanoparticles. (2) in order to facilitate the study of photocatalytic performance of ZnO photocatalyst, as a kind of efficient degradation of organic pollutants, the absorption range of its special structure can adjust the composite light, and through the PL spectrum of defects state, gas sensor of ZnO nanorods, ZnO NRs), sensor, have an impact on the light absorption and the photocatalytic ability of the composite material.
- Q:Is the graphite oven heating evenly?
- It is possible that at this stage the deuterium lamp signals are negative peaks. That is, molecular absorption is negative.
- Q:Does a graphite crucible react with any substances during use?
- No, a graphite crucible does not react with any substances during use.
- Q:What are the different methods of preventing graphite crucible deformation?
- There are several methods that can be employed to prevent graphite crucible deformation. These methods are aimed at maintaining the structural integrity of the crucible and ensuring its longevity. 1. Proper Handling and Usage: The first and foremost method is to handle the graphite crucible with care and avoid subjecting it to unnecessary mechanical stress. This includes avoiding sudden temperature changes, impact or dropping the crucible, and using appropriate tools for handling. 2. Preheating: Before subjecting the crucible to extreme temperatures, it is advisable to preheat it gradually and evenly. This helps in reducing thermal shock and prevents deformation caused by rapid expansion or contraction. 3. Material Selection: Choosing the right type of graphite material for the crucible is crucial. High-quality graphite with appropriate thermal and mechanical properties should be selected, considering the specific application requirements. This ensures that the crucible can withstand the intended operating conditions without deforming. 4. Reinforcement: In certain cases, reinforcing the crucible can be beneficial. This can be achieved by using a protective coating or lining on the inner surface of the crucible, which provides additional strength and resistance to deformation. 5. Cooling Techniques: Implementing proper cooling techniques post-use can also aid in preventing crucible deformation. Gradually cooling the crucible in a controlled manner can help alleviate stress and minimize the risk of deformation. 6. Regular Maintenance: Crucibles should be inspected regularly for any signs of wear or damage. Any cracks, chips, or deformations should be addressed promptly to prevent further deterioration. Regular cleaning and proper storage also contribute to maintaining the crucible's structural integrity. By implementing these methods, the risk of graphite crucible deformation can be minimized, leading to improved performance, longer lifespan, and reduced costs associated with replacement or repairs.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium And Copper, Brass,Clay Graphite Crucible
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























