Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Product Description
Specifications for Graphite Silicon Carbide Crucible For Aluminum Melting :
1.Long working lifetime: its working lifetime is increased 3-5 times over normal clay-crucible due to the compact body formed under high pressure.
2.High thermal conductivity: high-density body and low apparent porosity greatly improve its heat conductivity.
3.New-style materials: new heat conduction material ensures faster heat conductivity and pollution-free product, reduces adherent slag.
4.Resistance to corrosion:better anti-corrosion than normal clay-crucible.
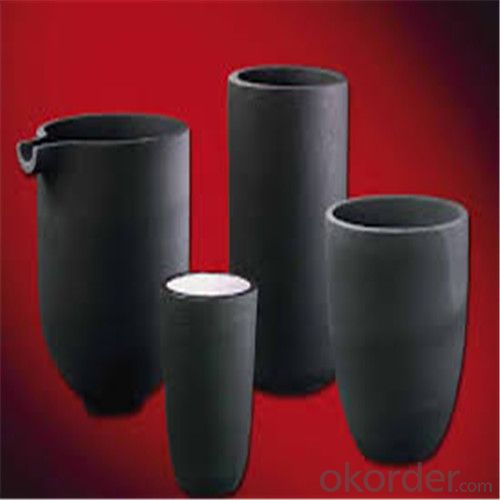

Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
Physicochemical Properties
Type of Crucible | Type S | Type D |
Carbon Content/% | ≥38 | ≥45 |
Bulk Density/(g/cm3) | ≥1.70 | ≥1.85 |
Apparent Porosity/% | ≤29 | ≤21 |
Compression Strength/MPa | ≥20 | ≥25 |
Refractoriness/°C | ≥1400 | ≥1400 |
Type S: Clay graphite crucible
Type D: Isostatic pressing graphite crucible
Cited from CNS China National Standard of Graphite Crucible, which is solely drifted by TIANFU company.
Content Composition
C% | Sic% | AL2O3% | SIO2% |
45%-50% | 20%-30% | 10%-12% | 15-25% |
- Q:What are the carbon elements? What are their structures? What are their properties and uses?
- At the vertex of the carbon atom and the carbon atom adjacent vertices by SP hybrid orbital overlap to form a bond, three sigma bonds each carbon atom was a pentagonal edges and two hexagonal edges. Three sigma bond of carbon atoms is not coplanar, the bond angle is about 108 degrees or 120 degrees therefore, the whole molecule is spherical. A p orbital of each carbon atom with the rest of the overlap each other to form a containing 60 pi electron closed shell electronic structure, so in the spherical cage and the cage around the pi electron cloud. Molecular orbital calculations show that footballene delocalized can greatly.
- Q:What is the purpose of using a graphite crucible?
- The primary function of a graphite crucible is to contain and endure high temperatures in diverse industrial procedures. Graphite possesses exceptional refractory properties, which means it can withstand intense heat without easily melting or reacting with surrounding materials. This makes graphite crucibles highly suitable for tasks involving metal melting, casting, and purification. Graphite crucibles find widespread usage in foundries, laboratories, and manufacturing facilities that require temperatures surpassing the melting point of most metals. The crucible serves as a vessel for the molten metal, preventing its escape and ensuring precise control over the melting process. Moreover, graphite crucibles exhibit outstanding thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat transfer to the substance being melted. This facilitates uniform heating and consistent melting, resulting in the production of high-quality end products. Additionally, graphite's high thermal shock resistance allows for rapid heating and cooling cycles without causing any harm to the crucible. Graphite crucibles are also chemically inert, meaning they do not react with the majority of substances. This renders them suitable for handling various corrosive materials or compounds that have the potential to react with other materials. The inert nature of graphite guarantees the preservation of the purity and integrity of the materials being processed. In conclusion, the purpose of employing a graphite crucible is to provide a long-lasting, heat-resistant, and chemically inert container for high-temperature operations such as melting, casting, and purification. The ability of graphite crucibles to endure extreme heat, exhibit excellent thermal conductivity, and remain chemically inert makes them indispensable tools in a wide array of industrial applications.
- Q:What are the different methods of preventing contamination from graphite dust?
- There are several methods of preventing contamination from graphite dust, including using proper ventilation systems to remove airborne particles, implementing vacuum or wet cleaning methods to remove dust from surfaces, using personal protective equipment such as masks and gloves, and regularly maintaining and inspecting graphite equipment to minimize dust production.
- Q:What are the common defects found in graphite crucibles?
- Some common defects found in graphite crucibles include cracks, erosion, contamination, and thermal shock. Cracks can occur due to thermal cycling or excessive stress, compromising the structural integrity of the crucible. These cracks can lead to leakage or failure during use, rendering the crucible unusable. Erosion is another common defect, especially when the crucible is used with aggressive or corrosive materials. Over time, the graphite can wear away, reducing the crucible's capacity or causing it to break down prematurely. Contamination is a significant issue in graphite crucibles, as impurities can contaminate the materials being processed. This can result in poor product quality or unwanted reactions. Contamination can occur due to poor crucible manufacturing practices, improper cleaning, or the use of low-quality graphite. Thermal shock is a defect caused by rapid temperature changes, which can lead to the crucible cracking or breaking. This defect can occur if the crucible is subjected to extreme temperature variations without proper preheating or cooling precautions. To mitigate these defects, it is essential to choose high-quality graphite crucibles that are resistant to thermal shock and erosion. Proper handling, preheating, and cooling procedures should be followed to prevent thermal shock. Additionally, regular inspection and maintenance can help identify any cracks or erosion early on, allowing for timely repair or replacement.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for electrode production?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for electrode production. Graphite is an excellent material for electrodes due to its high melting point, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity. Graphite crucibles provide a suitable environment for melting and shaping metals to form electrodes, making them a common choice in electrode production processes.
- Q:Can a graphite crucible be used for melting plutonium?
- No, a graphite crucible cannot be used for melting plutonium. Plutonium has a very high melting point and extreme reactivity, which requires specialized crucibles made from refractory materials like ceramics or metals that can withstand its corrosiveness and high temperatures.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for alloy preparation?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for alloy preparation. Graphite is a suitable material for crucibles due to its high melting point, excellent thermal conductivity, and chemical inertness. It can withstand high temperatures and is commonly used in metallurgical processes for smelting and alloying different metals.
- Q:Graphite electrode, high temperature resistant oxidation coating, formulation technology
- Technology first, graphite crucible, anti-oxidation coating, water inorganic environmental protection paint, no volatile substance at high temperature and normal temperature. ZS-1021 Weihuanai closed high temperature coating itself with acid and alkali, the quenching medium of any reaction, chemical reaction can effectively protect the graphite crucible under high temperature, can effectively prevent the graphite crucible in high temperature oxidation rate reached more than 95%.
- Q:Can graphite crucibles be used for thermal analysis?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for thermal analysis. Graphite has excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for various thermal analysis techniques such as thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Its inert nature also allows for accurate measurement and analysis of thermal properties of the sample.
- Q:Can a graphite crucible be used for high-temperature reactions?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for high-temperature reactions. Graphite has a high melting point of around 3,500 degrees Celsius, making it suitable for withstanding extreme temperatures. It also has excellent thermal conductivity, which allows for efficient heat transfer and uniform heating of the reactants. Additionally, graphite is chemically inert and has low reactivity, making it resistant to corrosion and suitable for various chemical reactions. Therefore, a graphite crucible is commonly used in high-temperature applications such as melting metals, pyrolysis, and other thermally-driven reactions.
1. Manufacturer Overview |
|
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Year Established | |
| Annual Output Value | |
| Main Markets | |
| Company Certifications | |
2. Manufacturer Certificates |
|
|---|---|
| a) Certification Name | |
| Range | |
| Reference | |
| Validity Period | |
3. Manufacturer Capability |
|
|---|---|
| a)Trade Capacity | |
| Nearest Port | |
| Export Percentage | |
| No.of Employees in Trade Department | |
| Language Spoken: | |
| b)Factory Information | |
| Factory Size: | |
| No. of Production Lines | |
| Contract Manufacturing | |
| Product Price Range | |
Send your message to us
Refractory Crucibles Sic Crucible For Melting Copper/Brass/Aluminum
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
New products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























